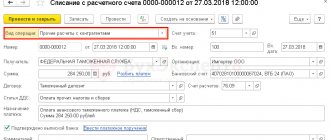
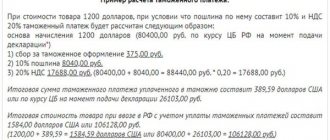
Despite the fact that customs duties are essentially fiscal payments, i.e. taxes, legislation in this area is much more complex than tax legislation. The rules for paying taxes are codified in a single document - the Tax Code and several additional legal acts. Customs legislation is differentiated into domestic legislation, the general legal field of the customs union - the EAEU, and international norms. It is not easy for novice participants in foreign trade activities to understand the vast space of provisions on customs payments and their most important part - benefits. What benefits exist, how full and partial exemption from customs duties occurs, how to preserve the right and what deprives it - all the nuances of customs preferences are in the article.
Benefits of customs duties: concept and features
Currently, a benefit is defined as a certain advantage in the import/export or transit movement of commercial products, personal property, personal belongings in the form of an absolute exemption from the transaction of transferring established amounts of duties. It is important to note that such a benefit is not subject to personal income tax.
It is necessary to add that, in addition to giving a particular citizen or structure the opportunity to exclude the payment of duties, the benefits of customs duties are often expressed in some simplification of the mechanism associated with the transportation of commercial products or other things across the border. Currently, the category under consideration is called tariff benefits. Thus, they do not imply any mitigation for individuals in the process of inspecting their belongings, as well as the passage of a commercial product into the territory of the Russian Federation.
Types of concessions when crossing the border
The legislation provides for various preferences for citizens and enterprises. They vary depending on the destination of the goods (things). Thus, a special zone with a large number of concessions is the Community of Independent States (CIS), which has been creating its own economic zone for many years.
There are the following types of benefits at customs:
- Tariffs associated with mandatory payments:
- Liberation
- Decrease
- Return
- Relaxation in cargo clearance procedures
- Changes in control standards
Hint: Each benefit is described in the relevant by-laws. In particular, the instructions contain information about:
- Which of the categories of persons crossing the border is it provided?
- To what extent
Types of customs benefits
All the exceptions specified in the previous chapter for individuals and various types of associations are determined by the following classification in accordance with the types of their application:
- Benefits that are used in the process of registering commercial products or personal belongings of a citizen.
- Customs benefits of the Customs Union, which are applied during control directly at the border.
- Tariff preferences (by the way, they received such an interesting name relatively recently).
It should be emphasized that customs benefits today are provided as an opportunity associated with non-payment of current duties, refund of amounts, or reduced duty rates. By the way, by refund of amounts in this case it is necessary to understand the return of those funds that were previously paid in accordance with the full amount. Currently, the provision of benefits on the payment of customs duties is possible for manufacturers of commercial products produced in the CIS. Nevertheless, the manufacturer undertakes to undergo the registration procedure in the CIS. This condition cannot be excluded under any circumstances. It is important to add that the country of origin of a commercial product is today confirmed by providing a product certificate or declaration.
Appealing a refusal to grant tariff preferences
Customs may refuse to provide tariff preferences by making an appropriate decision. What to do in this case? Appeal the customs decision to court in accordance with the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation.
To appeal, the applicant must:
- prepare an application to the court according to the rules established by the procedural code
- send one copy of the application to customs as an interested party
- after these actions, submit an application with evidence of your innocence to the court
- the court is obliged to notify the participants of the date and time of consideration of the application
- the applicant will need to take part in the process, voicing his position on the case
- after hearing the participants in the process and examining the case materials, the court will make a decision, which may recognize the refusal of customs to provide tariff preferences as illegal
Benefits for registration and control
The provision of benefits for the payment of customs duties to individuals and various types of associations is carried out on the basis of the current Customs Code of the Russian Federation, as well as currently valid legislative acts, the content of which corresponds to the topic under consideration. Thus, the following categories of persons can take advantage of the special procedure for paying customs duties during registration and control:
- Foreign persons.
- Couriers of embassies and consulates of foreign countries.
- Intergovernmental societies of an international nature, as well as representations of certain countries in their composition. In addition, it would be advisable to include here the staff of the represented institutions.
