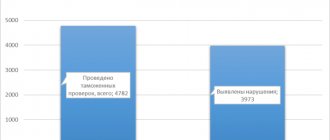
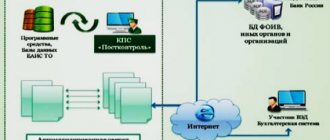
When carrying out customs control, in a number of cases issues arise that require special knowledge to resolve. This occurs, for example, when it is necessary to obtain clarification regarding any cargo, information in documentation, or a vehicle. In such cases, a customs examination is appointed. When carrying out customs control of certain types of products, this procedure is mandatory. Let's look further at what it is.
General information
Customs examination during customs control is a study performed by specialists with scientific knowledge. It is necessary to resolve issues in the field of cross-border transportation of goods. The following features of customs examination should be highlighted:
- The implementation of the procedure is based on the application of special knowledge in various fields of technology, art, science or craft.
- The appointment of a customs examination, as well as its preparation and direct execution, must be carried out in compliance with the established legal regulations. It defines the responsibilities and powers of specialists and other interested parties, as well as the main stages of the research itself.
- At the end of the examination, a conclusion is given. The authorized bodies consider this act when making decisions regarding the future fate of the cargo.
Objects of research
The subject of customs examination is the actual data established and examined during customs control. This information mainly relates to checking the cargo to determine whether the information contained in the declaration and other documents corresponds to the name, value, quantity, and origin of the product transported across the border. Researchers must have knowledge not only in the field of supervision, but also in other areas. One of these industries is merchandising. Both customs examination and other control measures require strict compliance with the norms established by law. The objects of research may be:
- Documentation containing information about the transported cargo and vehicle.
- Products and vehicles that are under customs control.
- Documentation containing data on the performance of actions (operations) regarding cargo and vehicles.
Thus, customs examination can be carried out regarding everything that is in one way or another connected with the transportation of transport and products across the border.
Research objectives
The main goal of customs examination is to protect the Russian market from low-quality products. Its achievement requires the concentration of various efforts, since the research must be carried out from different positions. In this regard, specialists face several important tasks at once. First of all, a thorough examination of the documentation must be carried out. To determine the quality of products, certificates and details are studied. These papers act as supporting documentation and are the most important subject of verification.
At the same time, specialists always need to comply with the deadlines for customs examination. Frequently, cargo including food arrives at the border point. Most of these products are perishable goods. In such cases, specialists need to do their work as quickly as possible. Often, customs examination of documentation acts only as the first stage, and certificates do not always correspond to the actual quality of the cargo. In this regard, some types of products undergo epidemiological testing. It allows you to detect potentially dangerous cargo and prevent it from entering the territory of the state. All this concerns not only food. Cargoes containing highly toxic compounds are also transported across the border and are also checked. For them, in particular, chemical customs examination is provided.
In what cases is an independent customs examination most often ordered?
Applications for expert inspection of customs cargo are most often submitted in the following cases:
- Confirmation of the issued HS codes is required. For this purpose, the real chemical and physical qualities of the product are identified and revealed;
- It is necessary to find out whether the product/substance/substance belongs to narcotic, psychotropic and other prohibited groups of products;
- There is a need to determine the country of origin. In the case of clothing, furniture or household appliances, such a check will help avoid the import into the country of contraband products that were originally intended for the market of another state;
- Checking the cargo for its cultural or artistic value. Such expertise allows us to effectively combat the illegal trafficking of antiques.
Often an independent audit is organized to determine the real average market value of imported products. Often, unscrupulous entrepreneurs deliberately underestimate the price of imported goods, which is why they pay less duty, and then sell the products at their real cost. As a result, the state loses on customs duties.
Fees
Customs examination ensures payment of all mandatory fees. For the supplier, the duty acts as an additional expense. In this regard, some carriers try to evade payments. To identify such facts, a thorough inventory of products and accompanying documentation is carried out. During this procedure, duties are also calculated taking into account the market value of the products. Previously, solving the problem was complicated by the lack of necessary equipment at checkpoints. However, recently the procedure has been significantly simplified. Now at checkpoints there is equipment installed that checks the weight of cargo and shows its unaccounted quantity.
Procedure for carrying out customs examination: basic requirements
The study by the official must be agreed upon with the head or deputy head of the supervisory body. This is ensured by the adoption of an appropriate resolution. The official, in turn, makes a decision that a customs examination will be performed (a sample document is presented in the article). The act specifies:
- Reasons for performing the study.
- Name of body or full name. specialist responsible for carrying out customs examination.
- Questions to be addressed in the research.
- List of documents and materials that are made available to the specialist.
