With remote release (R) of goods, a participant in foreign economic activity (FEA) saves his time, since he can release the cargo from the border point (after crossing the border) without personal presence at the customs office.
Electronic declaration simplifies the customs clearance process and increases the productivity of customs officers and the number of deliveries of the declarant. In this article we will talk about the rules for working with hydrocarbons, knowledge of which will speed up the process of interaction with government agencies.
What is remote release of goods
Remote cargo release is a new technology used by customs and regulatory authorities to actually check the condition of the transported goods anywhere in the country. Initially, the use of electronic declaration centers (EDC) was used within the framework of the new Customs concept to regulate and control transportation in territories located near the Russian border.
The main goal of the new Customs concept is to optimize the redistribution of functions of customs posts located in border zones and internal regions of the state. The expected result is a reduction in the load on posts located in large populated areas and a reduction in the need for long-term storage of cargo. The new rules reduce the costs of storing and transporting products, which reduces the final cost of the goods.
Decisions of the EAC Board dated January 16, 2021 No. 2 and No. 4 set out the rules regarding the structure and format of the cargo declaration. The acts regulating the procedure for working with the Federal Customs Service (FCS) also include Order of the Federal Customs Service of Russia dated January 24, 2008 No. 52 “On the introduction of information technology for submitting information to customs authorities in electronic form...”.
Reference. According to Art. 104 of the EAEU Customs Code “General Provisions on Customs Declaration”, instead of electronic declaration, you need to use an ordinary one (on paper) if there are problems with electricity or Internet connection at customs.
Procedure technology
Items are declared electronically either independently or with the help of a customs broker, but the procedure in both cases includes:
- Collection of documents and their translation into XML format (declaration of goods, declaration of customs value and list of documents presented).
- Transfer of these papers to the electronic archive of the declarant.
- Filling out a declaration in the program, after which the package of documents is sent to customs. Once “Remote edition” is selected, changing it to regular edition will no longer be possible. All accompanying documents from the first point and the declaration are transferred to customs automatically after the opening of the customs clearance procedure.
- The customs office reviews the application and, after successfully passing the check, assigns it a unique number (UID) in the electronic system. If the declaration is unsuccessful, the declarant receives a refusal with an explanation of the errors made. After they are corrected, the check is repeated.
- Sometimes cargo inspection is required. Employees are notified of this in a message (its receipt must be confirmed). After the inspection, an act is written, a copy of which is sent to the declarant.
- After successful completion of all stages of production, the status “Release authorized” is assigned.
- If necessary, corrections are made to the ED after the cargo is released from customs.
The customs representative (if hired) will represent the declarant's interests in this process, complete all required forms, and promptly respond to the customs inspector's questions regarding the verification of the declaration.
In rare cases, customs requests paper documents confirming the information in the declaration. But this happens when employees have various doubts about the release after inspection of the cargo (especially when the information in the declaration and the actual data do not agree).
Analysis of the EAEU Customs Code from experts of the Legal Department of TELS Group of Companies
The Customs Code, unified for the countries of the Eurasian Economic Union, which entered into force on January 1, 2021, contains many innovations and is inherently a breakthrough document compared to its predecessor - the Customs Code of the Customs Union.
Experts from the Legal Department of the TELS group of companies highlighted the main significant points that significantly distinguish the new Customs Code and in the near future, as all its provisions are implemented, they will change the practice of customs clearance and release of goods.
Before a substantive consideration, let us outline one general point: from the primary regulation of the customs sphere by national Customs Codes and twenty international agreements, which often contradicted each other, the EAEU countries moved to regulating customs clearance processes by the unified EAEU Customs Code. The document has become much broader and includes transitional provisions that indicate how to act if additional EEC Decisions have not yet come into force at the time the code comes into force.
The main innovations of TC:
Priority of electronic declaration over paper declaration
The new Code establishes the priority of electronic declaration and designates only certain cases when declaration can be carried out in paper form.