- Representatives of delegations, as well as their members.
- Consular officials, members of diplomatic staff, representatives of government agencies involved in transit movement within the Russian Federation.
How does registration work?
At the border, you must provide documents confirming your right to a specific exemption. The list depends on the type of object, the status of the carrier, the country of import, etc. For example, these:
- The inheritance must be confirmed with a certificate
- Personal property must be accompanied by documents proving the date of acquisition and value (receipts)
- If the equipment is a share of the authorized capital, constituent documents are needed
- A declaration is sufficient for non-payment of excise duty.
- Refugees provide the relevant document
- Manufacturers - certificate and so on
When importing goods into the territory of the Customs Union, there are benefits (preferences) for the payment of customs duties for certain groups of goods, aimed at supporting the economies of least developed and developing countries, as well as at the implementation of international agreements on economic and other types of cooperation.
The division of countries for which benefits on the payment of customs duties has been established is carried out into the following groups:
Commonwealth of Independent States
Benefits for paying customs duties
Important! When importing any goods produced on the territory of member countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States, import customs duties are not charged.
Conditions for using customs duties benefits
Providing the customs authority with the original certificate of the country of origin of goods, form ST-1. This certificate is issued by the Chamber of Commerce and Industry of the country producing the goods.
Developing countries
Goods that are subject to preferential customs duties originating in developing countries
| Group or code of the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity of the Customs Union | Name of product |
| 02 (except 0203, 0207) | Meat and edible meat by-products |
| 03 (except 0305) | Fish and crustaceans, mollusks and other aquatic invertebrates (except sturgeon and salmon, as well as caviar from them) |
| 04 | Milk products; bird eggs; natural honey; edible products of animal origin, not elsewhere specified or included |
| 05 | Animal products not elsewhere specified or included |
| 06 | Living trees and other plants; bulbs, roots and other similar parts of plants; cut flowers and decorative foliage |
| 07 | Vegetables and some edible roots and tubers |
| 08 | Edible fruits and nuts; citrus fruit peel or melon rind |
| 09 | Coffee, tea, mate, or Paraguayan tea, and spices |
| 1006 | Rice |
| 11 | Products of the flour and cereal industry; malt; starches; inulin; wheat gluten |
| 12 | Oilseeds and fruits; other seeds, fruits and grains; medicinal plants and plants for technical purposes; straw and fodder |
| 13 | Natural shellac, unrefined; gums, resins and other plant juices and extracts |
| 14 | Plant materials for making wickerwork; other products of vegetable origin, not elsewhere specified or included |
| 15 (except 1509, 1517 - 1522 00) | Fats and oils of animal or vegetable origin and their breakdown products; prepared edible fats; waxes of animal or vegetable origin |
| 16 | Prepared products of meat, fish or crustaceans, molluscs or other aquatic invertebrates |
| 1801 00 000 0 | Cocoa beans, whole or crushed, raw or roasted |
| 1802 00 000 0 | Husks, shells, skins and other cocoa waste |
| 20 (except 2001 10,000 0, 2009 50, 2009 71, 2009 79) | Processed products of vegetables, fruits, nuts or other plant parts |
| 2103 | Products for making sauces and ready-made sauces; mixed flavorings and seasonings; mustard powder and ready-made mustard |
| 2104 | Ready-made soups and broths and preparations for their preparation; homogenized compound prepared food products |
| 2401 | Raw tobacco; tobacco waste |
| 25 (except 2501 00 91, 2529 21 000 0, 2529 22 000 0) | Salt; sulfur; earth and stone; plastering materials, lime and cement |
| 26 | Ores, slag and ash |
| 3003 | Medicines (other than goods of heading 3002, 3005 or 3006), consisting of a mixture of two or more components, for therapeutic or prophylactic purposes, but not put up in dosage forms or in forms or packages for retail sale |
| 32 | Tanning or dyeing extracts; tannins and their derivatives; paint putties and other mastics; printing paint, ink, ink |
| 3301, 3302 | Essential oils...; resinoids...; mixtures of aromatic substances... |
