The information is of interest to those who carry out or are just planning to engage in foreign economic activity for commercial and non-commercial purposes, as well as for those who plan to transport personal belongings, luggage, vehicles and receive international mail crossing the border of the Russian Federation. Knowledge of the specifics of customs operations in 2021 and proper execution of documents will allow you to avoid unnecessary expenses and carry out customs clearance as quickly and efficiently as possible.
What are customs duties
Customs duties include payments collected for the provision of customs services for clearance, storage and customs escort of goods, regardless of their commercial affiliation. The declarant can be the owner of the declared property himself or a third party who replaces him and is endowed with the necessary powers.
The amounts of customs duties are calculated on the basis of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 863 of December 28, 2004 “On the rates of customs duties for customs operations.” The calculation is based on the customs value of the goods in Russian rubles. The amount of customs duties is limited and cannot exceed 100,000 rubles.
When exporting goods outside the Russian Federation that are not subject to export customs duties, the rates of customs duties do not depend on their value.
Limits for duty-free imports
Individuals have the right to import goods into the Russian Federation duty-free if:
- their total cost does not exceed 500 Euro;
- their weight is no more than 25 kg.
Important: both conditions must be met simultaneously. If one of the limits is exceeded, you will have to pay a fee. These limits apply to the import of goods by road, rail, and water transport. If crossing the border is carried out by plane, then the restrictions are as follows:
- weight no more than 50 kg;
- cost up to 10,000 Euro.
Legal entities are deprived of the opportunity to import goods duty-free. This is due to the fact that the crossing of cargo belonging to a legal entity is regarded as the importation of goods for the purpose of selling it for commercial gain.
Customs duty rates in 2021
For the convenience of site users, tables have been compiled to make information easier to perceive. In 2021, previously approved rates continue to apply.
When submitting a declaration for goods electronically, customs duties are paid in the amount of 75% of the established ones.
Customs Clearance Fees
The following tariffs for customs operations apply to goods (import and export) (clause 1 of the Decree of the Russian Federation on customs duty rates).
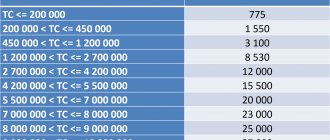
Table 1.
Rates for customs clearance (including 75% for electronic declaration)
| Customs value of goods | Customs duty amount |
| Up to 200 thousand rubles inclusive | 375 rubles |
| From 200 thousand rubles 1 kopeck to 450 thousand rubles inclusive | 750 rubles |
| From 450 thousand rubles 1 kopeck to 1200 thousand rubles inclusive | 1500 rubles |
| From 1200 thousand rubles 1 kopeck to 2500 thousand rubles inclusive | 4125 rubles |
| From 2500 thousand rubles 1 kopeck up to 5000 thousand rubles inclusive | 5625 rubles |
| From 5000 thousand rubles 1 kopeck up to 10000 thousand rubles inclusive | 15,000 rubles |
| From 10,000 thousand rubles 1 kopeck | 22500 rubles |
When registering goods for export that are not subject to customs duties and taxes, the actual price in Russian rubles indicated in the accompanying documentation (purchase and sale agreements, invoices) is used for calculation.
Please help make this article better. Answer just 3 questions.
Table 2.
Rates for customs clearance of separately allocated items.
| Product type | Type of transaction | Customs duty amount |
| Securities denominated in foreign currency | Import, export | 500 rubles, subject to registration of the package in one declaration |
| Goods for personal use not used for business activities | Import, export | 250 rubles (except for passenger cars designated in heading 8703) |
| Passenger cars from heading 8703 for personal, family and home use | Import, export | The calculation is as specified in Table No. 1. |
| Air, sea, river, mixed types of vessels | Temporary import, temporary export, processing on or outside the customs territory | 10 thousand rubles per vessel, unless otherwise provided |
| Goods not subject to export customs duties | Export | 1 thousand rubles, provided that the declaration indicates only goods not subject to export customs duties |
If one declaration indicates goods subject to and non-taxable with customs duties, then the calculation is carried out by addition - 1 thousand rubles for non-taxable goods and the corresponding amount from Table 1 for goods subject to customs duties.
