11.07.2016
Customs carrier is a legal entity licensed to conduct relevant activities and engaged in the movement of goods (cargo) under the control of customs, or a person responsible for the transport on which goods are moved. The customs carrier is endowed with rights and responsibilities that he must fulfill in accordance with current legislation. The company uses the services of customs carriers, but, having received its status, can carry out transportation itself, significantly saving money.
Who is a customs carrier
Before Russia became a member of the Customs Union (July 1, 2010), a customs carrier was considered a legal entity registered in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation and included in the register of customs carriers maintained by the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation (Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation) and regional customs departments. Accordingly, two types of customs carriers can be distinguished:
- All-Russian - carry out transportation within the territory of Russia.
- Regional – carry out transportation within a certain region.
The customs carrier was provided with a certificate for 5 years on its inclusion in the appropriate register.
The activities of customs carriers were regulated by legislative acts such as: Administrative Regulations for the performance of the state function of maintaining a register of customs carriers, approved by the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation (Order No. 1351 of October 31, 2007), and the Customs Code of the Russian Federation.
Everything has changed since July 1, 2010. Now a legal entity of a member country of the Customs Union that meets the requirements of Article 19 of the Customs Code of the Customs Union can become a customs carrier. From now on, the customs carrier carries out the transportation of goods in accordance with the customs procedure of customs transit, without limiting itself to activities within a certain area, i.e. in the Customs Union zone. The customs carrier confirms its status with a certificate of inclusion in the register of customs carriers, issued by the federal executive body in the field of customs law. The certificate is issued for an indefinite period, but every year confirmation of customs duties paid is required. The payment method can be any: transfer of funds, issuance of a bank guarantee, conclusion of a guarantee agreement. The activities of the customs carrier must comply with the following legislation: articles of the Customs Code of the Customs Union from 18 to 22, 224, 367; Articles 54, 55, 57, 58, 59, 66, 67, 68 “On customs regulation in the Russian Federation” No. 311-FZ of November 27, 2010; Regulations of the Federal Customs Service for the provision of public services for maintaining a register of customs carriers (Order No. 1992 of September 30, 2011).
Definition of the concept
In the simplest sense, a customs carrier is a company that has a special right to transport uncleared goods. Using such a service, companies avoid paying customs duties and escorting cargo by customs officers.
From the legislative side, two requirements are imposed on companies of this type of activity: the status of a legal entity and the availability of an appropriate license from the State Customs Committee of Russia.
When are customs carrier services required?
The services of customs carriers can be mandatory or voluntary.
You can voluntarily use the services of a customs carrier on the initiative of the interested party, having notified the customs authority. It is imperative to use the services of a customs carrier when an official at the customs office of departure has suspicions of non-compliance with customs law. Based on data on the goods being transported, taking into account the specificity of customs cargo transportation, the official takes upon himself the decision to transport the products at the stage of customs declaration by the customs carrier.
This is what the official does in relation to the following goods:
— Goods prohibited for import into the Russian Federation and export from the Russian Federation, and, if necessary, transportation of such products between customs authorities;
— Goods that cannot be sold without a license, certificates or subject to supervision by government agencies.
How does a customs carrier work?
The relationship between the sender, the carrier, the recipient of the product and the customs carrier is fixed by agreement.
A customs carrier transports goods under the control of customs, at the discretion of the customs office of departure or in connection with the interests of persons in the transportation of goods. If the customs office of departure has made a decision on the transportation of products by a customs carrier, then it is binding on the sender, carrier, recipient and customs carrier.
The carrier's costs that arise during cargo transportation by a customs carrier are regulated between the sender, carrier, and recipient and are not subject to reimbursement from customs.
The transportation of products that are under the control of customs will be entrusted to a customs carrier if the customs assumes in advance that a simple carrier or his vehicles will not be able to comply with the legislation in the field of customs law.
The customs official, after ascertaining the status of the transported goods and all transportation factors, makes a decision on the transportation of goods under customs control. Interested persons can use the service of a customs carrier only if the customs authority is aware.
