23.11.2016
In order for the customs export procedure to go through as quickly as possible, it is important to carry it out in full compliance with the requirements of the law.
.
When going through the procedure, it is important to take into account that exported goods are taxed differently, not as it should be for goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation. Usually, to export abroad, you only need to pay duties and excise taxes
.
In addition, before the inspection begins, customs clearance
.
Schematically, customs clearance includes the following stages:
- checking the submitted documents, which provide the grounds and conditions for removal of exported goods
for the territory of the state customs;
- payment of taxes, fees that must be paid before the cargo leaves the country
;
- verification by the customs authority of the exporter’s strict compliance with the legal requirements for exported goods;
- release of goods from customs territory to another state.
Features of export registration
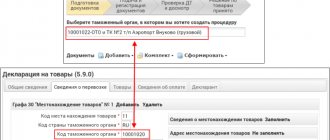
Registration at the customs point begins immediately after submission of the necessary documents (contract, data on the goods, certificates, information about the owner and purchaser). The exact list is formed depending on the product itself, its quantity, cost and many other characteristics. Next, fill out the customs declaration
.
This is a document drawn up in the form of an application, which contains exact data about the exported cargo and the vehicle
on which the goods will be delivered.
All these actions according to existing legislation are given 15 days.
, and the countdown begins from the moment the cargo is presented.
The customs declaration may be changed before it is fully processed
.
These changes are usually associated with clarification of cargo characteristics, supplier information and product certificates. Collection of accurate data is necessary for the correct preparation of a customs declaration
, because it is against this document that all excise taxes and duties will be calculated.
In turn, the size of all these payments
depends on many components. In most cases, only a customs broker can accurately determine whether changes to the declaration will be required or not.
Customs clearance of goods for export
Products that are exported from the territory of the Russian Federation irrevocably are subject to customs clearance of goods for export. Export products are registered with the Federal Customs Service in accordance with the Customs Code of the Customs Union. Customs clearance is impossible without paying duties and providing a certificate of origin. The event includes three mandatory stages:
- presentation of the cargo to the FCS control authorities;
- filing a customs declaration;
- making mandatory payments.
At the preliminary stage, the exporter or his legal representative - the broker notifies the Federal Customs Service of the arrival of the cargo in the control zone. Half an hour is allotted for this. In fact, product inspection is carried out at the request of FCS employees. Without their permission, the carrier has no right to leave cargo unattended, unload it, or move around the parking area. Customs clearance within the framework of export involves declaration. The declarant submits the TD in electronic form or on paper. The legality of the export is confirmed by the marks of the Federal Customs Service and the border customs authority. An important point is the payment of fees and duties. The basis for their calculation is the physical characteristics of the cargo consignment, and these are volume, weight and customs value.
Customs clearance procedure
All actions performed before customs clearance are called customs clearance
.
Usually this procedure is carried out by the exporter of the product
.
Clearance begins with the exporter informing the customs authority
that the cargo has crossed the post.
Next, the goods are placed in a customs warehouse, where they are controlled and placed under the customs export procedure. At this moment the declaration is also completed
.
As you can see, the customs procedure for exporting goods contains many nuances. Therefore, while going through all these stages, exporters may have various questions that they have not previously encountered. In order to avoid such problems, you need to contact a customs broker. Such a specialist knows everything about preparing the declaration and other documents.
for customs, and also understands all innovations in legislation.
In what cases is it appropriate to re-export goods?
It should be emphasized that re-export of goods can be carried out for various reasons. There is actual re-export of goods - this is when products are imported into the customs territory of a country for its use, but for some reason must be returned abroad. Accordingly, the actual re-export is the one that turned out to be such “in fact”, sometimes unexpectedly for the sender himself. And deliberate re-export is when the sender of the goods knows in advance that everything will be exported abroad again, and even during registration indicates this in the relevant documentation.
Based on the above, it becomes clear that in both cases, the re-export of goods is processed differently at the border. Re-export of goods carried out knowingly does not have VAT. It significantly reduces the cost of transporting goods. In this regard, this procedure is widely in demand among various enterprises that find their benefit in this customs procedure.
