Those who are just starting to engage in business in the field of foreign economic activity often make a serious mistake: they enter into transactions only on the basis of an analysis of the difference between the purchase price and the cost specified in the contract. The happy entrepreneur hopes to make a huge profit, but in reality it turns out that the export/import activity brought much less profit.
This happens due to the fact that many people forget to take into account the amount of customs duties when making calculations, which directly affects the cost of the goods and inversely affects the amount of profit. For this reason, it is very important to calculate potential customs duties before concluding a transaction. An experienced customs broker-declarant will help you do this correctly and quickly.
Do you want to figure it out, but don’t have time to read the article? Lawyers will help
Entrust the task to professionals. Lawyers will complete the order at the cost you specify
Solve the issue >
What are customs duties?
Customs payments are the general name for duties, taxes and fees collected by customs authorities from participants in foreign economic activity when they move goods, cargo, and vehicles across the border. Depending on the direction of movement of goods, import and export fees are distinguished.
The importer pays import duty (if any), excise tax (if the imported goods fall under the excisable category), value added tax (if the tax rate is not zero) and customs duty. The exporter, if the exported goods are not subject to export duty, will only pay customs duty.
The accrual of customs duties depends on the declared value of the goods, which, in turn, is related to the delivery conditions specified in the contract in accordance with INCOTERMS 2010. For example, under the terms of the transaction, you purchased goods under FCA conditions (free carrier / free carrier: the seller transfers the goods to the buyer at his warehouse or other clearly indicated place). Then, when importing it, the value that you will declare to customs must include the cost of the goods according to the invoice + the cost of delivery to the border.
An important point: customs value is always calculated in rubles. Let's return to our example - even if the invoice indicates the cost in foreign currency, you also paid for delivery to the border not in rubles, then customs will have to convert these amounts into rubles at the Central Bank exchange rate on the date of filing the declaration.
The HS code (commodity nomenclature for foreign economic activity) will help you calculate payments correctly. You can determine it yourself or with the help of an experienced declarant. If you cannot clearly determine the code, you can always send an official request to customs. Based on your description, they will determine the product code.
Pay for customs work
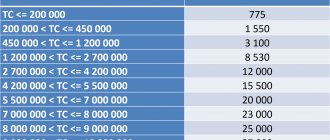
Customs duties are actually payment for the work of customs and inspectors, the amount of which is determined by the Government of the Russian Federation. The rate of customs clearance fee depends on the declared value of the cargo. When importing, the amount varies from 775 rubles. when the cost of the cargo is less than 200 thousand rubles. up to 30,000 rub. when the cost of cargo is over 10 million rubles.
In addition, you will have to pay a fee for terminal processing and storage of cargo in a customs temporary storage warehouse (TSW) . The tariffs at the terminals are different; the fee is charged according to the official price list and depends on the type and quantity of cargo and on the transport on which it arrived.
Calculation of customs duties according to the HS code
Why is the HS code so useful? In fact, this is the key to all the necessary information on customs payments. For example, you will be able to find out whether your product is excisable and whether you will have to pay duty. And if, in addition to the code, you know the country of origin of the product, then during import you can check whether there are preferential rates for it (so-called preferences). Please note that if there are preferences, you will need to request from the seller a document confirming the country of origin (most often this is a certificate of origin), this will reduce the import duty.
Important: if this is not the first time you are declaring a product of the same type, we still advise you to check all the information on taxes and duties on it, since customs legislation changes very often - duties or excise taxes may be canceled, or their size and order may change accruals.
Calculation of transaction value for identical goods
Another common method is to calculate the cost of a transaction with identical goods. This method can only be used in cases where another cargo with similar characteristics is delivered in the same period of time, which allows us to draw an analogy between their costs.
The technique is appropriate when the declarant does not have the opportunity to provide the entire list of necessary documents. In this case, the responsibility for drawing an analogy with an identical transaction falls on the declarant. If in the given example the cargo volume or some characteristics differ, then an adjustment is made using a mathematical proportion. If there are several similar examples of transaction costs for imported goods, then the lowest of them is taken as the basis for the calculation.
