Customs control, in general terms, is a set of measures carried out by customs authorities in order to ensure compliance with customs legislation.
When carrying out customs control, customs authorities proceed from the principle of selectivity and are limited only to those forms of customs control that are sufficient to ensure compliance with the customs legislation of the EAEU and the legislation of the EAEU member states, control over the implementation of which is entrusted to the customs authorities.
When selecting objects and forms of customs control, a risk management system is used.
When carrying out customs control, customs authorities do not require any permits, instructions or resolutions for its implementation.
Customs control is carried out by customs authorities in accordance with the customs legislation of the EAEU and the legislation of the EAEU member states. On behalf of the customs authorities, customs control is carried out by customs officials authorized to conduct customs control in accordance with their official (functional) responsibilities.
Customs control is carried out by customs officials in relation to:
- goods, including vehicles, transported across the customs border and (or) subject to declaration;
- customs declaration, documents and information about goods, the presentation of which is provided in accordance with the customs legislation of the Customs Union;
- activities of persons related to the movement of goods across the customs border, the provision of services in the field of customs affairs, as well as carried out within the framework of certain customs procedures;
- persons crossing the customs border;
- premises or open areas intended for temporary storage warehouses, customs warehouses, free warehouses, duty-free shops, or used by authorized economic operators.
Customs control is carried out in the customs control zone, as well as in other places determined by the customs authorities, where goods, vehicles and documents containing information about them are located, including in electronic form.
Customs control after the release of goods is carried out by customs officials by:
- checking the fact of release of goods,
- checking the accuracy of the information declared during customs clearance,
- as well as control over the intended use of goods (if the goods are released conditionally with the provision of benefits for the payment of customs duties, the provision of which is associated with restrictions on the use and disposal of such goods).
Tax authorities, internal affairs bodies and other law enforcement and government bodies inform customs authorities about the materials they have on violations of customs legislation, in the manner determined by agreements with the federal executive body authorized in the field of customs affairs.
In order to improve customs control after the release of goods and vehicles and strengthen international security, cooperation is carried out with international organizations and customs services of foreign countries.
Forms of customs control
According to Article 322 of the EAEU Customs Code, there are seven forms of customs control:
- obtaining explanations consists in obtaining by the customs authorities the information necessary for carrying out customs control;
- verification of customs and other documents and (or) information consists of checking a certain list of documentation in order to identify inconsistencies and violations in them;
- customs inspection is a form of control in which a visual inspection of goods, transport, cargo containers, and seals is carried out;
- customs inspection means that, in addition to external inspection, packages, containers and other cargo containers are opened for the purpose of a more in-depth study of the goods;
- personal customs inspection is applied only to individuals;
- customs inspection of premises and territories specializes in visual inspection of customs warehouses and storage facilities;
- Customs inspection is a form of control that is carried out by customs after the release of goods. More details should be said about this type.
The main principles of customs control after the release of goods and vehicles are:
- legality, transparency and accessibility of information on issues of customs control after the release of goods;
- validity to ensure equality of participants in foreign economic activity when choosing objects of customs control after the release of goods;
- selectivity, which allows, as a rule, to be limited only to those forms of customs control that are sufficient to ensure compliance with customs legislation;
- objectivity and independence of decisions made during customs control after the release of goods;
- harmonization of methods and procedures for conducting customs control after the release of goods with generally accepted international norms and practices;
- exclusion of unjustified interference and damage to the business activities of the persons being inspected;
- unity of the customs control system after the release of goods and uniform application of legislation during its organization and implementation.
What is customs control
Customs control is a list of actions carried out by customs authorities to ensure the legality of the clearance process.
When conducting inspections, the agency is guided by the principle of selectivity, which is based on a risk management system. Customs control is limited to measures sufficient for a particular case, without resorting to inappropriate methods.
Customs control after the release of goods is regulated by Chapter 16 and Chapter 19 of the EAEU Customs Code.
The objects of customs control after the release of goods and vehicles are:
1) goods and vehicles released into the territory of the EAEU for free circulation;
2) goods and vehicles released conditionally into the customs territory of the EAEU;
3) goods and vehicles exported from the customs territory of the EAEU;
4) goods of foreign origin that are in civil circulation on the territory of the EAEU;
5) activities of persons in the field of customs affairs.