| 3402 | Organic surfactants (except soap); surfactants, detergents (including detergent auxiliaries) and cleaning preparations, whether or not containing soap (other than those of heading 34.01) |
| 35 | Protein substances; modified starches; adhesives; enzymes |
| 3923 | Products for transporting or packaging goods, made of plastics; stoppers, lids, caps and other closures, made of plastic |
| 4001 | Natural rubber, balata, gutta-percha, guayule, chicle and similar natural resins, in primary forms or in the form of plates, sheets or strips or strips |
| 4403 41 000 0, 4403 49 | Other unprocessed timber, from tropical wood |
| 4407 21 — 4407 29 | Timber, sawn or split lengthwise..., from tropical wood |
| 4420 | Wooden mosaic and inlaid products; boxes and boxes for jewelry or cutlery and similar products, wooden; figurines and other decorative items, wooden; wooden furniture not included in Chapter 94 |
| 4421 | Other wooden products |
| 45 | Cork and products made from it |
| 46 | Products made of straw, alfa and other materials for weaving; basketry and wickerwork |
| 50 | Silk |
| 5101 | Wool not carded or combed |
| 5201 00 | Cotton fiber, not carded or combed |
| 53 | Other vegetable textile fibers; paper yarn and fabrics made from paper yarn |
| 56 | Cotton wool, felt or felt and non-woven materials; special yarn; twine, ropes, ropes and cables and products made from them |
| 5701 | Knotted carpets and other textile floor coverings, whether or not finished |
| 5702 10 000 0 | Carpets "kilim", "sumac", "kermani" and similar handmade carpets |
| 5705 00 800 0 | Carpets and other textile floor coverings, whether or not made, of wool or fine animal hair |
| 5808 | Braid woven in a piece; finishing materials without embroidery in a piece, except for machine-knitted or hand-knitted materials; tassels, pompoms and similar articles |
| 6702 90 000 0 | Artificial flowers, leaves and fruits and their parts; products made of artificial flowers, leaves or fruits, or other materials |
| 68 | Articles made of stone, plaster, cement, asbestos, mica or similar materials |
| 6913 | Figurines and other decorative items made of ceramics |
| 6914 | Other ceramic products |
| 7018 10 | Glass beads, imitation pearls, precious or semi-precious stones and similar small glass forms |
| 7117 | Bijouterie |
| 9401 51 000 0, 9401 59 000 0 | Seating furniture made of cane, willow, bamboo or similar materials |
| 9403 81 000 0, 9403 89 000 0 | Furniture made from other materials, including cane, willow, bamboo or similar materials |
| 9403 90 900 0 | Furniture parts made of other materials |
| 9601 | Processed and suitable for carving ivory, bone, tortoiseshell, horn, antlers, coral, mother-of-pearl, other materials of animal origin and products made from these materials (including products obtained by molding) |
| 9602 00 000 | Processed materials of plant or mineral origin, suitable for carving, and products made from them; molded or carved articles of wax, stearin, natural resins or natural rubber or modeling pastes, and other molded or carved articles not elsewhere specified or included; processed gelatin, unhardened (other than gelatin of heading 3503) and products made from unhardened gelatin |
| 9603 | Brooms, brushes (including brushes that are parts of machinery, instruments or vehicles), hand-held mechanical brushes without motors for cleaning floors, mops and feather dusters; knots and bundles prepared for the manufacture of brooms or brush products; paint pads and rollers; rubber squeegees (except rubber rollers for removing moisture) |
| 9604 00 000 0 | Manual sieves and sieves |
| 9606 | Buttons, snaps, snap fasteners, button molds and other parts of these products; button blanks |
| 9609 | Pencils (other than those of heading 96.08), colored pencils, pencil leads, pastels, charcoal pencils, writing or drawing chalks and tailor's chalks |
| 9614 00 | Smoking pipes (including bowl-shaped parts), cigar or cigarette holders, and parts thereof |
| 9615 11 000 0 | Combs, hair combs and the like, hardwood or plastic |
| 9617 00 000 0 | Thermoses and other vacuum vessels, assembled; parts thereof, except glass flasks |
| 97 | Artworks, collectibles and antiques |
Benefits for paying customs duties
When importing the above goods from developing countries, 75% of the import customs duty rate established by the Unified Customs Tariff of the Customs Union is charged (preference is provided)
Conditions for using customs duties benefits
Providing the customs authority with the original certificate of the country of origin of goods, Form A-1. This certificate is issued by the chamber of commerce and industry (other government bodies responsible for economic regulation) of the country producing the goods.
