International cargo transportation Customs carrier
To transport goods between customs posts in customs transit mode, the transport company VDNK operates. You simply won’t find anyone better than us...
- transportation of goods between customs posts
- Why do you need a customs carrier?
- prices for customs carrier services
- customs transit or VTT? concept of customs transit and VTT
- Is the customs carrier an exclusively Russian phenomenon?
- Is it profitable or unprofitable to hire a customs carrier?
- certificate of inclusion in the register of customs carriers
- sizes of our cars
When you work with customs carrier VDNK:
- you are sure that you hired a professional and not a bunch of intermediaries;
- you are minding your own business, and not training your erudition in matters of international freight transportation;
- you don't pay extra;
- you reduce the delivery time of your goods.
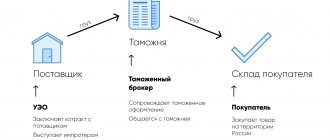
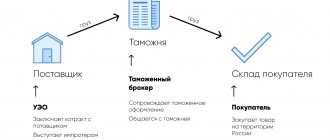
The status of a customs carrier guarantees our customers that cargo transportation will always be carried out with minimal risks of non-compliance with customs legislation, and the company’s obligations for the safety of cargo will be fulfilled. The status of a customs carrier can only be obtained by a transport company that has been operating in the international transport market for 2 years or more, and also has its own fleet of vehicles and has provided the Federal Customs Service of Russia with guarantees for payment of customs duties. We have our own fleet of 30 vehicles, which allows us to carry out international transportation of goods across the territory of the Customs Union independently, without involving other carriers. We don’t have a kit for a young illusionist; we will never become magicians. PKF VDNK LLC is a customs carrier (Certificate of inclusion in the register of customs carriers 10000/0363A dated 10/21/2014). Inclusion in the register of customs carriers allows us to carry out international transportation of goods under customs control throughout the territory of the Customs Union in accordance with the norms of internal customs transit. Previously, this was called transportation via VTT, now it is simply customs transit.
Why do you need a customs carrier?
A customs carrier is not Santa Claus. He comes to you more than once a year and does not give you caries. In contrast, a customs carrier carries goods under customs control. Issues when moving goods under customs control are always unique and difficult to predict. The simplest and most reliable way to resolve these issues is a customs carrier. One of the most popular services of a customs carrier is the transportation from one internal customs post (c/p) to another of cargo not yet released for free circulation. Such situations arise quite often: the cargo was mistakenly delivered to the wrong shipping terminal, or it turns out that the shipping terminal does not have the ability to process your type of cargo, for example, this shipping terminal does not work with ADR or excise cargo. The owner of the cargo faces two tasks: quickly find transport and provide the Federal Customs Service with security for payment of customs duties, while not forgetting to complete the entire package of documents for intra-customs transit (ICT). You can, of course, do this yourself and after a month or two, having lost a lot of time and energy, say to yourself: “I did it!” And the cargo will lie in a customs warehouse for which you have to pay. Or you can simply choose a customs carrier who has long guaranteed the payment of customs duties for you (and for its other clients), is familiar with the intricacies of intra-customs transit, will generate transit and transport documents and, finally, will actually deliver your cargo to the post you need. Its services will cost more than the services of a simple carrier, but this is understandable: the customs carrier has already paid for the guarantee from the Federal Customs Service. It simultaneously solves the problem of customs clearance and transportation of “problem” cargo, which, although it arrived in Russia, cannot be released into free circulation. And only those who have never encountered either customs or freight transportation can consider that it is worthless.
Is your cargo worth more than the TIR Carnet guarantee? – You need a customs carrier. The peculiarities of your cargo force you to follow a customs escort, which often happens at the Belarusian border (you cannot plan anything, you waste time and pay a lot of extra money) ? – You need a customs carrier. Before transportation, does customs require a guarantee of payment of customs duties? (The VAT rate for transit is 20%; to ensure transit, you will pay it along with the duty before transportation, and when the cargo arrives at the temporary storage warehouse, you will be charged 18%, and part of the funds will be suspended.) - You need a customs carrier. Are you carrying groupage cargo and the delivery points are located at different customs offices? – You need a customs carrier. Do you need to transport cargo from one temporary storage warehouse to another within the vehicle? – You need a customs carrier.
Land, into battle!
Export structure of the EU and China by mode of transport
The total volume of goods supplies between China and the EU countries reaches a colossal value - almost 110 million tons in 2021, Eurostat estimates. But the share of railway transit from this mass accounts for pitiful crumbs. Thus, in the structure of EU imports from China, rail transit was able to win a share of 1.6% (see Chart 5), in the structure of exports - 1.2% (see Chart 6).
It may seem paradoxical, but the volume of rail transit between the EU and China - not even in monetary, physical terms - is now inferior to the volume of cargo transported between them by air!