When selecting inspection objects, customs authorities carry out a comprehensive analysis based on many criteria: the reputation of a foreign trade participant, the index of its business activity, analysis of the results of previous inspections of its activities, etc.
Main advantages
Customs control after the release of goods was approved in 2012. Since then, this task has become a priority for the FCS. Throughout its existence, this strategy has shown its effectiveness in several aspects:
- reduction of costs for foreign trade participants related to storage of goods and downtime;
- reducing the number of searches;
- reduction of customs clearance time. Since deep control directly at the customs point itself is now carried out selectively. In cases where there are sufficient grounds for such a check. The time required for customs clearance and customs clearance of goods has decreased significantly;
- in 2021 alone, through control after the release of goods, violations were identified totaling 26.2 billion rubles. Every year, inspection methods are improved. Compared to 2018, the efficiency of one inspection doubled and amounted to 7.7 million rubles.
Customs control after the release of goods: current trends, problems and prospects
Key words: customs control after the release of goods, optimization, technology, Eurasian Economic Union, TKPVT divisions, foreign economic activity.
At the present stage of development of relations between the member states of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), a set of measures is being actively implemented aimed at implementing the principle of shifting the emphasis of customs control from the stage of customs declaration and release of goods to the stage after the release of goods, including for the purpose of crime prevention.
This principle assumes a more simplified and effective process of organizing customs control after the release of goods [2].
Customs control after the release of goods is a set of activities carried out by customs authorities after the release of goods and during the circulation of goods imported into the customs territory, through customs inspections and other forms of customs control, including using a risk management system, based on the categorization of participants in foreign economic activity (FEA). ) in order to ensure compliance by the inspected persons with the customs legislation of the EAEU and the legislation of the Russian Federation on customs [6, p. 8].
The changes that have occurred in the foreign trade of the Russian Federation over the past few years have affected previously firmly established patterns and trends. By these we can mean: changes in the list of countries with which the Russian Federation maintains partnerships, the structure of foreign trade turnover, the logistics of the movement of goods and a reduction in the volume of customs declaration of goods.
The main factors that determined these changes include the following:
1) the impact on the structure and dynamics of Russian foreign trade of the global financial and economic crisis and the imposed sanctions;
2) adjustments in the field of state regulation of foreign trade, as well as integration processes within the framework of the Eurasian Economic Union [4, p. 50].
Already today, certain simplifications have been given to a number of participants in foreign trade activities at the activity stage, followed by monitoring and control at the stage after the release of goods. Within the framework of this approach, based on the results of an analysis of the performance indicators of foreign trade participants, they are categorized based on the potential risks of violating customs legislation.
The work to suppress violations in the field of customs and ensure the complete collection of customs duties, taxes and other payments is based on intradepartmental and interdepartmental interaction. Fruitful interaction has been established with the Federal Tax Service of Russia, especially in terms of selecting objects of control, as well as identifying interrelated violations in the field of foreign economic activity, and combating payment evasion schemes [3].
Currently, the level of interdepartmental interaction has changed dramatically. The Eurasian Economic Commission is working to integrate the information systems of the customs services of the EAEU member states and other government bodies on the basis of the EAEU integrated information system. This is done to ensure “traceability” of the movement of goods from the moment they cross the customs border of the EAEU to their final consumer.
Directions for optimizing customs control after the release of goods:
1) interaction with the business community, whose representatives take an active part in discussing innovations in customs legislation and developing proposals for improving customs technologies in the field of customs control after the release of goods;
2) the possibility of using audit reports during customs control. The auditor's report can be an additional source of information about the general condition of the organization, or certain areas of its activities, including foreign economic activity, as well as about financial stability and the quality of internal control. Such information can undoubtedly be used when customs authorities analyze the activities of foreign trade participants when determining the level of risk and their category (Fig. 1);
3) development of a technology for conducting customs inspections based on electronic documents and information, which is being developed by GUTKPVT together with other divisions of the Federal Customs Service of Russia;
Rice. 1. Possibilities of using audit reports during customs control
4) the use of “electronic desk inspection” technology, which will significantly reduce the time of conducting such an inspection in relation to participants in foreign trade activities with a low level of risk of violating customs legislation. In the past, inspection activities were based on conducting spot checks, without analyzing the impact of inspection results on the declaration of identical or similar goods, or on the industry as a whole (Fig. 2);
Rice. 2. Desk customs inspection based on electronic document management
5) application of an integrated approach. It lies in the fact that when preparing and conducting a customs inspection, we take into account the interrelated factors that created the conditions for violation of customs legislation, and we carry out active intradepartmental and interdepartmental interaction. One of the tools for implementing an integrated approach to customs control after the release of goods is the mechanism of intradepartmental and interdepartmental interaction, as well as interaction with large business communities, based on agreements concluded with the Federal Customs Service of Russia;
6) carrying out comprehensive verification activities in certain market sectors, affecting several regions at the same time. The measures taken, which included legislative initiatives and technical solutions, contributed to the launch of self-control mechanisms and decriminalization of industries, the creation of open and fair competition.