Least developed countries
Goods eligible for customs duties originating from least developed countries
| Group or code of the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity of the Customs Union | Name of product |
| 02 (except 0203, 0207) | Meat and edible meat by-products |
| 03 (except 0305) | Fish and crustaceans, mollusks and other aquatic invertebrates (except sturgeon and salmon, as well as caviar from them) |
| 04 | Milk products; bird eggs; natural honey; edible products of animal origin, not elsewhere specified or included |
| 05 | Animal products not elsewhere specified or included |
| 06 | Living trees and other plants; bulbs, roots and other similar parts of plants; cut flowers and decorative foliage |
| 07 | Vegetables and some edible roots and tubers |
| 08 | Edible fruits and nuts; citrus fruit peel or melon rind |
| 09 | Coffee, tea, mate, or Paraguayan tea, and spices |
| 1006 | Rice |
| 11 | Products of the flour and cereal industry; malt; starches; inulin; wheat gluten |
| 12 | Oilseeds and fruits; other seeds, fruits and grains; medicinal plants and plants for technical purposes; straw and fodder |
| 13 | Natural shellac, unrefined; gums, resins and other plant juices and extracts |
| 14 | Plant materials for making wickerwork; other products of vegetable origin, not elsewhere specified or included |
| 15 (except 1509, 1517 - 1522 00) | Fats and oils of animal or vegetable origin and their breakdown products; prepared edible fats; waxes of animal or vegetable origin |
| 16 | Prepared products of meat, fish or crustaceans, molluscs or other aquatic invertebrates |
| 1801 00 000 0 | Cocoa beans, whole or crushed, raw or roasted |
| 1802 00 000 0 | Husks, shells, skins and other cocoa waste |
| 20 (except 2001 10,000 0, 2009 50, 2009 71, 2009 79) | Processed products of vegetables, fruits, nuts or other plant parts |
| 2103 | Processed products of vegetables, fruits, nuts or other plant parts |
| 2104 | Ready-made soups and broths and preparations for their preparation; homogenized compound prepared food products |
| 2401 | Raw tobacco; tobacco waste |
| 25 (except 2501 00 91, 2529 21 000 0, 2529 22 0000) | Salt; sulfur; earth and stone; plastering materials, lime and cement |
| 26 | Ores, slag and ash |
| 3003 | Medicines (other than goods of heading 3002, 3005 or 3006), consisting of a mixture of two or more components, for therapeutic or prophylactic purposes, but not put up in dosage forms or in forms or packages for retail sale |
| 32 | Tanning or dyeing extracts; tannins and their derivatives; dyes, pigments and other coloring substances; paints and varnishes; putties and other mastics; printing paint, ink, ink |
| 3301, 3302 | Essential oils...; resinoids...; mixtures of aromatic substances... |
| 3402 | Organic surfactants (except soap); surfactants, detergents (including detergent auxiliaries) and cleaning preparations, whether or not containing soap (other than those of heading 34.01) |
| 35 | Protein substances; modified starches; adhesives; enzymes |
| 3923 | Products for transporting or packaging goods, made of plastics; stoppers, lids, caps and other closures, made of plastic |
| 4001 | Natural rubber, balata, gutta-percha, guayule, chicle and similar natural resins, in primary forms or in the form of plates, sheets or strips or strips |
| 4403 41 000 0, 4403 49 | Other unprocessed timber, from tropical wood |
| 4407 21 — 4407 29 | Timber, sawn or split lengthwise..., from tropical wood |
| 4420 | Wooden mosaic and inlaid products; boxes and boxes for jewelry or cutlery and similar products, wooden; figurines and other decorative items, wooden; wooden furniture not included in Chapter 94 |
| 4421 | Other wooden products |
| 45 | Cork and products made from it |
| 46 | Products made of straw, alfa and other materials for weaving; basketry and wickerwork |
| 50 | Silk |
| 5101 | Wool not carded or combed |
| 5201 00 | Cotton fiber, not carded or combed |
| 53 | Other vegetable textile fibers; paper yarn and fabrics made from paper yarn |
| 56 | Cotton wool, felt or felt and non-woven materials; special yarn; twine, ropes, ropes and cables and products made from them |
| 5701 | Knotted carpets and other textile floor coverings, whether or not finished |
| 5702 10 000 0 | Carpets "kilim", "sumac", "kermani" and similar handmade carpets |