Now customs clearance in paper form is allowed only in the following cases:
- when placing goods under the customs procedure of customs transit;
- in relation to goods for personal use;
- in relation to vehicles of international transport;
- in relation to goods sent to MPO, when using transport (transportation), commercial and/or other documents, including those provided for by international treaties, as a customs declaration;
- in other cases determined by the Commission and the legislation of the member states, if provided by the Commission.
Declaration in writing can also be made if the customs authority is unable to accept an electronic declaration due to a malfunction of the information system.
Declaration without unnecessary documents
The new Customs Code provides for the possibility of submitting a declaration for goods, as well as a transit declaration or a declaration for a vehicle, without submitting to the customs authority the documents on the basis of which they were completed. Previously, this was not possible, and this led to duplication of electronic documents with paper ones.
Documents and/or information necessary to carry out customs operations may not be provided to the customs authority if information about such documents and/or other information necessary to carry out customs operations can be obtained by customs authorities from their information systems, as well as information systems of organizations EAEU member states. In such cases, declarants indicate information about these documents in the customs declaration or provide them in another way in accordance with the Customs Code.
New in advance information
Submitting preliminary information to customs authorities about goods imported into the territory of the Eurasian Economic Union is an obligation.
Now the composition of preliminary information (PI) is divided into 2 types depending on the purposes of presentation:
- PI submitted for risk assessment purposes is a mandatory part;
- PI submitted to speed up customs operations and optimize customs control, which is provided at the request of the foreign trade participant.
Depending on the purpose of providing preliminary information, the composition of the information provided is determined.
At the same time, the composition of information, structure, format, procedure and deadlines for submission, procedure for generating PI, etc. will be determined by the EEC. Separate solutions will also be developed for PI in air, road and rail transport.
Automatic release and automatic registration of declarations
According to the old Customs Union Customs Code, customs operations were carried out only by a customs inspector. The EAEU Customs Code introduces the possibility of performing certain customs operations in an automated mode, without the participation of customs officials.
Product release time
The release of goods must be completed by the customs authority within 4 hours from the moment of registration of the customs declaration. But... If the customs declaration is registered less than 4 hours before the end of the customs office's opening hours, then release is carried out within 4 hours from the start of the customs office's opening hours
The release time for goods can be increased to 1 working day in the following cases:
- if the customs authority requests documents confirming the information declared in the customs declaration; a decision was made to conduct customs control in other forms or to apply measures to ensure customs control;
- the declarant applied to the customs authority with a reasoned request to change (add) the information declared in the customs declaration
- the declarant did not comply with the requirement of the customs authority to change (add) the information declared in the customs declaration
It is allowed to extend the period for the release of goods by 10 days with the permission of the head of the customs authority for:
- carrying out or completing initiated customs control;
- fulfilling the requirement of the customs authority to change (add) the information declared in the customs declaration
- providing security for the fulfillment of the obligation to pay customs duties, taxes, special, anti-dumping, countervailing duties upon release of goods before completion of the verification of documents and information or when a customs examination is appointed.
Changing delivery location
It is allowed to change the place of delivery of goods without completing the customs procedure of customs transit, if such a place of delivery is located in the same region of activity of the customs authority as the place of delivery of goods originally established by the customs authority of departure.
The procedure for performing customs operations related to obtaining permission from the customs authority to change the place of delivery of goods is determined by the EEC
Completion of the customs transit procedure
To complete the customs procedure for customs transit, a transit declaration and other documents are submitted to the customs authority of destination:
- for goods transported by road – within 3 hours from the moment of their arrival at the place of delivery of goods;
- in relation to goods transported using water, air or rail transport - within the time established by the technological process (schedule) of the port, airport or railway station during international transport, or another period established by the legislation of the Member States on customs regulation
On behalf of the carrier, the above actions can be performed by persons acting on behalf of the carrier, if this is permitted in accordance with the legislation of the Member States on customs regulation
Forms and measures of customs control
The approach to customs control procedures has changed significantly. In the old Code, all customs control instruments were called forms (there were 12 of them). The EAEU Customs Code defines 8 forms of customs control and 13 measures that will ensure them.
