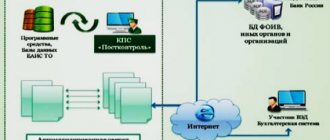
History of the World Customs Organization
The World Customs Organization (WCO) is located in Brussels and is an intergovernmental international organization. WTO members include customs services of almost all countries of the world. The main activity of the WTO is the development of international instruments and conventions aimed at:
- classification of goods,
- assessment of customs value,
- customs duties,
- combating crime and counterfeit products,
- protection of intellectual property, etc.
The main focus of the WTO is on institutional development programs. These programs provide support for reforms and modernization of customs authorities. The World Customs Organization developed a Harmonized System, which described the goods and gave them a certain classification. In addition, two agreements were introduced by the WTO:
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
- agreement on the application of Article VII of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade of 1994 (customs valuation),
- agreement on the rules for determining the country of origin of goods.
The history of the creation of a world customs organization dates back to the origins of the European Customs Union Study Group, which was created in September 1947. The initiative belonged to France. The tasks of this Group included studying economic and technical issues regarding the creation of a customs union by Western European countries with the corresponding GATT rules. The group worked until 1947 and held 6 meetings, at which aspects of the formation of harmonious customs legislation were determined.
In 1950, as a result of the work of the group at the Brussels Convention, the Customs Cooperation Council (CCC) was created. In January 1953, the 17 members who founded this Council were inaugurated. In the 90s, the STS was renamed the World Customs Organization.
Note 1
To date, the World Customs Organization has included more than 170 customs services, which control more than 90% of the market.
Finished works on a similar topic
Coursework World Customs Organization 440 ₽ Essay World Customs Organization 260 ₽ Test work World Customs Organization 220 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Administration [edit]
The WCO Secretariat is headed by the Secretary General, who is elected by WCO members for a five-year term. The current Secretary General of the WCO is Kunio Mikuriya from Japan, who took office on January 1, 2009. The WCO is governed by the Council, which gathers all members of the Organization once a year at a meeting chaired by an elected chairman. Additional strategic and management guidance is provided by the Policy Committee and the Finance Committee. Several WCO committees, such as the Harmonized System Committee, the Standing Technical Committee, the Customs Valuation Technical Committee, the Rules of Origin Technical Committee, the Capacity Building Committee and the Security Working Group, provide a platform for the development of tools and best practices. on customs competences.
WTO objectives
The WCO is a recognized global center for customs expertise, which plays a leading role in the formation of customs legislation. This organization is aimed at developing customs affairs. The activities of the WTO are formed depending on the requests of members of this organization. Innovative tools and best practices are recognized as the basis for the work of the WTO.
Note 2
The main goal of the WTO is to increase the efficiency of customs services, through measures that would increase tax collections, strengthen national security and overall positive statistics on foreign trade.
Tools[edit]
To achieve its objectives, the WTO has adopted a number of customs instruments, including, but not limited to, the following:
1) International Convention on the Harmonized System of Description and Coding of Goods (HS Convention)
was adopted in 1983 and came into force in 1988. The HS nomenclature of multipurpose goods is used as the basis for customs tariffs and for the compilation of international trade statistics. It includes approximately 5,000 product groups, each identified by a six-digit code, organized into a legal and logical structure with clearly defined rules to achieve a uniform classification. HS is also used for many other purposes, including trade policy, rules of origin, controlled goods monitoring, internal taxes, freight rates, transport statistics, quota controls, price monitoring, national accounts, and economic research and analysis.
2) International Convention for the Simplification and Harmonization of Customs Procedures (Revised Kyoto Convention or RKK)
was originally adopted in 1974 and subsequently revised in 1999; The revised Kyoto Convention entered into force in 2006. The RCC includes several key guiding principles: transparency and predictability of customs controls; standardization and simplification of the goods declaration and accompanying documents; simplified procedures for authorized persons; maximum use of information technology; minimum necessary customs controls to ensure compliance with regulations; use of controls based on risk management and audit; coordinated actions with other border agencies; and trade partnerships. It promotes trade facilitation and effective controls through its legal provisions, which detail the application of simple but effective procedures and provide new and binding rules for their application. The WTO's Revised Kyoto Convention is sometimes confused with the Kyoto Protocol, which is a protocol to the Organization's Framework Convention United Nations on Climate Change (UNFCCC or FCCC).