| 5705 00 800 0 | Carpets and other textile floor coverings, whether or not made, of wool or fine animal hair |
| 5808 | Braid woven in a piece; finishing materials without embroidery in a piece, except for machine-knitted or hand-knitted materials; tassels, pompoms and similar articles |
| 6702 90 000 0 | Artificial flowers, leaves and fruits and their parts; products made of artificial flowers, leaves or fruits, or other materials |
| 68 | Articles made of stone, plaster, cement, asbestos, mica or similar materials |
| 6913 | Figurines and other decorative items made of ceramics |
| 6914 | Other ceramic products |
| 7018 10 | Glass beads, imitation pearls, precious or semi-precious stones and similar small glass forms |
| 7117 | Bijouterie |
| 9401 51 000 0, 9401 59 000 0 | Seating furniture made of cane, willow, bamboo or similar materials |
| 9403 81 000 0, 9403 89 000 0 | Furniture made from other materials, including cane, willow, bamboo or similar materials |
| 9403 90 900 0 | Furniture parts made of other materials |
| 9601 | Processed and suitable for carving ivory, bone, tortoiseshell, horn, antlers, coral, mother-of-pearl, other materials of animal origin and products made from these materials (including products obtained by molding) |
| 9602 00 000 | Processed materials of plant or mineral origin, suitable for carving, and products made from them; molded or carved articles of wax, stearin, natural resins or natural rubber or modeling pastes, and other molded or carved articles not elsewhere specified or included; processed gelatin, unhardened (other than gelatin of heading 3503) and products made from unhardened gelatin |
| 9603 | Brooms, brushes (including brushes that are parts of machinery, instruments or vehicles), hand-held mechanical brushes without motors for cleaning floors, mops and feather dusters; knots and bundles prepared for the manufacture of brooms or brush products; paint pads and rollers; rubber squeegees (except rubber rollers for removing moisture) |
| 9604 00 000 0 | Manual sieves and sieves |
| 9606 | Buttons, snaps, snap fasteners, button molds and other parts of these products; button blanks |
| 9609 | Pencils (other than those of heading 96.08), colored pencils, pencil leads, pastels, charcoal pencils, writing or drawing chalks and tailor's chalks |
| 9614 00 | Smoking pipes (including bowl-shaped parts), cigar or cigarette holders, and parts thereof |
| 9615 11 000 0 | Combs, hair combs and the like, hardwood or plastic |
| 9617 00 000 0 | Thermoses and other vacuum vessels, assembled; parts thereof, except glass flasks |
| 97 | Artworks, collectibles and antiques |
Benefits for paying customs duties
When importing the above goods from least developed countries, import customs duty is not charged (preference is provided)
Procedure for providing benefits
It is important to know that the provision of customs tariff benefits today is only appropriate in the case of strict compliance with the standards for the movement of commercial products or personal belongings directly within the country. It is necessary to add that in 2021, benefits for registration and subsequent control cover the cost of commercial products that belong to organizations and representative offices of international importance, officials or personnel of these companies, some foreign companies and their relatives, as well as the costs of their transportation. The implementation of the event occurs as follows:
- Mail is not officially opened and, accordingly, does not undergo an inspection procedure.
- The presented rule is also relevant in relation to the so-called consular bag containing documents.
- It is advisable to apply the exclusion of personal search in case of border crossing to the above-mentioned citizens, as well as representatives of certain structures.
additional information
It is important to add that the pouch and mail can be unpacked if there is some suspicion that only documentation and commercial products are inside. Nevertheless, for this, one way or another, compelling reasons are needed. Current Russian legislation provides for the opening of mail through the efforts of the country's authorized representatives (the declarant), and not customs officers. You should know that when registering things that are transported across the customs border, customs duty benefits, which are of a social nature, apply only to things imported directly from abroad.