When a decision is made to transport products by a customs carrier or a decision to further transport by a common carrier, it is imperative to provide and take into account the following factors:
— The transport of a common carrier must comply with the rules established for vehicles;
— Possibility to provide customs support for products, goods, transport, documents by customs officials; — Nature of products: goods that are subject to high import customs duties; excisable goods; products that are subject to control by various government agencies.
— Product status, i.e. it is necessary to determine whether the customs regime includes the collection or non-collection of customs duties, excise taxes, VAT, as well as the use or non-application of economic policy measures such as quotas, licensing, etc.
— The customs authority must have information about the carrier: about its organizational and legal form, solvency, conscientious fulfillment of obligations to customs, information about the owner of the property, the cost of fixed assets, popularity in the market for transportation services, whether transportation is the main or additional type of activity, carries out carrier single or stable cargo transportation, etc.
— Other factors that give reason to believe that goods, transport, documents may not be delivered to the customs authority of destination or customs duties will be unpaid.
When paying customs duties, as an exception, a decision may be made to transport goods by a customs carrier in relation to the following goods:
— Prohibited goods for import into Russia, export from Russia;
— When the transportation of goods must be carried out between customs authorities;
— Imported goods requiring licensing;
— Goods controlled by other government bodies, but if control was not carried out by them;
— Products subject to certification.
When a customs carrier is involved in transporting products, customs declaration and delivery control must be carried out in strict accordance with the legislative acts of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation regarding the application of the customs regime for transit and delivery of products under customs control.
The customs carrier may use for transportation, in addition to its own vehicle and equipment in the form of trailers, semi-trailers, containers, similar vehicles and equipment of third parties.
What does customs carrier status mean?
Many people wonder what is the difference between permission to participate in international road transport (TIR) and the status of a customs carrier obtained?
Let's list these differences:
1. A customs carrier has the right to transport products by various modes of transportation: rail, sea, road and air transportation, while persons who have received TIR access have the right to transport goods only by road.
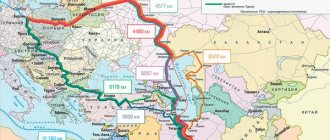
2. The customs carrier enjoys its status in the territories of states that are members of the Customs Union, while if the carrier has TIR access, he can carry out cargo transportation in the territories of the 55 states parties to the 1975 Convention.
3. Entry into the register of customs carriers is carried out by the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation, while admission to TIR is issued by the Association of Road Carriers (ASMAP) in agreement with the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation.
4. The limit of guarantee obligations to customs for a customs carrier is at least 200,000 euros, and for a TIR carrier - 60,000 euros, which allows the customs carrier not to use customs escort (convoy) of expensive and valuable goods worth more than 60,000 euros.
It is beneficial for large businesses to have the status of a customs carrier, as this gives it certain advantages:
1. The status of a customs carrier allows you to transport goods throughout the territory of the Customs Union
without applying measures to comply with customs transit. Accordingly, there are no costs for customs duties, customs escort, or taxes on imported products. The absence of expenses for customs escort saves not only money, but also time. The regular absence of taxes and customs duties makes the carrier’s activities easier. A carrier who does not have the status of a customs carrier is obliged to contribute financial resources, enter into a surety agreement, or provide a bank guarantee each time cargo transportation is carried out. It's very uncomfortable. This is how the “institute of customs carrier” appeared, the purpose of which is to make the activities of customs carriers more accessible.
The carrier presents a certificate to customs and, under its control, transports cargo, but each year pays a lump sum of customs duties and taxes in the amount of at least 200,000 euros.
Possibility of transporting expensive cargo, which is many times higher than the cost of paying customs duties and taxes. For example, a company received permission for customs cargo transportation and issued a bank guarantee for 8.5 million rubles, since it has the status of a customs carrier, it can transport goods whose value exceeds this amount. Accordingly, if the customs carrier’s license states the security amount is 8.5 million rubles, then the carrier can stably transport goods whose value is 16 million rubles. If the carrier does not have a license, he will have to pay a security amount of 16 million rubles. For each shipment of valuable goods, a common carrier will have to confirm security in the form of a cash deposit, bank guarantee or surety agreement.
