Quick links
Customs representative services / AEO services (customs clearance for a broker) / Price lists and contracts / Consolidated cargo (TO) / Moscow (TO) / Vladivostok (TO) / St. Petersburg (TO) / Customs lawyer / Consultation on customs issues / Contacts / Call / Send a letter
Export of lumber from Russia to Europe from the OnlogSystem company - transparent work scheme, flexible pricing, favorable tariffs.
Russian timber and products made from it are traditionally in demand in countries near and far abroad in the furniture, construction and carpentry industries. Therefore, the export of lumber to Europe is a common phenomenon, but at the same time quite labor-intensive and specific in terms of procedures and required documents. The experience of the Onlog System company includes both the delivery of lumber to European countries and the accompanying passage of customs formalities.
Transportation of lumber for export to Europe
The optimal method of transporting lumber and timber depends on a number of factors:
- Batch volume;
- Route;
- Delivery time restrictions.
Russia exports the largest volumes of timber to the west to Finland, Germany, the Netherlands, Great Britain, Poland, Estonia, Italy, Latvia, and Lithuania. The geographical location of countries determines the prevailing transportation options. Trucks are usually used for transportation over relatively short distances; it is more profitable to transport timber from Siberia to England as part of a multimodal delivery scheme. Road delivery covers all European countries, suitable for exporting batches of saw logs, veneer logs, boards, small medium and sized timber. Border crossing takes place in the Pskov, Smolensk, Bryansk, Leningrad regions or in the Republic of Karelia. Large consignments shipped from the North-West region are delivered to European buyers by motor ships. The advantage of sea transportation is its low cost, although it is inferior in speed to land transport. Rail transportation is actively used for deliveries to Finland and the Baltic countries, which have the same gauge as the Russian Federation, as well as for routes with a length of more than 4,000 km that have no alternatives. Air travel is extremely rarely used to deliver lumber to Europe due to its high cost. Transportation of wood as part of groupage cargo to Europe is possible, but this type of product is extremely rarely shipped in small quantities. The use of a multimodal scheme helps to optimize logistics costs arising when transporting lumber and timber. Talk to
specialistsour company to clarify the cost and delivery time of lumber along the route you are interested in.
Cost of processed wood
When exporting wood to Europe, the question arises about the cost of the product itself. The price of such a product depends on various factors. In particular, it is worth noting:
- exact location of the site and cut;
- product humidity level;
- type of wood, etc.
If a product is made from larch, then it is rated higher than its counterpart made from spruce or pine. The cost increases after drying because the moisture is completely removed. As a result, the possibility of cracks appearing is eliminated.
Features of export of lumber to Europe
Coniferous wood species are most often exported from Russia: larch, pine, spruce. In recent years, there has been a tendency to limit the export of such commodity items, which is manifested in quotas and protective duty rates on lumber supplied without licenses. For example, for logs from white fir of the Abies alba Mill. species, 3 meters long and 17-19 cm in diameter with the HS code 4403231100, the export customs duty rate is set at 80%, but not less than 55.2 euros per cubic meter. The same goods, shipped under a license from the Ministry of Industry and Trade within the established tariff quotas, are subject to a duty at a rate of 13%. Export supplies of lumber from hardwood are carried out without licenses. Each EAEU HS code for exported timber and lumber has certain requirements for the description of the goods in column 31 of the DT, without which the release cannot be carried out: type of wood, Latin name, dimensions, method of production, type of processing. Customs authorities especially carefully monitor the declared customs value and quantity of exported timber, since this affects the amount of payments collected. During the inspection of DT, customs has the opportunity to clarify with the manufacturer the place of origin of the product, request a forest declaration and other information. Before shipping lumber to Europe, it is necessary to undergo phytosanitary control by the Rosselkhoznadzor authorities. Counterparties try to warn in advance about the requirements for an international phytosanitary supply certificate (IPC). For some goods in the forest and lumber category, places for customs operations have been established.
Transportation Features
Exported lumber is placed in block packages, transport packages or transported wrapped in a special film. Lack of proper packaging may result in refusal of customs clearance.
Transportation can be carried out by sea, rail, road vehicles or multimodal, i.e. several modes of transport along one route.
Sea transport is used mainly for the delivery of timber from the most remote countries, especially those from where it is impossible to transport lumber by land. Delivery to the port is carried out in gondola cars, and upon arrival at the port of destination, the lumber is reloaded onto another type of transport and delivered to the recipient.
Direct rail routes are used if you need to deliver cargo to countries in Southeast Asia. The lumber is carefully fixed to prevent it from moving during transit. This is a fairly fast delivery method.
It is important to properly secure the load when transporting by road, since lumber on the road can not only be damaged, but also damage the vehicle and cause injuries. If long logs are transported, specially equipped timber trucks are used to transport them.
The organization of transportation is complicated by climatic conditions, seasonality, and mountain routes. These features should be provided for at the planning stage.
Note! Lumber is accompanied by a documentary description of quantitative and qualitative characteristics.
Export customs clearance of lumber
We provide services for export customs clearance of timber and lumber. Cooperation is possible in 2 different formats:
- under an agency agreement or export of lumber on a turnkey basis. Current rates are published on our website.
- within the framework of an agreement with a customs broker, which involves representing the interests of the importer with the customs authorities when declaring goods. Information about the cost of the service is also available for review.
Still have
questions about exporting lumber? Write or call us to clarify information and place your application!
