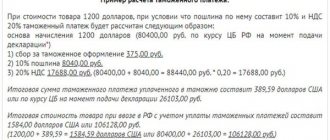
Duty is one of the customs payments that are paid for the import and export of goods. People call duty all customs payments, but in addition to the duty itself, the state also takes:
- VAT - value added tax from 0% to 20% depending on the type of product;
- Indirect taxes , which are paid when importing gasoline, alcohol, cigarettes and other excisable goods;
- Customs duties are payments that customs takes for clearance support services, that is, the work of inspectors. They depend on the cost of the product and as of August 15, 2020 range from 375 to 22,500 rubles.
We will tell you how to calculate customs duties for business and give examples of real calculations.
Definition of payments
Depending on certain conditions of the international transaction, all additional costs associated with the storage and transportation of goods, as well as customs duties, are included in the final cost of the products that are sold or purchased.
For example, the importer of products pays value added tax, import duty, customs duties, as well as excise duty for a group of excisable goods. In turn, the exporter pays a fee for completing the declaration (does not apply to products that are subject to export duty).
The so-called risk group includes products that are in high demand on the world market, as well as those that are strategically undesirable to be exported outside the territory of the state.
How to calculate customs duties? First of all, it is necessary to find out the HS code and calculate the customs value. This can be done through an official request to customs.
What does the HS code indicate when calculating?
Thanks to it, you can calculate nominal payments, find out what duties still need to be paid and what permits need to be obtained. You can also find out whether the state has any benefits when calculating customs duties.
Calculating the customs formula - step-by-step instructions
Step 1. Determine the HS code
Each product has its own HS code, which will help determine the size of both customs duty multipliers.
Various databases are used to select codes. A free option is available on the TKS website https://www.tks.ru/db/tnved/tree - enter a keyword in the search bar and look for your product in the list of results. You can search manually through the list of product group sections.
The disadvantages of the TKS database are that it is not always updated in a timely manner and does not contain a complete list of materials necessary for customs clearance - customs orders, decrees, regulations, and so on.
Professionals use paid databases - for example, VED Info. It costs 7,500 rubles per month of registration and 3,190 rubles per month of subscription. All updates are immediately uploaded there and there is complete information on the order of registration for each product.
Some programs do not guarantee the correct selection of code - practical experience is needed here. You need to remember this when choosing whether to declare the cargo yourself or contact a broker.
Step 2. Determine what we calculate the duty from
Customs duties can be ad valorem - they are calculated based on the value of the cargo - and specific - they are calculated based on the number of units, weight, and so on. There are also combined duties: when you choose the option where the size is larger or combine both options. Which option to choose is indicated by the HS code.
Step 3. Multiply by the bet
You can determine the rate by the HS code; any database or search engine will tell you the rate. This is the easiest step.
Determination of duty
This is a tax imposed on cargo when it crosses the border of a state. There are the following types of duties (they have different formulas for calculating customs duties):
- ad valorem (calculation of customs duties using a percentage of the contract value of a batch of products);
- specific (payments can be calculated in monetary terms for each unit of production);
- combined (both the first and second conditions are taken into account).
Rates are reviewed regularly, and sometimes preferential conditions are introduced under which rates are changed or canceled altogether. To know how to calculate the customs value of goods, you need to be aware of current changes.
Customs duties on imported goods
Import customs duties in 2021 will not apply to goods valued at less than €500 transported by road, bus, rail or sea. There is no need to pay a fee in 2021 if the weight of accompanied and unaccompanied baggage is 25 kg or less (in 2021 - 50 kg). Duty-free air transport is allowed to import 50 kg of cargo worth no more than 10 thousand euros.
Customs duties on imports from China (Aliexpress) in 2021 will be 15% of the amount exceeding the threshold value and 4 euros for each kilogram in excess of the established limit.
Duty-free threshold for individuals for orders from Aliexpress in 2021:
- parcel weight - no more than 31 kg;
- the maximum cost of a parcel is 50 euros;
- You are allowed to order goods for any amount per month.
If the limit is exceeded, then customs duty on the import of goods is paid. You can bypass the payment only by asking a friend who lives in another country, where such limits do not apply, to order the product and bring it to Russia. Aliexpress immediately sends information to customs after payment for the goods. Therefore, it does not matter what price the seller indicates on the box - customs officers will still know the real price.
Value added tax
There is no need to pay VAT when exporting products. At the same time, all imported goods are divided into three categories, each of which is assigned a certain VAT rate.
- first group: VAT – 18% (most of the imported goods);
- second group: preferential VAT rate - 10% (a number of food and children's products);
- third group: VAT – 0% (equipment that has no analogues in the importing country).
The decision on what equipment belongs to the third group is made by the state government.
How is VAT calculated for an importer? It is calculated from the sum of the contract value of the goods, excise tax and duty. Tax is calculated from this amount (according to the interest rate). To calculate, you can use the online customs duties calculator. As practice shows, such a calculation effectively simplifies the process of paying taxes when importing.
Payment must be made before submitting the declaration.
VAT on imports from EAEU countries
In case of mutual trade with the former union states, VAT on imported goods or services is calculated according to an elementary scheme, and the payment of the budget fee is made to the treasury account of the territorial tax inspectorate.
The object for VAT taxation in the case of imports from the EAEU powers is determined as the cost of the purchased commodity mass, increased by the amount of excise duty (if necessary). The moment of formation of the tax base is determined by the calendar date when the imported goods are recorded in warehouse accounting. The amount of VAT is determined by simply multiplying the cost of purchased commodity products and the required tax tariff.
