homeCustoms payments
Customs payments are duties, taxes and charges levied by government agencies from participants in foreign economic activity (FEA) when moving cargo, goods and vehicles across the customs border of the Customs Union (CU).
According to paragraph 1 of Article 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part one), customs authorities enjoy the rights and bear the responsibilities of tax authorities to collect taxes when moving goods across the customs border of the Customs Union in accordance with the customs legislation of the Customs Union and the legislation of the Russian Federation on customs affairs, this Code (Tax), other federal laws on taxes, as well as other federal laws.
The subject of customs duties and taxes are goods transported across the customs border in accordance with Article 51 of the Customs Code of the Eurasian Economic Union - EAEU Customs Code. (previously see Article 75 of the Customs Code of the Customs Union - TC CU).
The basis for calculating customs duties depending on the type of goods and applied types of rates is the customs value of goods and (or) their physical characteristics in kind (quantity, weight, taking into account its primary packaging, which is inseparable from the goods before its consumption and in which the goods are presented for retail sale, volume or other characteristics) (Article 51 of the EAEU Labor Code).
The tax base for calculating taxes is determined in accordance with tax legislation.
Types of customs payments
Article 46 of the EAEU Customs Code defines the following types of customs payments:
- Import customs duty;
- Export customs duty;
- Value added tax;
- Excise tax;
- Customs duties;
- Special, anti-dumping and countervailing duties.
Customs duty is a mandatory payment levied by customs authorities in connection with the movement of goods across the customs border of the Union, in accordance with Article 2 of the EAEU Labor Code (previously see Article 4 of the CU Customs Code). There are import and export duties. The amount of duties charged varies depending on the type of goods and the category of foreign trade participant and is indicated in the Unified Customs Tariff of the Eurasian Economic Union (UCT). A number of goods (cars, petroleum products) have high import and export customs duties. Individuals transporting goods for personal use across the customs border are exempt from paying duties (for goods that are not goods for personal use, see Appendix No. 6 to Decision No. 107).
Value added tax (VAT) is a type of customs payment that is assessed when goods are imported into the territory of the Customs Union. There are two types of VAT: 0%, 10% or 20% (until 12/31/18 it was 18%). The amount of VAT depends on the type of goods (for some goods a preference is given - 0%).
Excise duty is a type of indirect tax and is imposed on excisable products (petroleum products, cars, alcohol and tobacco products), that is, on goods for which the demand does not change due to an increase or decrease in their value.
Customs duties are mandatory payments levied for customs authorities performing customs operations related to the release of goods, customs escort of vehicles, as well as for performing other actions Art. 47 Labor Code of the EAEU (formerly Article 72 Labor Code of the Customs Union).
customs duty
Customs duty
Customs VAT
Customs excise duty
Documents and information on customs payments
- Customs payment codes (View)
- Instructions for paying customs duties (Watch)
How to pay?
The following month after the import of goods (regardless of the date), before the 20th, you must provide receipts for payment of indirect taxes to customs officers. It is also necessary to add documents giving the right to import these goods into the country. In addition, supporting documents must be submitted.
The procedure for collecting indirect taxes in the customs union after the adoption of new rules does not depend on customs, since all transactions are carried out through the tax authorities. Since the duty rate is 0, no customs service is involved.
Usually the payer himself determines the amount to be paid, but in certain situations regulated by law, the customs authorities either assign the amount themselves or require additional taxes to be paid.
By default, the duty is paid in national currency, but can be converted into any foreign currency at the current exchange rate of the central bank.
Customs duties calculation calculator
Customs value
Customs duty rate %
Example of customs payment calculation:
If the cost of the goods is 1200 dollars, provided that the duty on it is 10% and VAT 20%, the customs payment will be calculated as follows: accrual basis 1200 dollars (80,400.00 rubles at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation at the time of filing the declaration *) 1) fee for customs clearance 375.00 rub. 2) 10% duty 8040.00 rub. 3) 20% VAT 17688.00 rub. (80400.00 + 8040.00 = 88440.00 rub. * 0.20 = 17688.00 rub.)
The total amount of customs payment paid to customs will be 389.59 US dollars or at the Central Bank exchange rate at the time of filing the declaration 26,103.00 rubles.
The total cost of goods when imported into the Russian Federation, taking into account customs duties, will be 1,584.00 US dollars or 106,128.00 rubles.
(1200.00 + 389.59 = 1584.59 US dollars or 80400.00 + 26103.00 = 106128.00 rubles)
| Calculation by payment types | ||||||
| View | Accrual basis (RUB) | Accrual basis (USD) | Bid % | Amount of customs payments at the time of registration in rubles. | Amount of customs payments in the contract currency (USD) | |
| customs duty | RUB 80,400.00 | 1200,00 $ | RUB 375.00 | 5,59 $ | ||
| Duty | RUB 80,400.00 | 1200,00 $ | 10% | 8040.00 rub. | 120,00 $ | |
| Excise tax | is not a subject to a tax | is not a subject to a tax | 0.00 rub. | 0,00 $ | ||
| VAT | RUR 88,440.00 | 1320,00 $ | 20% | 17688.00 rub. | 264,00 $ | |
| The customs payment will be: | 26103.00 rub. | $389.59 | ||||
* — In our example, the Central Bank exchange rate at the time of filing the declaration is taken at the rate of 67 rubles per 1 US dollar
Attention! Customs duties are paid in the currency of the country in which the goods are customs cleared.