Full conditional exemption from customs duties and taxes
Duty is a type of customs payment along with customs duties and taxes.
The obligation to pay it arises when goods are cleared for crossing the customs border and, as a rule, concerns imports - the fiscal and protectionist functions of duties are performed. In rare cases, export and transit are subject to taxation.
Therefore, the preferential and preferential system is applicable to the import of goods and depends on their types and value, manufacturer, destination and the chosen customs procedure.
What other categories of benefits are there?
Today, the provision of customs benefits is regulated by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Customs Tariffs”. Thus, tariff advantages are applied as a special permit associated with the absence of the need to pay tax, a reduced amount of the actual payment, or the establishment of a quota related to the following positions:
- Commercial products produced in developing countries that apply the system of preferences of the Russian Federation.
- Commodity products produced in countries that, together with the Russian Federation, form a free trade zone or a customs union.
Features of the movement of goods within the Customs Union
Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan form a special interstate zone. It is called the Customs Union. Governments have developed a set of rules and measures to improve circulation throughout the entire space:
- Products
- Resources
- Work force
The goal of the CU is the rapid development of the domestic market, as well as the introduction of new methods and technologies to improve the economic climate. The development of rules is carried out by a special commission of the Customs Union - a supranational body that replaces the government.
The Commission has developed a classification of relaxations, including:
- Various benefits
- Multi-level preferences
- Facilitation of registration procedures
Import and export duties: what benefits exist?
The concept of customs duty on the transportation or export of a commodity product is provided for during customs clearance. The export (export) amount of the current tax is levied in case of crossing the border, but is used quite rarely. It should be noted that import duties are currently widely used. Customs benefits in payment are provided for the import of certain products into the country from developing countries in the form of a complete exemption. In addition, no duty is paid for items that meet certain requirements in terms of country of origin or intended purpose. In addition, individuals are exempt if they import a car that is involved in transportation of international importance; equipment; technical supplies; Fuel and lubricants for the satisfactory functioning of the presented transport.
Benefits of the vehicle
The rules for granting preferences within the CU space are determined by three parties. They depend on the development of the country in a particular industry.
To raise the level of commodity producers, the weakest counterparty enjoys a discount of up to 75% on tariffs. In addition, enterprises that cannot compete with partners in the same industry from the allied states are exempt from paying the mandatory fee.
There are a number of procedures to facilitate crossing cordons within a vehicle:
- Temporary admission of imported materials. It involves the use of goods for a certain period (decision of the CU Commission No. 331)
- A number of goods are transported across borders under special conditions (No. 329)
- Special economic zones are allocated for joint development, where preferences increase
- In some cases, non-tariff regulation conditions apply
Export abroad
It is important to note: if the equipment specified in the previous chapter, as well as materials, are exported abroad in order to carry out the functions of servicing Russian vehicles directly on the territory of a foreign state, customs duties are not charged. Providing benefits for the payment of customs duties is relevant for the following categories of a material nature:
- A product of maritime activity obtained by citizens of the Russian Federation.
- Personal belongings of citizens of foreign countries.
- National and foreign currency.
- Transit product.
- Humanitarian assistance.
- Fire-technical products.
- Materials and equipment for purposes related to the implementation of programs of socio-economic importance.
- Commercial products imported in accordance with the rules of the leasing agreement.
The most promising industries for startups in the Kaliningrad region:
The Kaliningrad region is a dynamically developing region with good prospects for development in many sectors of the economy.
Based on the minimum volume of investment over three years, we can identify several of the most promising industries for development:
- IT, web media, R&D;
- medical industry companies;
- the sphere of tourism and recreational activities, manufacturing, fishing, fish farming, agriculture;
If we talk about the most developed industries in the Kaliningrad region at the moment, we can highlight:
- mechanical engineering, the development of which will be facilitated by the auto cluster we are creating;
- shipbuilding;
- pharmaceuticals, the development of which we plan to carry out on the basis of the existing Ecobaltic technology park, which has all the necessary infrastructure certified according to international standards (GMP);
- IT and microelectronics, the development of which is ensured by the presence of the largest cluster of the radio-electronic industry in Europe (Technopolis GS);
- The agro-industrial complex includes livestock farming, crop production, the fishing industry, and food production (the climate of the region is favorable for this).