The same situation is observed in the EU’s foreign trade with Japan and South Korea, where rail transport accounted for 0.7% (see chart 7) and 0.9% (see chart of trade volume (in physical terms), respectively.
trade volume (in physical terms), respectively.
Thus, Russian railways theoretically still have a colossal volume of freight base that has not yet been covered, but is potentially attracted to railway transport.
Structure of EU trade with Japan by mode of transport
The shipper's choice of delivery method depends on the time and cost (delivery cost) associated with it. At the same time, the time spent can themselves be assessed in monetary terms and become an important argument in favor of a particular type of transport.
Let's explain the situation with a simple example. Rail transport is significantly inferior to sea transport in terms of price. Hans-Joachim Schramm and his Chinese colleague Xu Zhang report in their study , the total delivery cost will be $6,400 per forty-foot container (FEC) for rail transport and $2,400 for sea transport. At the same time, in terms of delivery times, everything is exactly the opposite: railway transport using container trains (as follows from the schedule of the China Railway Container Transport Company, CRCT) can be completed within 15 days, and delivery of cargo by sea (as follows from data from the leader of global maritime transport Danish Maersk) will take up to 35 days “directly” and 45 days according to the real schedule (with calls at intermediate ports along the route).
Structure of EU trade with South Korea by mode of transport
At the same time, during the entire delivery period, capital, which has a value (expressed in bank interest), is frozen in the transported cargo. The faster the cargo is transported, the lower the cost of frozen capital.
The same freezing of capital can be observed when it is necessary to store cargo and complete transport (train or ship). So, if a railway container train operates with dozens of containers (within 71 on Russian railways), then the average capacity of a container ship on the Asia-Europe route, as reported by Review of Maritime Transport 2021, is now 15 thousand TEU.
Ultimately, as the consulting company BCG points out, taking into account the cost of working capital, delivery of goods by rail becomes economically feasible if their unit cost exceeds $13.5/kg. The Institute of Economics and Transport Development (IEDT) estimates the equal-efficiency point to be slightly lower, at $10/kg. A wide range of engineering products, consumer goods, and prepared foods fall within the given framework.
Unit value of goods in EU trade with China
What do these Equal Delivery Efficiency marks provide? If you calculate the unit cost of goods in EU trade with China for 2021, depending on the type of transport used, it becomes clear that for railways this figure is 12–13 dollars/kg, for air transport the unit cost of goods also goes sky-high given, but for sea transport it is in the range of 3–4.7 dollars/kg (see Chart 9).
This means that not all trade turnover in Europe and the Asia-Pacific region can be considered as a potential cargo base. But when moving to individual product groups, it becomes clear that there is potential for attraction. Let's say, for the same flow in traffic between China and Europe, with a cut-off threshold of 13.5 dollars/kg, over 8.6 million tons are stacked, and with a cut-off threshold of 10 dollars/kg - up to 16 million tons. In export supplies from the EU to China, these figures will be 4.1 and 4.2 million tons, respectively. These figures - 10-15% of the existing trade turnover - can be considered as a transit cargo base potentially attracted to railway transport.
And in the same way, there is great potential for attracting additional volumes of cargo in the EU's communications with Japan and South Korea.
Prices for customs carrier services
Those who encounter transportation under customs control for the first time often ask the question: “Why is it so expensive?” You need to understand that prices for transportation via VTT are much higher than usual for transportation. Otherwise, you could turn to any carrier, of which there are many on the market, but what you need is a customs carrier. For comparison: transporting two pallets weighing 1 ton from Sheremetyevo to Domodedovo by a regular carrier will cost about 5,000 rubles, and a customs carrier will charge you three times more than 15,000 rubles for a day of work. Why is it so expensive: because in addition to the vehicles themselves, these vehicles must be equipped for international transport, obtain a certificate for each, the carrier company must have access to international transport and a proven work experience of at least 2 years, provide the Federal Customs Service with a deposit in the amount of 200,000 euros , have liability insurance according to CMR and also complete a bunch of different bureaucratic formalities. This is precisely why there are not many customs carriers and the prices for their services are much higher.
Here are our working prices for cargo transportation under the VTT customs transit procedure.
How does an SDEK parcel reach our hands?
Most postal transport transports parcels from different stores. First, warehouse workers load them onto vehicles and attach accompanying documents to the packaging.
Parcel delivered by SDEK
They indicate the recipient's address and some additional information. The route that SDEK transport must travel is formed by operators based on the recipient’s residential address. Next, the parcel can go through several sorting points, where it will also be processed by the operator and sent on its further journey.
SDEK truck
Bypassing several such transshipment points, the parcel will reach the recipient’s city through transit points. At this moment, he will receive a message on his mobile phone (if it was linked to his SDEK account). You can also see the message in your personal account in the application and on the company website. The recipient needs to take a document confirming his identity with him and go to the parcel delivery point specified in the contract.