At the close of the quarter in which import transactions involving the movement of goods from the EAEU were carried out, the Russian importing company (IP) is obliged to submit a VAT declaration to the fiscal authority. The document must be submitted by the 20th day (inclusive) of the month following the reporting period.
Important: the “import” VAT declaration is submitted in the form of a “paper” document. Electronic reporting is used only by those taxpayers whose staff exceeds 100 people.
Simultaneously with submitting the VAT return, the importer is obliged to pay tax according to the banking parameters of “his” tax department. The payment order applies a separate BCC for VAT when importing from neighboring countries.
How to calculate
How to calculate customs duties correctly?
Export: if the product is not included in the list of goods according to which the export duty is determined, you only need to pay a registration fee (from 500 rubles).
Import: if there are no special conditions, then it is necessary to calculate VAT as a percentage of the sum of the customs value of the consignment of goods and the clearance fee. A registration fee must be added to VAT. The amount received will constitute the payment.
When using an online calculator, it is necessary to determine the code of the imported product, as well as its quantity and the customs value of the imported product. You must also indicate the country of origin of the product. All required data should be entered into the specialized form of the calculator, and the calculations will be made. It is important to calculate these payments in advance in order to be able to properly plan the company’s budget.
VAT rates for the import of goods and services
For taxation of goods or services imported from abroad, standard tax rates are applied - 0%, 10%, 18%. To correctly use the required percentage during customs clearance and VAT calculations, follow the proposed algorithm:
- identify the product code according to the Unified Customs Tariff of the Customs Union ;
- compare the code with the lists of goods taken into account at a 10% rate ;
- in the absence of the required code in the specified lists approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, a rate of 18% .
The specificity of the calculation and payment of “import” VAT is the fact that the required calculations must be made before the item of trade leaves the customs post. Payment of VAT is made directly to the customs authority, as part of the mandatory payments for clearance.
The importer independently determines the tax base, product code and the amount of VAT required to be paid. If a problematic situation arises when customs applies a higher tax rate than the one calculated by the declarant, the importer can appeal to a higher customs authority.
The importer is given 15 days from the date the cargo crossed the Russian border to pay VAT when drawing up a customs declaration. Each day of delay in remitting tax will “cost” the buyer 1/300 of the key rate, multiplied by the full value of the cargo according to the declaration.
In what cases and by whom is STP used?
Goods imported into Russia are subject to aggregate customs duties only for individuals under the following conditions:
- the goods do not belong to the category of cargo for personal use and are intended for commercial activities;
- when importing vehicles that are not intended for public roads (snowmobiles, ATVs, etc.);
- Vehicles that can accommodate no more than 12 people (including motorcycles, mopeds, scooters, trailers) move across the border;
- when importing cars and other motor vehicles with electric motors;
- import of motorized freight vehicles with a carrying capacity of no more than 5 tons;
- units of water and air transport that were not registered in Russia are transported.
Import into the territory of the Russian Federation by individuals of goods intended for personal use is subject to cumulative customs duties in the following cases:
- the customs border is crossed by a person more than once a week;
- the total cost of the cargo exceeds 650 thousand. rubles and/or a total weight of 200 kg (STP applies only to the part in excess of the norm);
- if the imported product weighing more than 35 kg cannot be divided (consists of one copy or a disassembled set);
- imported alcoholic or tobacco products exceed the permissible limit for import by no more than 5 times (the first category means wine, beer and malt drinks);
- the cargo is sent to an individual who does not cross the border of the Russian Federation (this does not apply to cases of international mail).
Thus, the aggregate customs payment applies exclusively to the category of individual.
When calculating STP, the rates of duties and excises established by Russian legislation are applied. For clearance of cargo imported by individuals and subject to aggregate customs duties, a customs fee of 250 rubles is paid. Are there any problems in the field of foreign trade?
Don’t know how to solve them at the lowest cost? Contact EIG professionals, because solving foreign trade problems is our job!
Or contact us by phone,
Or via email
What goods are subject to excise duty?
An excise tax is an indirect federal tax that must be paid on certain goods and services. Their list is given in Art. 181 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- ethyl alcohol from food and non-food raw materials, including denatured, raw alcohol, distillates;
- alcohol with an ethyl alcohol content of more than 0.5%, beer, wine materials;
- cigarettes, cigars, hookah tobacco and other tobacco products;
- diesel fuel, motor oils for diesel and injection engines;
- straight-run gasoline;
- grape;
- vapes and liquids for them;
- cars and motorcycles;
- and other types of goods.
If you import goods from the list given in Art. 181 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, to Russia, they must pay excise taxes. Exporters (those who export excisable products from the Russian Federation) are not required to pay excise tax.
Some excisable goods are exempt from excise taxes upon import. Aviation kerosene, benzene, paraxylene, orthoxylene and petroleum raw materials fall into this category (Article 183 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters from the Ministry of Finance).
Further sales of imported excisable goods will not be subject to excise taxes.
Excise tax on export
When exporting, no excise tax is paid. This increases the competitiveness of excisable goods and supports domestic producers. The procedure for exemption from excise tax is regulated by Art. 184. Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to the requirements of tax legislation, it is necessary to provide a bank guarantee to the tax service or enter into a surety agreement (letter dated June 30, 2021 N SD-4-3/12690). The bank guarantee obliges the declarant to pay excise tax if the necessary documents confirming the fact of export of the goods are not provided on time. The surety agreement exempts you from paying excise tax if the documents are provided on time, according to the agreement. If the terms of the contract are not met, the guarantor will have to pay excise tax.