Based on the results of inspection activities, there is a positive dynamics of growth in the budgetary efficiency of customs inspections.
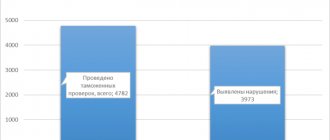
In 2014, after the release of goods, customs control units carried out 6,684 inspection activities in relation to legal entities, individuals and individual entrepreneurs; in 2015, their number was: 4,782 customs inspections, of which 3,973 were effective [1].
Analyzing the data of past years, we can conclude that there is a positive dynamics in customs control after the release of goods, the amounts of additional accrued and collected customs duties are increasing every year, and the results of the inspection activities of customs authorities are improving (Fig. 3).
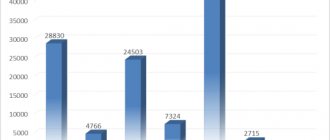
Rice. 3. Additional customs duties and penalties accrued, fines imposed, billion rubles. [1]
Based on the activities carried out by the departments of TKPVT, in January-June 2021, 3,412 inspection activities were carried out in relation to legal entities, individuals and individual entrepreneurs, of which 2,087 were in the form of customs inspections, including inspections based on signs of violation of legislation 1,693 (resulting - 1,508 , effectiveness – 89.1%).
The recovery rate was 48.8%, which is 12.3% more than in January-June 2015 (36.5%). In January-June 2021, based on the results of the inspection activities of the TKPVT units, 2,095 cases of accidents and 143 criminal cases were initiated, penalties were imposed in the form of fines in the amount of 780.7 million rubles, and 90.1 million rubles were collected. [1].
In order to prevent the movement of goods prohibited for import into the Russian Federation in places close to the Russian-Kazakh and Russian-Belarusian sections of the state border of the Russian Federation, there are 35 mobile groups that carry out customs control activities.
Statistics show a stable increase in performance indicators of customs control units after the release of goods throughout the study period. The Federal Customs Service of Russia strives to simplify customs procedures and reduce the administrative burden on participants in foreign economic activity, which will ultimately lead to a reduction in the time spent by participants in foreign economic activity on moving goods across the customs border of the EAEU. Moreover, at present, the priority of work within the framework of post-release control “is not the amount of additional accrued payments, but the amount of collected ones, because the difference between these figures causes debt to the state” [5].
The particular importance of this area of activity of customs authorities raises the question of the need to develop a set of tasks aimed at increasing the efficiency and improving the organization of the activities of customs control units after the release of goods.
Ensuring the implementation of the development of customs control after the release of goods is possible by implementing the following measures:
1) improving the existing post-control mechanism and introducing new approaches to conducting verification activities based on taking into account the global experience of WCO member countries;
2) application of a systematic approach to organizing customs control after the release of goods when selecting inspection objects to obtain results with the necessary economic effect;
3) automation of analytical work and control technologies after the release of goods.
Thus, the efficiency of the organization and effectiveness of the application of customs control after the release of goods is one of the most important tasks of the customs service of the Russian Federation. The implementation of foreign trade, the simplification of customs rules in the context of ensuring economic security and replenishing the federal budget determine the development of measures to modernize and improve customs control after the release of goods. This includes the development of draft standards, methods of conducting audits in the customs sector, forms for reflecting the results, introducing amendments to the Code of Administrative Offenses of Russia on the composition of violations and measures of responsibility of auditors for false presentation of information. It is also necessary to develop a list and procedure for accreditation of auditors and requirements in order to control the level of their qualifications for auditing issues in the field of customs affairs.