Links to regulatory documents:
Federal Law “On Export Control” dated July 18, 1999 N 183-FZ Decision of the Board of the Eurasian Economic Commission dated April 21, 2015 N 30 “On non-tariff regulation measures”
Main directions of export and export of lumber, boards, timber timber
Lumber and wood, in principle, are very popular in European countries. This is a valuable raw material that has high practical properties. The material itself is environmentally friendly, so it is used in the following areas:
- Construction. It is used to produce elements of the supporting and secondary structure of the building, lay the floor, and perform finishing.
- Production of household products used in the household and kitchen. These are many small and small objects made of wood.
- The production of decorative and functional interior items, which are inherited by relatives and become museum exhibits.
Wood is a valuable resource that needs to be protected, so the process of its customs clearance is very important. It must be fast and legally correct.
List of main mandatory documents:
- A foreign trade contract and annexes (specifications) to it must contain detailed and comprehensive information about the terms of delivery in accordance with INCOTERMS; agreed product quality standards and a list of documentation confirming compliance with the standards; terms of payment; features of transportation and insurance; liability of the parties; the procedure for shipment and acceptance of goods; procedure and deadlines for submitting claims regarding quality, quantity and delivery time. Legal support recommended;
- Transaction passport;
- Invoice, packing list;
- Certificate of origin, which is issued by the Chamber of Commerce and Industry;
- Phytosanitary certificate - issued by the territorial department of Rosselkhoznadzor, as well as in some cases by bodies accredited by Rosselkhoznadzor for this purpose at the place of loading of goods upon inspection.
Before the start of customs clearance, the exporter must be registered with the customs office and pay customs duties.
Special requirements apply to filling out gr. 31 customs declaration. The following letters and permissions may also be required :
- Technical documentation describing technological processes, characteristics and properties of the final product (standards, regulations)
- An examination report or an expert opinion based on a test report to confirm the classification code of a product.
- A letter to the customs office at the place of shipment for permission to export and customs clearance of timber;
- Application to customs for permission to clear customs on the received detachment.
[edit] Indicators
[edit] Export value
The value of lumber exports from Russia ($ billion):
- 2017: 3,944[20]
- 2018: 4,503[21]
[edit] Physical volume of exports
Physical volume of sawn timber exports from Russia (million m3):
- 1995: 5.9[22]
- 2005: 14.8[23]
- 2009: 16.2[24]
[edit] Other
In 1994, 6.28 million cubic meters of lumber worth $669 million were exported from Russia.[25]
In 2003, Russia exported 6.48 million tons of lumber worth $1.19 billion.[26]
Exports of lumber from Russia in 2006 amounted to 9.74 million tons (8% more than in 2005) worth $2.32 billion.[27]
At the end of 2007, Russia exported 10.7 million tons (15.9 million cubic meters) of lumber worth $3.25 billion.[28][29]
In 2010, 9.92 million tons of lumber worth $3.02 billion were exported from Russia.[30][31]
Procedures upon arrival
When importing wood into Europe and in particular Germany, the registration procedures are as follows:
- arrival at the customs point for customs clearance and provision of shipping documents (invoice, packing list, specification and phyto certificate). The validity period of the phyto certificate depends on the country of destination. For the EU it is 14 days. In most cases, the importer will need to provide the arrived quarantine cargo upon arrival for inspection by quarantine authorities, followed by the issuance of an import quarantine certificate;
- for further processing it is necessary to provide documents on product quality;
- pay import duties and VAT. In Germany, wood has a VAT rate of 19%.
For a buyer in Germany, as for any European company, one of the most important conditions for cooperation is strict adherence to the agreed delivery times. That is why we recommend that you turn to professionals in matters of delivery and customs clearance of lumber.
Logistics has many years of experience in organizing international cargo transportation and customs clearance of specific cargo, representative offices and warehouse terminals in Europe, which allows you to receive guaranteed qualified assistance in Russia and in the country of import.
[edit] History
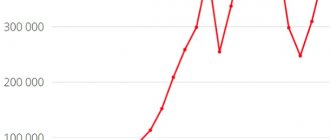
Dynamics of sawn timber exports from Russia, in million tons (in 1999-2010) and $ billion (in 1994-2010)
Main article
:
History of lumber exports from Russia
By 1996, lumber exports from Russia had decreased to 4.65 million cubic meters. Subsequently (1997-1998), exports stabilized. In mid-1998, the US dollar exchange rate in Russia was 6.2 rubles, profitability in sawmill production in Russia in 1998 was at the level of 1.8%, which did not contribute to the development of lumber production in small enterprises.[3]
In August 1998, an economic crisis broke out in Russia, the ruble was devalued, and a year later the US dollar exchange rate increased 4 times compared to 1998. Economic recovery has begun in Russia. The cost of lumber production in dollar terms has decreased significantly - the efficiency of lumber exports has become high. In just three years (1999-2001), sawn timber exports in Russia increased by 65% compared to 1998, to 7.70 million cubic meters.[4]
In 2004, lumber exports from Russia reached a record level as favorable policies stimulated foreign direct investment.[5]
On July 1, 2007, increased duties were introduced on roundwood exports. This measure is intended to stimulate domestic production and export of lumber.[6][7]
In 2011, the volume of exports of processed timber from Russia amounted to 11.1 million tons (18.8 million cubic meters). According to experts, the main reasons for the increased interest of importers in Russian lumber are a significant increase in their quality due to the use of modern sawmill technologies in production and high transport accessibility.[8][9][10]