2. Possibility of multimodal transportation.
The customs carrier has a certain advantage of using various types of transport during transportation. Consequently, he can import products by air transport of a customs carrier, and then use road transport.
3. Possibility of reasonable use of the vehicle fleet.
When cargo is transported under the international road transport (TIR) procedure, he must strictly comply with the compliance of his vehicles with the requirements put forward by certain states. European countries strictly monitor compliance with environmental requirements for transport entering their territory. But if the carrier has the status of a customs carrier, he can use transport in the territory of the Customs Union that is far from new, which is prohibited from entering European countries. Carriers who have both the status of a customs carrier and TIR access are doing very interesting things. Cars that meet European standards (Euro 4, 5) go to European countries to pick up goods, then, for example, the cargo is shipped to Belarus, and later the goods are transported by an old MAZ customs carrier to their destination in Russia. Those. The carrier, operating expensive vehicles on the roads of Europe, keeps the cars in good condition, while using older representatives of the fleet for transportation within the country.
4. Possibility of transporting your own (and attracted) cargo from ports.
For carriers who have their own vehicles and constant deliveries of goods arriving at seaports, it is very convenient to transport not only their own goods, but also the goods of third parties. If you have the status of a customs carrier, the carrier picks up your container from the port and takes it to the customs office of destination. Often, huge American trucks are used for such transportation, which are not suitable for traveling to European countries.
Responsibilities
If the company is conscientious, then it has all the necessary licenses, which imply a clear list of responsibilities. Any carrier is responsible not only to its client, but also to the state, like a customs declarant. All types of transport companies listed above have equivalent responsibilities, and their only difference is the geography of transportation.
Each company engaged in this type of transportation is obliged to:
- deliver uncleared cargo and accompanying documentation to their final destination without compromising their integrity and packaging;
- comply with delivery times and routes;
- keep records of transportation and timely submit data about them to customs authorities;
- load and unload goods yourself - as a rule, this point is stipulated in the contract between the carrier and the client;
- observe measures to prevent accidents during transportation, and if they occur, ensure the safety of the goods;
- prevent unauthorized use of transported cargo.
The best option for transporting uncleared cargo is the services of specialized logistics companies. Cooperation with them allows you to save not only time, but also money.
When choosing a customs carrier, pay attention to the availability of the appropriate license, experience and customer reviews.
The easiest way to transport goods that have not cleared customs is with the help of a reliable customs carrier.
Where to obtain a customs carrier license
Many people say “customs carrier license,” but the actual name of the document is “Certificate of inclusion in the register of customs carriers.” The form of such a certificate, confirming the status of a customs carrier and the procedure for its use, is determined by the decision of the Customs Union Commission No. 260 of May 20, 2010 “On the forms of customs documents.”
The certificate is issued by the customs office of a member country of the Customs Union, which includes legal entities in the register of customs carriers. In the Russian Federation - this is the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation, in the Republic of Kazakhstan - the CTC of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Kazakhstan, in Belarus - the State Customs Committee of the Republic of Belarus. This certificate is issued in 2 copies. One is sent to a company that is included in the register of customs suppliers or given to a company representative when providing a power of attorney to receive a certificate and passport. The company, having received the certificate, makes the number of copies it needs, duly certifies them by affixing the signature of the manager, the seal of the organization and issues it to its drivers, who are required to present this document to the customs authorities. Another copy of the certificate is stored in the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation. Information about the company and the issued certificate is entered into the register.
Is it profitable or unprofitable to hire a customs carrier?
If you have an inexpensive cargo, few HS codes and everything goes to one customs office, then it will be cheaper to hire a regular carrier, and the TIR Carnet will be the cheapest option, there are more such carriers, and their rates are lower, they were not spent on FCS guarantees and compliance with many other requirements.