3) ATA Convention and Temporary Entry Convention (Istanbul Convention).
Both the ATA Convention and the Istanbul Convention are WTO instruments governing the temporary importation of goods. The ATA system, which is an integral part of both conventions, allows the free movement of goods across borders and their temporary entry into customs territory with exemption from duties and taxes. Goods are covered by a single document known as an ATA carnet, which is protected by an international guarantee system.
4) Arusha Declaration on Customs Integrity
was adopted in 1993 and revised in 2003. The Arusha Declaration is a non-binding document that provides a set of basic principles to promote integrity and combat corruption in customs administrations.
5) SAFE Safety Standards Framework to Secure and Facilitate Global Trade
were adopted in 2005. The SAFE Framework is a non-binding tool that provides security and supply chain simplification standards for internationally traded goods and enables the integration of supply chain management across all modes of transport, strengthening network arrangements between customs administrations to improve their ability to identify high-risk consignments. risk, promotes cooperation between Customs and the business community through the concept of an authorized economic operator (AEO), and supports the smooth movement of goods through secure international trade supply chains.
6) Columbus program
is
program
aimed at promoting the modernization of customs and the implementation of their standards to ensure security and ease of global trade.
In 2005, the WTO adopted the Framework of Standards for Secure and Facilitating Global Trade,
an international customs document containing 17 standards that promote the security and facilitation of the international supply chain.
Due to its complexity, the WCO has launched a capacity building program called the Columbus Program
which focuses on assessing the needs of WCO members using the WCO Diagnostic Tool. The WCO defines capacity building as “activities that strengthen people's knowledge, abilities, skills and behavior and improve institutional structures and processes so that an organization can effectively achieve its mission and objectives in a sustainable manner.”
Links[edit]
- "OMC | La OMC y la Organización Mundial de Aduanas (OMA).” www.wto.org
. Retrieved November 18, 2021. - "Organización Mundial de Aduana (OMA) - National Service of Aduana del Ecuador" (in Spanish). Retrieved November 18, 2020.
- Kormych, Boris. "EUROPEAN CUSTOMS UNION STUDY GROUP: DEVELOPMENT OF EU CUSTOMS LAW". Quote journal requires |journal=(help)
- https://www.aduana.cl/organizacion-mundial-de-aduanas-oma/aduana/2007-03-01/121223.html
External links [edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to World Customs Organization . |
- Official website
- B. Kormych Study group of the European Customs Union: development of EU customs legislation
| vthose international organizations | |
| Intergovernmental organizations | |
| Cultural IGOs |
|
| Authoritative control |
|
Essence and conditions of integration
Integration International economics Customs
In recent decades, complex processes of convergence and interpenetration of the economies of several countries have been taking place in the world economy, aimed at creating a single economic organism, which is called integration. It permeates the most diverse aspects of the economic and political life of integrating countries.
Integration as the highest manifestation of the internationalization of economic life, as a result of a very high level of international division of labor and cooperative relations. We can say that in this case, international economic relations become so strong that there is a deep interdependence of the processes of national reproduction.
Integration (from the Latin integer - whole) means the unification of economic entities, the deepening of their interaction, the development of connections between them. Economic integration occurs both at the level of the economies of entire countries, and between enterprises, firms, companies, and corporations. Economic integration is manifested in the expansion and deepening of production and technological ties, the sharing of resources, the pooling of capital, the creation of favorable conditions for mutual economic activity, and the elimination of mutual barriers.
Economic integration (integration, from Latin integration - restoration) is the interaction and mutual restructuring of the economies of different countries, leading to their gradual economic unification. At the interstate level, integration is carried out through the formation of regional economic associations of states and the harmonization of their domestic and foreign economic policies. Interaction and mutual restructuring of economies is manifested, first of all, in the gradual creation of a “common market” - in the liberalization of conditions for the exchange of goods and the movement of production resources (capital, labor, information) between countries.