Customs duty
Not all goods are subject to customs duties. You can find out whether the goods you are declaring are such, using the HS code. As we have already said, there are duties on the export and import of goods. In addition, duties are differentiated depending on the method of their calculation:
- ad valorem rate: calculated as a percentage of your declared customs value (for example, the import duty on natural pearls with the HS code 7101100000 will be 10%);
- specific rate: charged in monetary terms per unit of goods (for example, the duty for importing rubber boots with code 6401100000 will be 0.75 euros per pair);
- combined rate: combines the principles of calculating ad valorem and specific rates (for example, the export duty on rapeseed not intended for sowing with code 1205109000 will be 6.5%, but not less than 11.40 euros per ton. That is, even if 6 .5% of the customs value per ton of rapeseed will be less than 11.40 euros, you will still have to pay this rate).
Also, the amount of import customs duty depends on the country of origin. The basic duty rate is 100%, for goods from developing countries it will be 75%, and for goods from least developed countries it will be 0%.
An important point: importers and exporters are trying to reduce the cost of goods for customs, thus minimizing the duty. Please note that for goods subject to duty, customs in most cases will ask you to provide a cost estimate with the provision of all supporting documents (contracts, invoices, acts, waybills, etc.). If there are doubts about the reliability of the information provided, the cost is adjusted according to side of increase - accordingly, the duty increases.
Fees
Keep records of exports and imports using the simplified tax system in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Currency accounting and work instructions, taxes, automatic salary calculation and reporting in one service Get free access for 14 days
Customs duties are payments collected by customs authorities for their services for registration, storage and maintenance of goods.
Customs duties apply to all types of goods regardless of their origin. The amount of the fee depends on the declared customs value of the goods. If you submit a declaration for goods electronically, you can pay the fee with a 25% discount.
Excise tax
This type of customs payment is relevant only for imports. An excise tax is a tax on certain product groups. This tax applies to the same goods that are excisable within the country - alcohol, tobacco products, cars, motorcycles with a certain engine power.
The full list of excisable goods, as well as tax rates, are specified in the Tax Code. The rate will always be in rubles per unit of goods (piece, liter, kilogram, ton). Important: the importer is required to pay the excise tax before submitting the declaration to customs.
What is import tax
Keep records of exports and imports using the simplified tax system in the Kontur.Accounting web service.
Currency accounting and work instructions, taxes, automatic salary calculation and reporting in one service Get free access for 14 days
These are fees that the state collects from a subject of foreign economic activity. And the object of taxation are goods and services that are imported into the territory of another state. The purpose of the import tax is to regulate trade turnover in the domestic market, support national producers and replenish the state budget.
The Accounting Dictionary classifies all fees and charges other than VAT as import taxes. Although when importing goods into Russia, the importer is required to pay VAT along with other fees. The calculation of the procedure and amount of deductions is regulated by the Tax and Customs Codes. In this case, VAT on imported goods is transferred along with customs duties to the Federal Customs Service.
VAT
Goods exported outside the country are not subject to VAT. This payment is relevant only for imported goods. There are several types of tax rates:
- full (VAT - 20%): most of the goods imported into the country fall under this category;
- preferential (VAT - 10%): this includes some types of goods for children, as well as some food products;
- zero (VAT - 0%): applies only to high-tech products, and to those that have no analogues on the domestic market. The list of such products is established by the Government and is regularly updated.
In order to correctly calculate this customs payment, you need to remember an important nuance: if the declared goods are subject to duty and/or excise tax, VAT must be calculated from the amount of the value declared to customs, duty and excise tax. For example, the cost of goods according to the invoice is $2,500, transportation of goods to the border is $200, the goods are not excisable, but are subject to a 6.5% duty, and there are no VAT benefits. Then the cost of the goods indicated in the declaration is: 2500 + 200 = 2700 dollars.
The fee to be paid will be: $2,700 * 6.5% = $175.50. Accordingly, we will calculate VAT from the following amount: 2700 + 175.50 = 2875.50 dollars. Then the amount of VAT payable is 2875.50 * 20% = $575.10.
Do not forget to convert this amount into rubles at the Central Bank exchange rate on the day of filing the declaration. Important: unlike VAT on goods within the country, this payment for import must be made along with the rest before filing the declaration, and not at the end of the quarter.
Payment procedure and terms
Customs duties must be paid by the declarant. They are deposited into the account of the customs authority, which controls the declared goods after the customs value has been announced. Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs do this by bank transfer.
The actual transfer of customs payments to the account of the customs authority must be made in the form of an advance before the completed customs declaration is submitted for control. This is necessary to register the declaration in the customs database.
If the advance payment turned out to be higher than the amount that was actually needed, the excess can be returned upon the appropriate application of the declarant.