Customs transit or transportation via VTT?
Previously, in accordance with the Customs Code of the Russian Federation (TC RF), customs transit was divided into VTT and MTT:
- internal customs transit (ICT) – customs procedure;
- international customs transit (ICT) – customs regime,
According to the new Customs Code of the Customs Union (CU CU), the concept of regime is absent. Only customs procedures take place.
Article 215 of the Customs Code of the Customs Union gives the following definition of customs transit.
Customs transit is a customs procedure in accordance with which goods are transported under customs control through the customs territory of the customs union, including through the territory of a state that is not a member of the customs union, from the customs authority of departure to the customs authority of destination without paying customs duties and taxes using prohibitions and restrictions, with the exception of non-tariff and technical regulation measures.
Decision of the Customs Union Commission (CUC) N 289 dated June 28, 2010, approved the form of the transit declaration (TD) and its additional sheets, Instructions on the procedure for filling out the TD. Commission decision No. 289 came into force on the territory of the Customs Union (CU) on January 1, 2011.
Cargoes that are transported under customs transit have not yet been released for free circulation (have not undergone customs clearance), and therefore require a special regime, which is controlled by customs authorities.
During customs transit, any goods are transported, except those whose transportation is prohibited by the legislation of the Customs Union. Customs transit is carried out only with the permission of the customs authority. To obtain permission for customs transit, a transit customs declaration (TD) is submitted to customs.
Is a customs carrier an exclusively Russian phenomenon?
Foreigners sometimes do not quite understand (or do not understand at all) what a customs carrier is. This is because the organization of transportation in Russia and in the European Union in practice follows different principles. In theory, everything is the same: in both cases, moving uncleared cargo requires a transit declaration and a guarantee/guarantee of payment of customs duties. But in the EU, any ordinary carrier can transport this cargo, because he only carries the cargo, and an expedition is responsible for it, issuing a transit declaration, which has the authority to do so. But in Russia? In theory, nothing prevents you from obtaining a certificate of security for the payment of customs duties on your cargo at your customs post, issuing a guarantee through an insurance company and hiring a regular carrier without a diploma, and it will be cheaper. But in practice, obtaining the same guarantee may take two weeks, and insurance coverage will require expenses. The customs carrier, therefore, is not the only, but the only effective way in Russian realities to move cargo under customs transit conditions.
Expert opinion
As Maxim Shishkov, head of the strategic marketing department of FESCO TG, noted, we can endlessly reduce transit time, improve quality and maintain a competitive price, but sooner or later we will face infrastructural limitations. The capacity of ports and railways in Russia and other transit countries is not infinite. Already now, when planning the growth of transit cargo traffic, it is necessary to think about increasing the capacity of the infrastructure for the export of potential volumes of cargo.
Based on materials from the website of the transport and logistics company FESCO.
Is it profitable or unprofitable to hire a customs carrier?
If you have an inexpensive cargo, few HS codes and everything goes to one customs office, then it will be cheaper to hire a regular carrier, and the TIR Carnet will be the cheapest option, there are more such carriers, and their rates are lower, they were not spent on FCS guarantees and compliance with many other requirements.
If you have expensive cargo, this means that if the amount of customs duties that will need to be paid upon arrival of the cargo at customs is at least slightly higher than the value of 60 thousand euros, then additional costs (taking into account the convoy in Belarus, transit registration and UK guarantees Arsenal in Krasnaya Gorka) will amount to at least 25 thousand rubles. If it’s not a whole load, but a combined load, even more. Not counting the loss of time to open a shooting gallery on an expedition in Europe (even if it’s just a few hours, but you could travel with a customs carrier at that time), waiting for a convoy at the parking lot in Kozlovichi (up to 2 days), registration at Krasnaya Gorka (another day) . In the worst case scenario, 4 days are lost. It's a lot.
Therefore, in this case, it would definitely be more correct to hire a customs carrier.
The parcel is no longer tracked or is delayed in a transit city
It often happens that SDEK clients, when tracking shipments, cannot wait for the parcel status to change from “In transit city” to “Awaiting receipt.” They often get lost in the warehouse, unusual situations arise on the roads, and data for identifying the parcel may be entered incorrectly. Often the accompanying sheet is lost among others. Now the SDEK company has a tense situation with its workforce. Due to the sharp increase in the number of clients, the previous number of employees cannot cope with their work.
SDEK service employee
On the website, the company apologizes and notifies customers that parcels may be delayed for up to one week [reasons for the delay]. If the package has been expected for more than a week, then it’s time to ask for help with your problem. Write to SDEK support at this email address or call the phone number: 8 800 250 6915.
SDEK service contacts