Shapes:
- Receiving explanations.
- Checking customs and other documents and/or information.
- Customs inspection.
- Customs inspection.
- Personal customs inspection.
- Customs inspection of premises.
- Customs inspection (desk, scheduled on-site).
- Unscheduled on-site customs inspection.
Measures:
- Conduct a survey.
- Request, demand and receive documents and/or information necessary for customs control.
- Appoint a customs examination, take samples and/or samples of goods.
- Identify goods, documents, vehicles, premises and other places.
- Use technical means of customs control, other technical means, watercraft and aircraft of customs authorities.
- Use customs escort.
- Establish a route for transporting goods.
- Keep records of goods under customs control and customs operations performed with them.
- Engage a specialist.
- Involve specialists and experts from other government bodies.
- Require cargo and other operations to be carried out.
- Carry out customs surveillance.
- Check the availability of a goods accounting system and the maintenance of goods records.
Deferment of payment of customs duties
The EAEU Customs Code provides participants in foreign trade activities with the opportunity to pay customs duties with a deferment of one month from the day following the day of release of goods, in accordance with the customs procedure for release for domestic consumption, but subject to payment of accrued interest.
for deferred determination of customs value is also being introduced . If, during the customs declaration of goods, their customs value cannot be determined on the date of registration of the declaration and there are no documents for its calculation, then the determination of the exact value of the customs value of the goods can be postponed. In this case, it is allowed to determine and declare the customs value of goods on the basis of the documents and information available to the declarant.
Based on it, all duties and taxes will be paid. However, once the exact cost is stated, additional payments will need to be made.
Authorized economic operator
According to the new rules:
- AEO status can only be obtained by a legal entity of a member state of the EAEU (previously a company could be a non-resident);
- the certificate that the AEO company will receive can be of 3 types, each of which involves a different list of special simplifications that it will use;
- AEO status can be obtained by customs representatives, warehouse owners, customs carriers and owners of customs warehouses (previously this could only be the declarant).
Now the AEO status will be recognized by all EAEU member states. Moreover, states that are not members of the EAEU will also be able to provide special simplifications to authorized economic operators on a reciprocal basis.
Legal Department of TELS Group of Companies
What is needed for electronic declaration
To successfully release cargo, you need to have an understanding of the current legislation, including the procedure for customs control and clearance, as well as learn about the creation and use of an electronic key (EC or EDS/ED - digital signature).
A foreign trade participant will have to create an account card in the register of institutions that have permission to create documents of this type, obtain an electronic signature, set up the appropriate programs for creating documentation and register or use the electronic declaration portal of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation. Some declarants who do not want to take on these responsibilities (with the exception of electronic signature) turn to a customs broker. This is a profitable option if there are no plans to work for export/import in the long term.
The list of necessary documentation for processing a cargo customs declaration (CCD) includes:
- foreign trade agreement, supply agreement, etc.;
- shipping documents for the goods (bill of lading, invoices, etc.);
- documents that served as the basis for assigning the goods a HS code;
- documents confirming the payment of customs duties;
- money orders;
- documents confirming the declared customs value;
- documents confirming compliance with non-tariff restrictions (licenses, safety certificates, certificates of conformity, veterinary certificates, etc.);
- power of attorney, if the declaration is carried out by an authorized person;
- package of company documents (statutory documents, tax registration certificate, certificate of entry into the Unified State Register of Data, statistical codes, certificate of open bank account).
If the declaration contains data that is not reflected in any of the listed documents, the list is supplemented with a document confirming this information. If there is no such document, employees are asked to authorize the release of goods and then provide the necessary papers.
Reference. Documentation that has been submitted previously does not need to be duplicated. It is enough to bring copies or a certificate stating that the documents were submitted.
When writing a declaration and submitting other documents in the language of one of the member countries of the Customs Union or in a foreign language, copies translated into Russian may be required.