If you have expensive cargo, this means that if the amount of customs duties that will need to be paid upon arrival of the cargo at customs is at least slightly higher than the value of 60 thousand euros, then additional costs (taking into account the convoy in Belarus, transit registration and UK guarantees Arsenal in Krasnaya Gorka) will amount to at least 25 thousand rubles. If it’s not a whole load, but a combined load, even more. Not counting the loss of time to open a shooting gallery on an expedition in Europe (even if it’s just a few hours, but you could travel with a customs carrier at that time), waiting for a convoy at the parking lot in Kozlovichi (up to 2 days), registration at Krasnaya Gorka (another day) . In the worst case scenario, 4 days are lost. It's a lot.
Therefore, in this case, it would definitely be more correct to hire a customs carrier.
What are the rights and obligations of a customs carrier?
We list the responsibilities of the customs carrier:
1. Obliged to comply with all requirements when transporting goods in accordance with the customs procedure for customs transit prescribed in the Customs Code of the Customs Union;
2. Obliged to keep records of products that are transported according to the customs procedure of customs transit, and to provide reports on the transportation of such products to customs authorities using information technology. The reporting form must comply with the laws of the member countries of the customs union, failure to comply with which may result in exclusion from the register of customs carriers;
3. Obliged to comply with the payment of customs duties and taxes, including the cases provided for in Art. 227-228 of the Customs Code of the Customs Union;
4. Bears an obligation of non-disclosure and non-use in one’s own interests, as well as non-transfer to third parties of information received from the sender, recipient or freight forwarder, if such information contains state, banking, commercial or other secrets.
5. Obliged to report all changes within 5 working days from the moment they occur (applies to information provided when included in the register of customs carriers);
Let us list the rights of the customs carrier, which are very limited:
- Has the right to transport products that are under customs control, without customs escort and without ensuring payment of customs duties (pledge of cargo or transport, guarantee obligations of a third party, depositing a certain amount of money into a deposit account);
- Has the right to receive payment in cash;
- Has the right to transport cargo both by its own transport and by the transport of third parties. In this case, vehicles must meet the requirements established by law;
- The right to demand fair distribution between the parties of the costs incurred by the carrier during the transportation of goods, but provided that this was specified in the agreement between the sender and the carrier;
- The right to participate in procedural actions: inspections, examinations.
Accompaniment procedure
The relevant Instruction, approved by the joint resolution of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Republic of Belarus and the State Customs Committee of the Republic of Belarus dated August 2, 2006 No. 208/61, stipulates the procedure for accompanying goods under customs control and transported by road. The customs escort procedure is carried out by the Security Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Republic of Belarus. In the Resolution of the Council of Ministers of July 4, 2006 No. 829 “On the establishment of tariffs for services for accompanying (mandatory escort) of goods and vehicles, including those under customs control, transported across the territory of the Republic of Belarus by road and rail (with the exception of services for customs escort)" stipulates tariffs for services for customs escort of goods and vehicles transported across the territory of the Republic of Belarus by road and rail (with the exception of customs escort services).
How is inclusion in the register of customs carriers carried out?
To obtain the status of a customs carrier and a certificate of inclusion in the register of customs carriers, it is necessary to submit an application to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation for inclusion in the register of customs carriers. The application must be filled out in an approved form and accompanied by a package of documents that prove compliance with all the necessary conditions by the potential customs carrier for inclusion in the register.
Let us dwell in more detail on the conditions for inclusion in the register of customs carriers and on the list of attached documents.
Conditions necessary for inclusion of a legal entity in the register of customs carriers:
1) On the date of submission of the application to the customs authority, the person must have at least two years of experience in transporting goods. As evidence, you can provide contracts for the carriage of goods for the previous 2 years, including invoices or CRM.
2) It is mandatory to provide security for payment of customs duties and taxes in a monetary amount of at least 200,000 euros, but taking into account the exchange rate that is established by the laws of the member country of the Customs Union on the date of provision of the security.
The company has the right to independently choose any method of security: depositing funds into the deposit account of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation, issuing a bank guarantee, concluding a guarantee agreement. Everything is clear with depositing money into a deposit account and concluding a guarantee agreement, but let’s take a closer look at issuing a bank guarantee.