- The period during which customs examination of goods will be carried out and a conclusion must be provided.
The decision must also indicate the specialist’s warning about liability for drawing up a knowingly false report based on the research results. Questions in the resolution cannot be subject to different interpretations and may not go beyond the competence of the authorized person. Any employee who has the necessary special knowledge to draw up an opinion can act as an expert. A specialist who is not an official of the authorized body may be involved in the research in accordance with the legislation of the CU member countries. Objects of examination and other materials that are necessary for drawing up the examination must be provided in sealed and packaged form. Large cargo is examined at its location.
Eurasian Economic Commission
APPROVED by Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated May 20, 2010 No. 258
The procedure for carrying out customs examination during customs control
I. General provisions
1. The procedure for conducting a customs examination during customs control (hereinafter referred to as the Procedure) was developed to implement the provisions of Chapter 20 of the Customs Code of the Customs Union (hereinafter referred to as the Code).
2. This Procedure determines the organization and procedure for conducting customs examinations, including repeated examinations during customs control by customs experts (experts).
II. Terms used in this Procedure
3. The following terms and their definitions are used in this Procedure:
1) central customs authorities:
for the Republic of Belarus – the State Customs Committee of the Republic of Belarus;
for the Republic of Kazakhstan – the Customs Control Committee of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
for the Russian Federation – Federal Customs Service.
2) the customs authority conducting the customs examination:
for the Republic of Belarus - a customs authority that has a structural unit that conducts customs examinations;
for the Republic of Kazakhstan – Central Customs Laboratory;
for the Russian Federation – Central Forensic Customs Administration.
3) structural units of the customs authority conducting customs examination:
for the Republic of Belarus – structural units of the customs authority conducting customs examination;
for the Republic of Kazakhstan – regional customs laboratories;
for the Russian Federation - forensic services, expert research departments (branches) of the Central Forensic Customs Administration.
III. Sending materials, documents, samples and specimens for customs examination
4. When conducting a customs examination, the authorized official of the customs authority who appointed the customs examination shall send to the head of the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting the customs examination a decision on the appointment of a customs examination and the materials, documents, samples and specimens necessary for its implementation, indicating the permission for modification, partial or complete destruction, destruction of materials, documents, samples and research samples.
5. The form of the decision to appoint a customs examination is established by the legislation of the member states of the customs union.
IV. Reception of materials, documents, samples and specimens for customs examination
6. The decision to appoint a customs examination and the materials, documents, samples and specimens attached to it are taken by the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting the customs examination on the day of their receipt.
7. Materials, documents, samples and specimens attached to the decision to appoint a customs examination are accepted in packaged and sealed form. The packaging contains explanatory notes and makes it impossible to access the contents without damaging it.
If materials, documents, samples and specimens are not packaged, the absence of packaging is indicated in the decision to appoint a customs examination.
V. Organization of customs examinations
8. Customs examination is carried out both on the premises of the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting customs examination, and outside, if this is necessary due to the nature of the research, or due to the impossibility of delivering materials, documents, samples and specimens for customs examination.
9. The organization of customs examinations is entrusted to the head of the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting customs examinations.
10. The head of the customs authority conducting customs examination has the right to delegate part of his powers to organize customs examinations to his deputies and heads of structural divisions of the customs authority conducting customs examination.
11. Materials, documents, samples and samples received for customs examination are examined by the head of the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting customs examination and transferred to the contractor during the working day, and if they are received on non-working days - on the first working day following weekend or holiday.
12. When considering received materials, documents, samples and samples for customs examination, the head of the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting customs examination examines the decision to appoint a customs examination, the scope of the upcoming study and on this basis determines:
a specific performer (performers) of the customs examination, as well as the leading customs expert (expert) when conducting a commission or complex customs examination;
deadline for customs examination;
the procedure for attracting specialists from other expert, scientific and other institutions to conduct customs examinations.
The head of the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting customs examination explains to the customs expert (expert) his rights and responsibilities provided for by the legislation of the member state of the customs union.
13. Customs examinations are carried out by customs experts who have received the right to independently conduct customs examinations in the relevant specialty in the manner established by the legislation of the member states of the customs union.
14. The assignment of a customs examination by the customs authority to another authorized organization conducting customs examination is agreed upon with the customs authority conducting the customs examination in the manner established by the central customs authority of a member state of the customs union.
VI. Organization of repeated customs examinations
15. Repeated customs examination is carried out in accordance with this Procedure on the grounds provided for by the Customs Code of the Customs Union.
16. To conduct a repeated customs examination, the conclusion (conclusions) of a customs expert (expert) on the previously conducted customs examination shall be submitted to the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting the customs examination, together with materials, documents, samples and specimens.