Customs clearance fees
Customs duty for customs escort is charged for escort of vehicles, railway transport, aircraft, water vessels in the amounts indicated in clause 5 of Art. 130 Federal Law No. 311 of November 27, 2010 “On customs regulation in the Russian Federation.”
Table 3.
Rates for customs escort
| Distance | For each vehicle | For each unit of rolling stock | For each aircraft | For each water vessel |
| Up to 50 km inclusive | 2000 rubles | 2000 rubles | 20,000 rubles regardless of distance | 20,000 rubles regardless of distance |
| Over 50 to 100 km inclusive | 3000 rubles | 3000 rubles | ||
| Over 100 to 200 km inclusive | 4000 rubles | 4000 rubles | ||
| Over 200 km | 1000 rubles for every 100 km, but not less than 6000 rubles | 1000 rubles for every 100 km, but not less than 6000 rubles |
Storage fees
If goods are stored in the warehouses of the customs authority, the declarant is obliged to pay for the service in accordance with Art. 130 of Federal Law No. 311-FZ “On customs regulation in the Russian Federation”.
Table 4.
Storage rates
| Warehouse type | Bid |
| Temporary storage warehouse of the customs authority | 1 Russian ruble for every 100 kg of weight per day |
| Specially equipped warehouses for storing certain types of goods | 2 Russian rubles for every 100 kg of weight per day |
Important. When calculating, rounding is done only upward, that is, partial 100 kg are counted as full 100 kg, and a partial day is equal to a full day.
For which goods are customs duties not charged?
Exemption from customs duties is regulated by Art. 131 FZ-311 dated November 27, 2010 “On customs regulation in the Russian Federation.”
Table 5.
List of goods exempt from customs duties
| Product type | Type of transaction |
| Goods of free (humanitarian) aid | Import, export |
| Property owned by diplomatic missions, consular services, official missions of foreign states and their employees | Import, export |
| Cultural property belonging to museums, archives, repositories of state or non-state ownership | Temporary import (admission), temporary export |
| Products intended for display at national exhibition events, including air shows | Temporary import, temporary export |
| Cash currency of the CU member states, with the exception of commemorative coins | Import, export by the central banks of these states |
| Goods with a total value of less than 200 € at the Central Bank exchange rate on the day of declaration | |
| Items used as supplies | Import, export |
| Goods owned by private individuals for household use | Import, export |
| International transport vehicles | Temporary import, subject to further use in international transport |
| Spare parts and equipment along with the vehicle | Import, export (Article 349 of the Labor Code of the Customs Union) |
Also, customs duty is not charged for the import/export of goods intended for sports competitions and filming, professional equipment intended for media production, scientific samples, and international mail.
Please help make this article better. Answer just 3 questions.
Procedure for paying customs duties
The basic procedure for paying customs duties is dictated by Article 84 of the Customs Code of the Customs Union. The payer of this duty is the declarant - a participant in foreign economic activity. It can be either a legal entity or an individual. Declarants are required to calculate the amounts payable (Article 76 of the Customs Code of the Customs Union), however, in the case of international mail, this obligation is performed by the state body (post office), without submitting a declaration.
In other cases, filling out the declaration is mandatory. In the case when a product is imported into the country, import duties are paid by the importer - the party that brought the product to Russia. When goods, on the contrary, are exported from the country, export duties are paid by the party that exports the goods.
When importing goods into the territory of the Customs Union, accrued customs duties are subject to transfer to a single account of the authorized body of the country in which they are accrued. After which the total amount of import customs duties is distributed among the member states of the customs union in the proportions established by contractual agreements. Today the proportions are as follows:
- Republic of Kazakhstan – 7.33%;
- Republic of Belarus – 4.70%;
- Russian Federation – 87.97%.