Release of goods. Conditionally released goods
| Workshop | / For legal entities |
Release of goods is an action of the customs authority, as a result of which the interested person has the opportunity to use goods in accordance with the declared customs procedure or in compliance with the conditions that are established for certain groups of goods.
The release of goods is carried out by an official of the relevant customs authority by making marks in the customs declaration and (or) other accompanying documents (commercial, transport, etc.) and entering information into the customs information system.
To successfully release goods, the interested party must:
— submit all necessary documents to the customs authority; — comply with all requirements and conditions of legislation when placing goods under the customs procedure; — pay or provide a guarantee of payment of all customs duties and taxes.
To submit the necessary documents and information, the customs authority may grant a delay, but not more than 45 days. The basis for granting a deferment is a written reasoned request from the declarant. The use of goods for which documents have not been provided (a deferment has been received) is limited.
The customs authority has a number of grounds for refusing to grant permission to release goods until the relevant documents and information are submitted. Such grounds include:
— a direct ban on the release of these goods until documents and information are submitted; — the period of foreign trade activity of the declarant is less than 1 year; — within 1 year, the declarant was brought to administrative responsibility for failure to comply with restrictions and (or) prohibitions on the import of goods into the customs territory of the Russian Federation or export.
The declarant is informed of the refusal in writing, stating the reasons for the refusal.
The legislation of the Customs Union provides for different release periods for different groups of goods:
— Goods to which customs duties are assessed on a general basis must be released within 1 business day following the day of registration of the declaration. — The release of goods placed under the customs procedure of temporary import or export is carried out within 4 hours from the moment of registration of the declaration. If the declaration is registered less than 4 hours before the end of the customs office’s working day, the goods are released within 4 hours from the start of the next working day. — If the preliminary declaration procedure is applied to goods, they are released within 1 business day following the day the goods are presented to the customs authority.
The product release period may be extended, but not more than 10 working days, for:
— providing guarantees for payment of customs duties; — submitting relevant documents or submitting a written request to extend the deadline for submitting documents; — carrying out additional verification in order to classify goods in accordance with the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity; — conducting an additional inspection in order to control the customs value of goods before providing guarantees for payment of customs duties; — requesting additional information and documents if inconsistencies are identified in the information provided to the customs authority; — payment of additionally accrued customs duties in the presence of a written application from the declarant.
Extension of the release period is carried out with the written permission of the head or other authorized official of the customs authority.
When releasing goods of one batch, the declarant has the right not to export already released goods from the temporary storage warehouse, in respect of which the release conditions are met until the release of the last goods of this batch.
Release of goods before filing a customs declaration
The legislation of the Customs Union provides for the possibility of releasing goods before submitting a customs declaration. To do this, the interested person must provide:
— commercial documents with the necessary information (sender, recipient, country of departure, name, purpose, description, classification code according to the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity, at least 4 first digits, gross weight, quantity, cost); - an obligation, in writing, to submit a customs declaration and provide documents and information. The obligation must indicate information about the purposes of using the goods and the customs procedure under which they are placed; — documents and information on compliance with restrictions and prohibitions.
When releasing goods before submitting a customs declaration, all necessary documents and information must be submitted by the 10th day of the month following the month of release of the goods.
If the customs authority carries out an examination in order to verify the reliability of the information provided, conduct a study of samples or specimens of goods, their technical documentation, the release of goods is carried out before receiving the research results only if guarantees are provided for payment of customs duties (taking into account possible additional charges).
The release of goods in the event of a crime or administrative offense can be carried out only if the goods are not seized or confiscated.
Conditionally released goods
Goods may be released conditionally. Conditionally released goods are goods placed under the customs procedure of release for domestic consumption. They have foreign status and are limited in use.