17. The conclusion of the customs expert (expert) of the repeated customs examination shall indicate:
place, start and completion date of the repeated customs examination;
grounds for ordering a re-examination;
information about primary and (or) additional customs examinations;
surname, name and patronymic of the customs expert (expert) who conducted the repeated customs examination, his qualifications;
name of the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting the customs examination (or place of work of the customs expert (expert));
a mark certified by the signature of a customs expert (expert) stating that he has been warned of administrative or criminal liability for giving a knowingly false conclusion of a customs expert (expert) during a customs examination;
questions posed to the customs expert (expert);
a list of documents, materials, samples and specimens presented to the customs expert (expert) for carrying out a customs examination;
content and results of research, indicating the methods used, assessment of research results, conclusions on the questions raised and their justification.
VII. Storage of materials, documents, samples and specimens received for customs examination
18. The head of the customs authority or other authorized organization conducting customs examination ensures the safety of materials, documents, samples and specimens submitted for customs examination, preventing changes in their quantity and/or condition, with the exception of destruction (expenditure) during the examination, destruction ( irretrievable loss) due to force majeure, changes in natural properties, or as a result of natural wear and/or loss under normal conditions of transportation (shipment) and/or storage.
19. Storage of materials, documents, samples and samples is carried out in accordance with the legislation of the member states of the customs union.
VIII. Return of materials, documents, samples and samples of customs examination after customs examination
20. After completion of the customs examination, materials, samples and specimens are packaged. The packaging excludes access to the contents without violating it, has the necessary explanatory notes and the signature of the customs expert (expert). The packaging is sealed with the seal of the customs authority or another authorized organization conducting customs examination.
21. The covering letter for the conclusion of the customs expert (expert) is drawn up in 2 (two) copies, signed by the head of the customs authority or its structural unit, or another authorized organization conducting the customs examination, or his deputy and contains:
information about the submitted conclusion of the customs expert (expert);
a list of materials, documents, samples and samples attached to the conclusion of the customs expert (expert), indicating their name, quantity and packaging;
information about materials, samples and specimens consumed (destroyed) during the production process, indicating their name and quantity.
22. The conclusion of a customs expert (expert), materials, documents, samples and specimens, together with a covering letter, are issued against signature to the official of the customs authority who appointed the customs examination, with the obligatory entry of the corresponding entry in the journal, or sent in the manner established by the legislation of the Member State customs union.
The form of the journal is determined by the central customs authority of the member state of the customs union.
IX. Final provisions
23. The central customs authorities of the member states of the Customs Union create a working expert group with the aim of developing unified scientific and methodological recommendations on the issues of expert support for the customs authorities of the Customs Union and resolving issues not regulated by this Procedure.
24. The results of a customs examination carried out in accordance with the customs legislation of the customs union are recognized in the customs territory of the customs union.
25. A commission examination with the involvement of customs experts (experts) of another member state of the customs union is appointed by the customs authority in agreement with the central customs authorities of the member state of the customs union.
26. The customs authority that appointed the customs examination shall inform the customs authority that conducted the customs examination of the measures taken based on the results of the customs examination.
Materials provided
To conduct a study, an authorized specialist or body must obtain:
- Resolution or determination ordering an inspection. The document must be sent to the head of the ECS, or CEKTU, or other institution where the research will be carried out, with a covering letter.
- Act (protocol) on sampling. This document is required especially in cases where chemical customs examination is carried out.
- A copy of the declaration and other papers containing information related to the subject of the study and necessary to clarify issues that have arisen.
- Objects of examination. These include vehicles, documentation, samples, physical evidence, etc.
- Samples for comparative analysis.
Sample certificate of examination of goods
The act is written in such a way that it can be understood not only by the expert’s colleague, but also by a person who does not have specific knowledge. This means that when forming it, highly specialized terms, complex, obscure phrases, etc. should be avoided.
- First of all, at the top of the document its name and number are indicated.
- Next, the date of drawing up the act and the place are indicated (here you need to write the name of the company that conducted the research and its address - if necessary), information about the expert is given - his position and surname.
- Then the basis for conducting the examination is written: here you need to indicate either the application number or the work order number (depending on the situation), then the date of its conduct.
- After this, data about the product is entered into the act: its name, category, grade, type, purpose, quantity and other identification characteristics, as well as the tasks facing the expert.
- Below is the manufacturer of the product: the name of the company and the country in which it is registered.
- Finally, the expert's opinion is indicated.