It is worth noting that without proper experience it is quite difficult to understand how the declaration is filled out and how customs duties are calculated. In this regard, it can be very difficult to do without the help of a customs representative. To eliminate stopping factors, it is better to enlist the support of professionals. This will prevent the imposition of fines, as well as the accrual of penalties and administrative arrest, which has already become common for such violations that are committed without direct intent, but due to ignorance or errors in calculation.
Contact JSC specialists for advice and comprehensive support!
We guarantee a qualified approach and strict observance of the interests and legal rights of clients. Find out the cost of customs clearance
Car import rates
To import a car you need to pay VAT, excise tax and customs duty on the car.
But it’s worth noting right away that the amount of customs duties on a car depends on the following characteristics of the car:
- What is its customs value?
- Legal status of the person who imports: natural or legal person.
- Engine volume.
- Power in kilowatts.
- Vehicle weight (vehicle weight is calculated in tons).
- Engine type.
- Year of manufacture (in other words, age).
How to clear a car through customs - customs auto calculator
There are only four ages:
- less than three years;
- from three to five years;
- from five to seven years;
- more than seven years.
In the latest amendments to the bill, it was decided to make a single rate for cars based on age and engine size.
So, if the car is less than three years old, then a combined rate of 54% applies. This does not apply to cars that were manufactured in the Russian Federation. But it is worth considering that the minimum bet is 2.5 euros.
Table. Calculation of customs duties based on engine volume for cars less than three years old.
| Price for 1 cm cube. (In Euro) | Minimum cost of the car (in rubles) | Maximum cost of the car (in rubles) |
| 2,5 | 325 000 | |
| 3,5 | 325 000 | 650 000 |
| 5,5 | 650 000 | 1 625 000 |
| 7,5 | 1 625 000 | 3 250 000 |
| 15 | 3 250 000 | 6 500 000 |
| 20 | 6,500,000 or more |
For cars that were manufactured in the Russian Federation, a single rate applies. It is equal to one euro per cm3.
Table. Calculation of customs rates based on engine volume for cars over five years old.
| Price for 1 cm cube. (In Euro) | Minimum engine capacity (in cm3) | Maximum engine capacity (in cm3) |
| 3 | 1000 | |
| 3,2 | 1000 | 1500 |
| 3,5 | 1500 | 1800 |
| 4,8 | 1800 | 2300 |
| 5 | 2300 | 3000 |
| 5,7 | 3000 or more |
For yachts, other categories of cars, boats, a single tariff rate of 30% of the cost of equipment is applied. For example, if the estimated value of the yacht is 20,000 euros, then the payment amount is 6,000 euros.
Classification
According to the current legislation, in 2021 the following types of customs duties are distinguished:
- Import customs duty. This payment is also called import payment.
- Export customs duty. Often this payment is called an export payment, since it is paid for the export of products outside of Russia.
Most goods are subject to import customs duties. This is primarily due to the fact that Russia in 2021 is actively “receiving” export products into its territory.
Import duties are imposed on all groups of goods imported into Russia. But it is worth remembering that according to customs rules, there are a number of goods allowed for import in a certain quantity. If they are imported in quantities exceeding the established norm, then customs duty is always paid.
Customs duty
The collection of customs duties on imported goods protects the domestic market of the Russian Federation from competition. Customs duties on imports are transferred to the Russian state budget. In recent years, it is these types of duties and taxes that have made up the bulk of the Russian Federation budget.
Customs duties and fees for the export of products are necessary to regulate the country’s foreign economic activity. They also replenish the Russian state budget.
What is allowed to be imported without paying duty?
If a person carries with him personal funds, not counting a car, the total amount of which does not exceed 500 euros, then he is not required to pay a customs duty. In this case, the total weight of goods or products cannot exceed 25 kilograms. This applies only to those goods that are transported by land (by car or train). These rules are in effect from January 1, 2021. If a person travels by air, then he can import goods worth up to 10,000 euros duty free.
Additionally, a person can carry:
- 50 cigars or two cartons of cigarettes. An alternative to cigarettes and cigars is tobacco in an amount of 250 grams.
- Three liters of alcoholic beverages.
In other words, if a person wants to import four or more liters of alcohol, then he is obliged to pay 10 euros to the Russian budget for each “extra” liter of alcoholic drink brought. But it is worth considering that you cannot transport more than five liters of such products for personal consumption. If a larger quantity of alcohol is transported, then the cargo is already considered commercial: additional documents must be submitted for it and an additional VAT of 18 percent and excise tax must be paid.
If the cargo is considered commercial, then the rate for alcohol is 0.6 euros for each liter of alcoholic beverages.