Calculation of customs duties can be made only after the customs value of the declared goods is known. The customs value of goods (CTV) is the sum of the cost of the goods and the cost of its delivery to the customs border (customs union for imports). If the cost of transportation can be found out from the carrier company, then the declarant can obtain the cost of the goods from the contract (agreement) of the foreign trade transaction.
Basic expenses
We have collected all possible customs duties and fees that must be paid when importing goods into Russia.
As a rule, the main costs during customs clearance borne by the importer of foreign products are:
Registration of documents by the carrier
When delivering cargo from Europe to Russia, the carrier must independently pay and complete the following paperwork:
- Shipping documents. These papers are issued by a European broker in the EU before entering the border zone:
- International bill of lading (CMR);
- Export declaration (EX-1). “Opens” on the territory of the EU upon registration, “Closes” at customs upon entry into the Russian Federation.
- Warranty certificate . This is a document backed by a bank guarantee, which ensures the payment of customs duties to Russian customs in the event that customs duties are not paid by the importer who imported the goods into Russia. The document is issued in the border zone on the territory of the Russian Federation, before leaving it.
How do I pay for paperwork?
Registration of shipping documents and a warranty certificate, as a rule, is included in the general rate of the transport company and is paid by the importer in the general invoice.
Customs clearance of cargo by broker
Payment to the customs representative/broker consists of the following work:
- Registration of customs declarations for goods. The cost of work depends on the number of HS codes. The more HS codes, the more labor-intensive the registration.
- Services of a temporary storage warehouse at a customs terminal (TSW TT) during customs clearance of cargo. Eride.ru tariffs include 48 hours of cargo storage at a TT temporary storage warehouse by default.
How is customs clearance paid?
Customs clearance is included in the comprehensive service of Eride.ru and is paid in the general invoice. If you have your own customs representative with whom you register the goods, then you pay him directly.
Customs payments: duties and fees
In order for customs to clear the border, the importer must pay:
- Customs duty on goods;
- Fee to the state for customs clearance. Advance payment;
- VAT payable upon release of goods into free circulation. Advance payment.
How are customs duties paid?
They are paid by the importer independently by bank transfer to the customs accounts . Eride.ru specialists will advise on payment of all customs duties. You can also use our special instructions.
Advance payments are
government fees for customs clearance and VAT. They are called advance payments, as they are paid before customs clearance into a separate customs account for advance payments.
Understanding the mechanism for calculating these costs, as well as the procedure for paying them, will be extremely useful for our reader.
There are a number of online customs payment calculators on the Internet, but none of them can explain to you the principle of their operation, so there remains room for doubt about the correctness and accuracy of the calculation.
We offer to calculate customs payments: duties, fees and VAT through our managers. Below we will describe how we do the calculation and give an example of such a calculation.
Benefits for paying customs duties
Tariff preferences - exemption from payment of import customs duties in respect of goods originating from countries that form a free trade zone together with the Russian Federation, or have signed agreements aimed at creating such a zone, or a reduction in the rates of import customs duties in respect of goods originating from developing or least developed countries using the unified system of tariff preferences of the Customs Union (Article 36 of the Law of the Russian Federation of May 21, 1993 No. 5003-1 “On the Customs Tariff”).
Tariff benefits are benefits in the payment of customs duties. They apply to goods produced in countries that have an agreement with the Russian Federation on the mutual provision of tariff preferences and benefits.
Tax benefits. These benefits, for example, include benefits for paying VAT when importing into the territory of the Russian Federation imported goods related to technological equipment, analogues of which are not produced in Russia (Article 150 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The amounts and types of benefits for the payment of customs duties are determined by the internal legislation of the EAEU member states.
Design features
Have you decided to become the owner of an imported car? Be prepared for the fact that first of all you will have to prove your solvency by depositing the guarantee amount. If you don’t know how to calculate the cost of customs clearance of a car, you can deposit an approximate amount into your account. In any case, unused funds will be returned by customs after complete border control.
Confirmation that you have deposited funds will be a receipt and certificate issued by the Federal Customs Service. With these documents it is much easier to travel abroad. You should also pay attention to how you will import the car: drive it yourself, sitting behind the wheel, or use container transportation. This determines whether you need to fill out the TD-6 declaration.
From January 2021, a mandatory condition for importing a car across the EAEU border is the installation of the ERA-GLONASS system on it. It must be purchased from JSC GLONASS, installed in a certified center, enter information about the VIN number and body number and obtain a vehicle design safety certificate from a special laboratory.
Payment of customs duties - procedure and terms
The obligation to pay customs duties is assigned to the declarant in accordance with Article 50 of the EAEU Labor Code (previously see Article 79 of the CU Labor Code). After calculating customs duties, the declarant deposits funds into the account of the customs authority, which carries out customs clearance of the declared goods. Individuals can deposit funds through specialized terminals on the territory of the customs post (if available). Legal entities can use a customs card or a card of the Round payment system, which allows them to make customs payments without delays.