If we are talking about the temporary import of goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, then in this case there is no need to pay import customs duties. In some cases, the importer pays this type of payment, but upon further export of goods from Russia, this duty is returned. Also exempt from paying import customs duties are Russian-made goods that were previously exported from the country and for some reason are returned back, without changing the quality characteristics of the goods.
It should be remembered that customs duties are paid in the currency of the country in which payment is due. In Russia, this is the Russian ruble, and payment is made by bank transfer to the account of the Federal Treasury.
But for individuals there is the possibility of paying in cash to the cash desk of the customs authority.
Article 73 of the Customs Code of the Customs Union provides for the possibility of making advance payments towards the payment of future commodity duties. They are also paid in the currency of the state in which duties will be charged.
A notable aspect is the possibility of requesting from the customs authorities a report on the expenditure of advance reports. The report is provided in written form. But payment of advances on customs duties is rare, because very often payments are written off to the Federal Budget as part of other income. Most often, this happens in cases where the customs authorities recognize the end of the period of “storage” of the payment in their accounts, although the law does not provide for deadlines for advance payments. When calculating the amount of customs payment, the declarant is stacked with three types of rates:
- ad valorem is a rate established as a percentage of the customs value of the goods;
- specific - this is a rate set as a fixed amount per unit of measurement of a product (liter, kilogram, etc.);
- combined is a rate that combines the characteristics of ad valorem and specific rates.
The interest rates themselves are established by the Unified Customs Tariff of the Customs Union - CCT CU (approved by decision of the Council of the Eurasian Economic Commission dated July 16, 2012 No. 54). Unlike customs duties and fees, the rates and amounts of which are determined by the customs tariff, the VAT rate and excise taxes levied when importing goods into the customs territory of the Customs Union are determined by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Clause 2, 3 and 5 of Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that when importing goods into the territory of Russia, tax rates of 10% and 18% are applied. Excise rates, in turn, are determined by Article 193 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Procedure and terms for payment of customs duties
Regulated by art. 128 Federal Law No. 311 “On customs regulation in the Russian Federation”
The fee for customs operations is carried out simultaneously with the submission of a customs declaration (incomplete, complete, periodic, temporary). During customs escort, payment must be made before it begins; during customs storage, before the goods are released to the owner or the person representing him.
Important. Payment of customs duties is made to the current account of the Federal Treasury in Russian rubles; individuals can pay in cash directly when passing through customs.
How to calculate customs duties
The amount of customs duty payment is determined for registration, escort and storage of goods according to Tables 1, 2, 3, 4. Based on the available data, calculation in 2021 is also performed by summing up individual items.
What is a cargo customs declaration? Sample filling The cargo customs declaration is included in the list of documentation required for foreign trade activities.
Cost and delivery time for a 20-foot container from China One of the undeniable advantages of sea container shipping is its low cost and versatility
Features of simplified customs clearance Its essence is that a participant in foreign trade activities receives a number of advantages that reduce the time for releasing goods, reduces the costs of storing and moving them across the territory of Russia
Structure of customs duties
For 9 months of 2021, receipts to the Russian budget from customs payments amounted to 3,218.50 billion rubles, when the total amount received to the Federal budget amounted to 10,440.60 billion rubles. Thus, the country’s income for this period amounted to 30.8% from customs payments.
The structure of this type of duties for the analyzed period is as follows:
- import customs duty – 0.1 billion rubles;
- export customs duty – 1,609.30 billion rubles;
- customs duty – 13.8 billion rubles;
- VAT – 1,545.90 billion rubles;
- excise tax – 45.90 billion rubles;
- other customs payments – 3.50 billion rubles.
In this situation, it should be remembered that import customs duties are distributed in the form of shares among the member countries of the customs union.
Data provided by the Federal Customs Service indicate that the basis of the structure of customs payments for 9 months of 2021 is import customs duty (50% of the total amount). This indicates the high importance of exports (export) and VAT (48% of the total amount) of Russian-made goods outside the customs union. The smallest share in the structure of customs duties is made up of other payments: excise tax - 1.4%, customs duty - 0.4%, other customs payments - 0.12%, import customs duty - 0.08%.