Conditionally released goods include the following goods:
— in respect of which benefits are provided for the payment of customs duties related to restrictions on the use and (or) disposal of goods. These goods acquire the status of goods of the customs union with the removal of restrictions on use after the termination of the obligation to pay customs duties; — the relevant documents of which are presented after their release. The transfer of such goods to third parties is prohibited, and if import restrictions are imposed to check quality and safety, their use is prohibited. These goods acquire the status of goods of the customs union after submitting all necessary documents to the customs authority; — the rates of customs duties for which in a member country of the Customs Union are lower than the rates established by the Unified Tariff. The use of these goods is limited to the territory of a given state. Such goods acquire the status of goods of the Customs Union after payment of all customs duties calculated at the rates of the Unified Tariff; — components of goods that are imported over a certain period of time in separate batches, disassembled or unassembled. Transfer of these goods to third parties is prohibited. They are considered conditionally released until the customs authority makes a decision on their release. — placed under the customs procedures of duty-free trade, customs warehouse, processing for domestic consumption, processing in the customs territory, re-export, temporary import, customs transit, special customs procedures. These goods are considered conditionally released until they are actually destroyed, exported outside the Customs Union, rejected in favor of the state, or acquire the status of goods of the Customs Union.
To acquire the status of goods of the Customs Union, re-placement of conditionally released goods under the customs procedure of release for domestic consumption is not required.
In case of violation of the conditions for the release of goods, the customs authority has the right to refuse to release the goods. The refusal must be made in writing, indicating the reasons that served as the basis for this decision and recommendations for eliminating them.
When these violations are eliminated, the customs authority may continue to release the goods if:
— these violations are not grounds for initiating an administrative or criminal case; — the goods have not been seized or the goods have not been confiscated.
Additionally on the topic:
General provisions on customs declaration. Basic terms used. Declarant. Rights and obligations of the declarant
Need some advice?
Ready-made solution for your business from CustomsExpert Consulting
When using publication materials, an active hyperlink to https://customsexpert.ru is required.
| Tweet |
Disqus commenting system
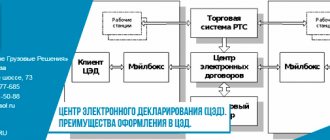
How to submit a customs declaration remotely
There are several options for filing a customs declaration in electronic format: through the portal of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation, using certified programs, through a customs broker.
The electronic method is strictly formalized. It requires a set of special hardware and software, so it cannot be called cheap.
To submit a declaration remotely, the operator needs the following:
- license to provide communication services;
- work permit with electronic signature;
- licenses issued by the FSB for services in the field of information encryption and maintenance of encryption devices;
- own subscriber points that meet information security requirements.
The declarant must certify all accompanying documents with a personal digital signature and send them to the operator filling out the declaration. After everything is sent:
- documents through the operator’s server enter the APS “Electronic Provision of Information” of the State Scientific Research Center of the Federal Customs Service of Russia, where the declarant’s access rights to the electronic declaration system and the reliability of the digital signature are checked;
- Through the channel of the departmental transport system of the customs authorities, the declaration enters the AIST RT-21 system (AIS “AIST-M”) of the customs post where the goods will be cleared.
Messages from the customs inspector travel back in the direction of the declarant (there may be several cycles).
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
Among the advantages of this method of cargo clearance:
- our country is approaching world standards - in most countries the “paper method” is almost no longer used;
- customs procedures accompanying the further release of goods are simplified;
- the foreign trade participant or his representative does not need to personally go to customs, but he retains control over the situation;
- contact between the post employee and the declarant is eliminated, at the same time the likelihood of corruption is reduced;
- the capacity of the border zone increases and trade turnover increases;
- the workload of customs officers is reduced;
- tax revenues flow into the state budget faster.
All documents for declaration must be scanned. Paper originals are stored for several years from the date of registration, which allows, if necessary, to restore all stages of the process and data if, for example, the electronic version is damaged or an investigation begins.
Note. For registration of goods under framework international contracts, the electronic format is the best. If in successive deliveries the nomenclature for imported products changes little, then a minimum amount of time is spent preparing documents for customs.
The disadvantages of the electronic system are minor:
- software glitches;
- restriction of access to the network for technical reasons;
- For constant conduct of foreign economic activity, a separate workplace and employee are required.