A bank guarantee and a surety agreement confirm the payment of customs duties and taxes, and are also a guarantor of the fulfillment of all obligations assumed to the customs authority. Basically, participants in foreign economic activity issue a bank guarantee, because it is not difficult to do in any bank or insurance company, but one must not forget that such a credit institution must be included in the register of legal entities that have the right to issue bank guarantees. The register, which was approved by the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation (order No. 1165 of June 2, 2011), is constantly updated.
Letter No. 01-11/109 of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation dated January 12, 2011 approved the form of the bank guarantee. A bank guarantee can be provided for no less than 200,000 euros (previously - 20 million rubles), taking into account the exchange rate on the day of provision of the bank guarantee in the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation.
Important! The bank guarantee is submitted to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation along with an application for inclusion in the register of customs carriers, but if changes are made to the bank guarantee, then it is necessary to provide the entire package of documents that was provided to the credit institution. Documents must be provided with a covering letter. The date and reference number on your copy of the cover letter will be evidence of the provision of a bank guarantee. Please note that registration of submitted documents may not occur on the day of their submission. During this time, the exchange rate may change, so it is better to take care of this in advance and issue a bank guarantee for 200-300 thousand rubles. more. For example, the euro exchange rate on the date of provision of the bank guarantee to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation is 40 rubles, therefore, 200 thousand rubles. x 40 = 8 million rubles. Add the risk of exchange rate changes of 300 thousand rubles, a total of 8.3 million rubles. But, if the security amount is not enough, the missing funds are deposited into the account of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation.
3) Permits for cargo transportation. If the legislation of a member state of the Customs Union requires any permit for cargo transportation, then the presence of such a document is strictly necessary. For example:
— The division of Rostransnadzor of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation at the place of registration of the legal entity issues licenses for the transportation of goods by sea and river vehicles, as well as certificates for admission to international road transport;
— The Federal Air Transport Agency of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation issues a license for the transportation of goods by air.
4) Documentary confirmation of ownership rights, economic management, lease, operational management of transported cargo and vehicles that are suitable for transporting goods under seals and stamps of customs authorities. Such supporting documents may be vehicle registration certificates, vehicle registration certificates, lease agreements, aircraft or ship leasing agreements, etc.
5) As of the date of application to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation, the potential customs carrier should not have any debts on customs payments, taxes and penalties on them. In this case, we are talking about a debt to the customs authority for non-payment of taxes and customs duties due to the submission of falsely declared data or, if cargo under customs control has never been delivered;
6) The applicant must not be brought to administrative responsibility for violations in the field of customs law for one year, in particular, under the following articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
— Article 16.1: provision of false information to customs authorities or false declaration;
— Article 16.2: false declaration;
— Article 16.3: non-compliance with prohibitions and restrictions on the import and export of goods;
— Part 1 of Article 16.9: complete or partial non-delivery of goods;
— Article 16.11: destruction, damage, removal, alteration or replacement of means of identification (seals and seals);
— Article 16.15: failure to submit reports to the customs authority;
— Part 2 of Article 16.23: carrying out activities as customs carriers included in the relevant register on the basis of invalid documents, or excluded from the register of customs carriers;
— Part 3 of Article 16.23: failure to report or failure to comply with the 5-day deadline for reporting to the customs authority about changes in the information specified in the application for inclusion in the register of customs carriers.
Accordingly, on the date of filing an application for inclusion in the register of customs carriers, the applicant cannot have decisions on the above articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation that have entered into legal force within one year before submitting the application to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation. For example, the application was registered with the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation on January 1, 2012, therefore, in the period from January 1, 2011 to January 1, 2012, the applicant should not have been prosecuted under the listed articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. However, a legal entity may submit an application one year after the date of entry into force of the final decision on an administrative offense. One resolution on an administrative offense that has entered into legal force will not be the reason for a reasoned refusal to include the applicant in the register of customs carriers. If the applicant has several administrative cases, then it is better to wait one year from the date of the last administrative decision that came into force, and then feel free to submit the necessary documents to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation for inclusion in the register of customs carriers.