Attention! When calculating customs duties, it is necessary to take into account fluctuations in exchange rates.
Deadlines for payment of customs duties. Customs duties are paid by the declarant in the form of an advance. They must arrive at the account of the customs authority before submitting the customs declaration.
Other possible expenses
There may also be costs associated with customs clearance:
- Registration of an electronic digital signature (EDS). If you will undergo customs clearance not under the seal of a customs broker, but under your own digital signature and you do not have one yet (on average, urgent registration of an electronic signature takes 1 day and costs 5,900 rubles one-time, Eride.ru helps you obtain an electronic signature);
- Payment for cargo demurrage at the TT temporary storage warehouse in excess of the standard (48 hours) limit established by Eride.ru in case of emergency situations related to cargo inspection. If this happened due to the fault of Eride.ru, we will bear these costs;
- Increase in customs duties in case of adjustment of the customs value of goods (CTV). We wrote in more detail earlier in the chapter about CTS;
- Fines from customs if the actual cargo does not correspond to the quantity declared in the documents according to quantitative and qualitative criteria. In this case, a case of an Administrative Offense will be opened.
How to pay customs duties, read the instructions
Customs clearance fee
The amount of the fee depends only on the cost of the car.
The new customs duty rates are effective from August 1, 2020.
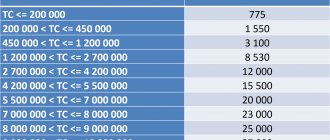
| Cost of the car, rub. | Cost of registration, rub. |
| up to 200,000 | 775 |
| up to 450,000 | 1 550 |
| up to 1,200,000 | 3 100 |
| up to 2,700,000 | 8 530 |
| up to 4,200,000 | 12 000 |
| up to 5,500,000 | 15 500 |
| up to 7,000,000 | 20 000 |
| up to 8,000,000 | 23 000 |
| up to 9,000,000 | 25 000 |
| up to 10,000,000 | 27 000 |
| over 10,000,000 | 30 000 |
Fees
How to calculate the amount of customs duty? To determine how much tax an importer must pay, there are several types of rates.
The ad valorem rate is a percentage of the cost of imported products. This rate does not have a fixed amount and is calculated individually each time. For example, an importing company buys equipment worth $4,000 abroad. The import duty for this product is 20%. Accordingly, you will have to transfer $800 to the customs authorities.
If the duty is levied in a specific amount on each unit of production, then such a rate is called specific . For example, a batch of 500 pairs of shoes is imported into the country, the rate for each pair is 30 euro cents. Therefore, the importer will have to pay a duty of 150 euros.
a combined works , which takes both principles into account. For example, a batch of clothing is imported, and a duty of 1 euro is charged on each unit of product. But at the same time, the total duty for the shipment must be at least 100 euros. Combined duty is the most common type of fee.
Goods that are not subject to customs duties include: personal belongings, currency, humanitarian aid, transit and leasing cargo, fish and seafood if they were obtained by a Russian vessel, periodicals and book products related to education, science and culture, if they are imported for libraries, archives and publishing houses.
Excise tax
The amount of excise tax on cars depends on the engine power.
The new rates are effective from January 1, 2021.
Current excise tax rates:
| Engine power | Excise tax rate |
| up to 90 hp | 0 rub. for 1 hp |
| 91 – 150 hp | 51 rub. for 1 hp |
| 151 – 200 hp | 491 rub. for 1 hp |
| 201 – 300 hp | 804 rub. for 1 hp |
| 301 – 400 hp | 1370 rub. for 1 hp |
| 401 – 500 hp | 1418 rub. for 1 hp |
| over 501 hp | 1464 rub. for 1 hp |
Documents that will be required
When entering the territory of Russia, you must present a considerable package of documents:
- original documents for the car and their copies (it is important that the data in the passport and on the body, engine, etc. completely match);
- customs receipt with a certificate issued before departure abroad;
- car insurance contract;
- GLONASS security certificate;
- customs declaration, which can be prepared in advance using the online form for pre-filling the passenger customs declaration
Insurance is important. The lack of compulsory insurance can be a significant argument for refusal to cross the border, and in some cases even threatens with a fine.
Recycling collection
The recycling fee is calculated using the following formula:
CS = BS × K
BS – base rate K – coefficient.
The base rate is determined by the category of the vehicle:
Coefficient values for individuals:
| For cars under 3 years old | For cars older than 3 years |
| 0.17 | 0.26 |
Coefficient values for legal entities:
| Engine capacity | up to 1000 cm3 | 1001 – 2000 cm3 | 2001 – 3000 cm3 | 3001 – 3500 cm3 | over 3500 cm3 | electric cars |
| Cars under 3 years old | 2.41 | 8.92 | 14.08 | 12.98 | 22.25 | 1.63 |
| Cars older than 3 years | 6.15 | 15.69 | 24.01 | 28.5 | 35.01 | 6.1 |