Also, there is a growing interest in medical and health tourism, the demand for which is formed by the nearest European countries, where treatment and medicine costs several times more. The Kaliningrad region has the advantages of a geopolitical location, an open and accessible economy, as well as clear and understandable conditions for investors. And throughout the entire region there is a special economic zone regime (preferential currency, customs and tax regime).
Customs duties, excise taxes, VAT
In this chapter, it would be advisable to consider customs benefits associated with the payment of other customs duties, including excise taxes, customs duties, and value added tax. It is important to note that with regard to the payment of the latter, there is currently the possibility of exemption only if the deadlines for the transportation of marketable products or personal belongings are met. In accordance with Article 150 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, benefits apply to certain positions discussed in the next chapter.
Benefits according to certain positions
Among the items subject to customs benefits, it is important to highlight the following points:
- Spare parts and components, technical equipment, which acts as a contribution to the capital of a legal entity.
- Medical equipment - when its completeness is in accordance with the certificate of Roszdravnadzor.
A value added tax of ten percent is established for:
- Medicines.
- Book product of a scientific and educational nature.
- Commercial products for children's and industrial purposes.
- Items of medicinal nature.
Excise tax
An excise tax should be understood as a tax of national significance, which is usually levied on consumer items imported from abroad. Thus, tax is not allowed to be paid on the following items:
- Humanitarian cargo.
- Complete objects (but not fixtures and spare parts).
- Items provided to the country upon refusal by the declarant.
- Items whose value does not exceed 100 euros as converted into national currency.
- Personal belongings belonging to foreign diplomatic representatives.
customs duty
Today it is customary to consider the customs council as payment for customs manipulations. Thus, it is advisable to levy a tax on personal property, transport, and heritage. It is important to note that in order to obtain an exemption, the declarant must indicate in the declaration the status of the property being imported as a personal contribution to the general property complex of the legal entity, as well as provide official confirmation, which is the constituent document. It should be added that the latter stipulates the procedure for contributing a share to the property of the association, equal to precisely this marketable product.
Basic information
Customs payments, which are paid to the budget of the Russian Federation by individuals and legal entities, constitute a large share of state income. Customs taxes are required to be paid, but the legislation of the Russian Federation contains conditions for the use of benefits or complete exemption from the tax burden.
In order to take advantage of the benefit, a person must fill out a customs declaration, indicating in it a description of the goods (purpose, volume, quantity). Each product requires confirmation in the form of documents.
Benefits for voluntary resettlement
In the final chapter, it would be advisable to outline the customs benefits that occur in the event of voluntary resettlement of compatriots living abroad to the Russian Federation. It is important to know that when relocating to a permanent place of residence, the following preferences are assumed in accordance with current Russian legislation:
- Exclusion of tax in the case of transportation of personal items to the countries of the customs union for immigrants and refugees.
- One way or another, things must be purchased before the date of arrival in the Russian Federation or before the status of special significance is assigned.
- In case of returning from a stay abroad for a temporary period, through the fifth paragraph of the third Appendix, citizens of the Russian Federation have the opportunity not to pay customs duties when the goods being transported are items of personal use and their value does not exceed five thousand euros in rubles.
It should be noted that citizens who received an inheritance abroad are given an exemption when the inherited property complexes are certified by a certificate. When re-importing previously exported commercial products, the latter are not subject to customs duties if they are in their original condition. If a citizen who does not plan to visit a foreign country applies to the services of a carrier, state duty is not paid for those commercial products whose weight does not exceed thirty-one kilograms, and the amount in rubles is thousands of euros.
In conclusion, it would be advisable to formulate the following conclusions:
- The provision of benefits is carried out on the basis of the current Customs Code.
- The benefits are extended exclusively to commercial products imported from other countries.
- Benefits for value added tax on commercial products are described in the Tax Code.
- Discounts on customs payments are determined in accordance with the commodity product of countries that have agreements with the Russian Federation.
- Duties are not paid for certain categories of commercial products.