Termination of the company's activities as a customs carrier
Conducting activities as a customs carrier may be terminated in the following cases:
- when the license to operate as a customs carrier has been revoked or cancelled;
- at the request of the customs carrier himself;
- when the license to carry out transport activities has expired, and the company has not applied to the customs authorities with a corresponding application for a new license before the expiration of this period.
If the activity of an enterprise as a customs carrier is terminated for any of the above reasons, then this decision is formalized in the form of an order by the head of the customs authority, or by order of the deputy head of a higher customs office, which issued a license to operate as a customs carrier.
If the license has been revoked, then the company will be charged fees equal to the customs fees for customs escort of goods in relation to all shipments carried out by the specified company as a customs carrier starting from the date the license was issued.
We briefly looked at who a customs carrier is, its responsibilities, requirements for obtaining a license to operate and the reasons why this company may be closed. Leave your comments or additions to the material.
What documents are required to become a customs carrier?
A legal entity must send to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation an application for inclusion in the register of customs carriers, drawn up in an approved form. The application must be accompanied by a package of documents confirming the information specified in the application, these are:
1) Constituent documents (copy of the charter);
2) Extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities;
3) Certificate of entry into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities;
4) Certificate of registration with the tax authority (TIN);
5) Permits for the transportation of goods. If the legislation of a member country of the Customs Union requires any permission for cargo transportation, then the presence of such a document is strictly necessary. The division of Rostransnadzor of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation at the place of registration of the legal entity issues licenses for the transportation of goods by sea and river vehicles, as well as certificates for admission to international road transport; The Federal Air Transport Agency of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation issues licenses for the transportation of goods by air.
6) Documents confirming the right of ownership, economic management, lease, operational management of transported cargo and vehicles (vehicle registration certificate, PTS, lease agreement, aircraft or sea vessel leasing agreement, etc.);
7) Certificate of approval of a vehicle for international transportation to transport cargo under customs seals and seals, the issuance procedure approved by the Decision of the Customs Union No. 676 of June 22, 2011. Such a certificate is required if the goods have seals and seals. A certificate is not required if transportation is carried out on a platform for oversized cargo or in a container.
 Original payment order or bank guarantee indicating payment of at least 200,000 euros;
Original payment order or bank guarantee indicating payment of at least 200,000 euros;
9) Documents confirming the availability of open bank accounts;
10) Contracts for the carriage of goods for the previous 2 years, including waybills or CRM. These documents serve as evidence that the applicant has transportation experience, which cannot be less than 2 years.
A package of documents is submitted to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation in the form of copies, duly certified (signed by the head and affixed with the organization’s seal), the charter can be notarized, but a bank guarantee or payment order must be provided in the originals.
When inclusion in the register of customs carriers is considered completed
There are two ways to submit an application to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation. The application with the attached package of documents can be sent to the correspondence box located in the reception office of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation at the address: Moscow, Novozavodskaya Street, 11-5 or sent by mail. According to the regulations of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation, the package of documents will be transferred to the department manager, who will register the application of the potential customs carrier no later than the date following the day the application was received. Next, the package of documents will be transferred to one of the divisions of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation for its consideration. The period during which the applicant must be included in the register of customs carriers should not exceed 40 days, in case of changes to the bank guarantee - no more than 15 days. But, as a rule, the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation does not meet these deadlines, since the application must go through a complex procedure for approval by various customs service specialists. Customs legislation is imperfect and constantly changing, and therefore various difficulties arise that prevent the rapid inclusion of applicants in the register of customs carriers.
There are precedents for filing applications without a bank guarantee. In order to reduce the risk of costs for issuing a bank guarantee, the company first receives a pre-approved decision of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation, then it is given 30 days to send the issued bank guarantee to the customs service. As an example, we can cite a large company that took advantage of the above right, but the original bank guarantee was sent to the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation after 32 days instead of the 30 declared. As a result, the company was given a reasoned refusal to be included in the register of customs suppliers, which entailed significant losses for the company and delayed the deadline for its inclusion in the register by up to 90 days. If FCS employees had called the company and reminded them of the need to bring the original bank guarantee, it would not have suffered such significant damage. There are examples where companies try to act through the management of the customs service, but these methods do not lead to positive results.