If necessary, the document can be supplemented with other information (for example, about what activities were carried out during the examination), as well as additional papers attached to the act can be indicated.
lead time
The examination period is established in Art. 378 of the Customs Code of the Customs Union. It should not exceed:
- Temporary storage period (two months) if the product is not released until the test result is received.
- Six months, if the examination is carried out in relation to a vehicle.
- Year - in other cases.
The examination period may be extended according to the rules established by the legislation of the CU member states. The duration of the study may be suspended at the request of a specialist to the body by whose decision it was started, for the provision of samples and additional materials, or in other cases provided for by the regulations.
Act on the results
At the end of the examination, a conclusion is drawn up. It is drawn up in writing in two copies. One of them remains with the institution that carried out the research, and the second - with the body by whose decision it was assigned. The conclusion indicates the place and time of the examination, by whom and on what basis it was carried out, the questions that were posed, as well as its results and content, conclusions and justifications.
Documents and materials illustrating the information present in the act are attached to it and act as its integral part. If during the research a specialist establishes circumstances of significant importance regarding which questions were not posed to him, he can include conclusions on them in the conclusion. When an examination is carried out by several authorized persons, the report is signed by all specialists. In case of disagreement, each employee formalizes his opinion separately. The customs authority transfers to the declarant or other interested parties (if known) who have authority in relation to products or vehicles, a copy of the specialist’s conclusion or message about the impossibility of giving it.
Who has the right to conduct an examination
People with special, narrowly focused knowledge are involved in conducting the examination. At enterprises, these may be specially trained employees who have undergone professional training and have appropriate qualifications confirmed by written certificates or diplomas.
If an organization does not have the opportunity to employ its own experts, then it may well resort to the services of third-party specialists.
In some cases, when the examination is carried out in relation to, for example, complex technical objects, a whole group of experts may participate in the study, each of whom belongs to a specific expert community and has specific knowledge.
Specialist rights
During the check, the employee can:
- Participate in specific actions during customs control with the permission of the authorized body.
- Get acquainted with materials that relate to the subject of research.
- Involve other specialists in performing the examination with the consent of the authorized body.
- Request additional information that is necessary to conduct the research.
- Refuse to issue a conclusion if the materials provided to carry out the inspection are insufficient, or if the specialist does not have the appropriate knowledge to carry out the examination.
Rights of the declarant or his representative
The legislation of the Customs Union establishes the legal possibilities for interested parties. In particular, the declarant or his representative has the right:
- Submit a reasoned challenge to the expert.
- Submit a request to raise any additional questions to obtain answers from a specialist.
- Apply for the appointment of a specific official to carry out the research.
- Be present during the inspection process (with the permission of the authorized body).
- Take samples and samples of products.
- Read the conclusion drawn up by a specialist based on the results of the study, or a message about the impossibility of giving it and receive a copy of the report.
- Submit a request to perform an additional or repeat inspection.
If the request of the declarant or his representative is satisfied, the person who appointed the examination makes an appropriate decision. If an application is rejected, the authorized officer must notify the applicant with reason.
Samples
During customs control, an authorized officer may take materials necessary to carry out the examination. A corresponding act must be drawn up regarding this. Its form is established by the federal executive body, which is authorized in the field of customs affairs. The act is drawn up in 2 copies, one of which is given to the declarant or his representative. In some cases, sampling is carried out in the presence of a specialist. Samples may be taken in minimal quantities sufficient to carry out the examination. Permission to take is issued if this procedure:
- Will not change product characteristics.
- Will not complicate customs control.
- Will not entail evasion of duties, taxes or non-compliance with restrictions and prohibitions established by Russian legislation regulating foreign trade activities.
When taking samples, a separate declaration is not submitted, provided that they are indicated in the general document for all products. An interested party may reduce the customs value of products by a hundred samples if they were selected by the authorized body and not returned within the prescribed time. Declarants and their representatives may be present during the sampling process and are required to assist employees, including performing cargo and other operations at their own expense. If samples and specimens were taken by other government agencies, they must notify the customs services. The rules in accordance with which the necessary materials are taken are established by the executive bodies of the federal government in accordance with the CU Code and other regulations of the Russian Federation. After the examination, samples and specimens must be returned to the owner, unless the materials must be disposed of or destroyed, or the cost of returning them exceeds their value.
Purpose of a customs examination, or why it is worth ordering an examination from us.
We offer all regular and new clients the following benefits:
- All checks are carried out by experts with specialized education in accordance with current legislation;
- We guarantee an independent and objective assessment;
- Our report can be used in legal proceedings as the basis of evidence;
- Our team will provide legal support and advisory assistance to all clients;
- We work without intermediaries, so we offer the best prices for all services.
To order an independent customs examination , fill out an online application or call our specialists at the numbers provided.