Literature:
- Results of the activities of customs authorities in implementing customs control after the release of goods for 2015 [Electronic resource] URL: https://www.customs.ru/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=23257:————2015-&catid= 343:2012-08-09-12-59-58&Itemid=1830&Itemid=2268 (date of access: 10/10/2016).
- Koknaeva M.D. Customs control system after the release of goods in the Russian Federation / Collection of materials from the international interuniversity scientific and practical conference “Current problems in the development of the theory and practice of customs economics.” M., 2013. pp. 73-77.
- Nemirova G.I., Kostin A.A., Kostina O.V. Current problems of the customs control system and methods for resolving them in the Eurasian Economic Union // Customs Affairs. 2021. No. 4. pp. 11-15.
- Petrov A.V., Ryabinskaya N.V. Evaluation of the results of customs control after the release of goods based on an analysis of the performance indicators of authorized units of customs authorities // Young scientist. 2021. No. 10.1. pp. 50-54.
- Seleznev V. Customs control: Results and prospects // Customs. 2021. No. 6 [389].
- Tuntaev R.I., Trubitsyn K.V., Chekushkin E.V. Customs control after the release of goods. St. Petersburg: Intermedia Information Center, 2015. 128 p.
Basic forms of post-release control
According to the Ural Customs Administration for 2021, the main forms of post-control by quantity were:
1. Inspection of premises and territories - 41%
2. Customs check - 26%
3. Receiving explanations - 22%
4. Customs inspection - 10%
5. Customs surveillance - 0.9%
6. Customs inspection - 0.1%
Customs considers inspection to be the most effective form. It is based on the results of customs inspections that large sums of money are collected. Therefore, in customs post-control reports, the first to be highlighted is the number of customs inspections carried out and the average amount of additional charges for them. Below is data for four years.
How to read statistics using the example of 2021 - customs carried out 2,437 inspections, the average inspection efficiency was 2.4 million rubles. Data for 2021 are for 9 months.
In 2021, customs assessed an additional 24 billion rubles as a result of customs inspections. The average amount of additional charges based on the results of one customs inspection was 15 million rubles, which is 2 times more than in 2021.
“Post-release control has become a very significant and solid fiscal instrument of the Federal Customs Service,” noted First Deputy Head of the Federal Customs Service Ruslan Davydov at the International Customs Forum. He added that the share of electronic checks after graduation will be increased from 5% in 2021 to 40% in 2024. Customs will actively develop post-control, and here's why.
In addition to effectively replenishing the budget with the help of post-control, customs will increase the speed of cargo release. It will expand the number of automatically issued declarations, and transfer secondary verification to control after release. In the next 5 years, companies will receive more requests from customs when the goods have already been released and sold.
Register with Avangard Direct to go through customs control with professionals.
Three new areas of post-control
Customs develops post-release controls using an array of accumulated data on the actions of companies and forecasting based on them.
Digital twin
Digital twin is a technology that is used in various fields. Thus, the Port of Rotterdam is implementing a digital twin to predict the behavior of all port operations. The technology will analyze the type of vessel, weather conditions, workload and provide a forecast time for unloading. Then optimizes the vessel's entry to reduce costs.
This is how customs will predict the actions of companies. A digital twin is a digital copy of a foreign trade participant, onto which data from previously identified violations and the company’s activity outside the customs system are superimposed.
The digital copy is intended to inform customs about a possible violation that was not detected by the risk management system during the release of the goods. According to customs, the technology will accurately determine the object of control after release. This will increase the collection of payments to the budget and eliminate the burden on honest businesses.
Customs monitoring and audit
Customs monitoring – monitoring the activities of companies engaged in foreign trade activities, with comparison of data outside the customs system.
Customs plans to compare customs data with tax risks, tax characteristics of companies, data from veterinary, phytosanitary controls, and technical regulators. This is how to create a three-dimensional digital picture of the company in order to find “anomalies” in its activities.
Customs audit was offered to businesses that want to voluntarily undergo an audit as when a company enters an IPO. Customs will use this data to study the company and implement a risk management system.