What rules are established by the customs authorities of a particular country also plays a significant role. The Russian Federation is no exception in this regard and sets its own deadlines, rules and requirements for goods subject to re-export. As already mentioned, goods for re-export can only be brought into the customs territory of our country for one year. Fees must be returned within six months.
Each country has its own rules and features of handling the customs regime for the re-export of goods. They are trying to get as much economic benefit as possible from it, but at the same time do it in such a way that the whole procedure is legal. In this regard, it is very important to accurately study the legislation of each country applicable to the re-export of goods, so that unexpected nuances do not become an obstacle to the implementation of a particular customs operation.
In the Russian Federation, re-export of goods is an independent customs regime that does not imply obligations for the participants to the customs authorities. The initiator of such relationships is often the importer, if the use of re-export of goods is more profitable and convenient for him than alternative options.
Today, the procedure for re-exporting goods is common due to economic sanctions.
Customs clearance of goods for export
Customs clearance of export goods or passing customs control consists of three stages.
First of all, the inspector checks the presence of all necessary documents, including checking the information specified by the declarant in the customs declaration.
After the inspector has checked all documents for compliance with their requirements, based on the results of such review, he may assign additional types of control. In particular, the cargo may:
- be partially or completely inspected with the opening of the packaging, up to the complete unloading of the container and the counting of all goods individually;
- undergo special instrumental control. For example, a container can be sent to undergo an IDC (inspection inspection complex), where the internal contents of cargo packages are examined using X-ray or infrared radiation;
- undergo control weighing;
- be subject to radiation or biochemical monitoring;
- be checked by dog handlers for the presence of drugs.
If in the process of these activities no comments are found on the part of the customs authorities, the inspector completes the work by issuing a declaration - puts his personal stamp on the customs order for the subsequent shipment of the goods to the destination.
The third stage includes full payment of not only the duties charged, but also other payments associated with the passage of cargo through inspection points for inspection, control, escort, sealing and storage.
Upon closer inspection...
Let us pay attention to such modes as export and re-export. The first implies that goods are exported from Russia without any obligations for re-import (Article 165 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 28 of Article 2 of the Federal Law on the Fundamentals of State Regulation of Foreign Trade Activities).
As for re-export, in this case previously imported goods must be exported back without paying import duties and taxes or with their return if they have been paid (Article 239 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In order for products to fall under the category of re-export, four conditions must be met (paragraph 1, paragraph 1, article 240 and article 242 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Firstly, on the day of crossing the customs border, the goods must already have defects or some discrepancies with the terms of the foreign economic transaction in terms of quantity, quality, description or packaging. For these reasons, they are returned to the supplier or another person specified by him.
Secondly, re-exported products must not have been used or repaired in our country (unless the use of the goods was necessary to detect defects or discrepancies resulting in return). Customs officers must be able to easily identify products placed under this regime. And finally, such goods must be exported from Russia no later than six months from the date of their importation.
For a number of entrepreneurs, re-export is convenient because if a manufacturing defect or other non-compliance with the terms of a foreign economic transaction that occurred at the time of import of goods is detected, the latter can be exported back after they have been released for free circulation.
Thus, the customs regimes for export and re-export are absolutely independent both in economic and legal senses. Therefore, the analogy of law, which is sometimes relied upon not only by firms, but also by judges, as well as its arbitrary application (see, for example, the decision of the Arbitration Court of St. Petersburg and the Leningrad Region dated March 5, 2008 in case No. A56- 3049/2008), is not applicable in this case.
So, from the above it is clear that when exporting, entrepreneurs pay all established duties and taxes, but when re-exporting, they do not. Hence the logical question: does a company that has used the re-export regime when importing goods subsequently have the right to claim VAT for deduction?
attention
Only goods that are in free circulation on the customs territory of Russia can be placed under the customs export regime, while the re-export customs regime applies only to foreign goods imported into our country.
How is the re-export of goods regulated?
One of the types of regulation of re-export of goods can be called currency control - measures that are taken to ensure that, by monitoring and controlling foreign exchange transactions, the economic, national and customs interests of one’s state are observed.
Currency control has strict regulations and a precise description of all its procedures, which the parties must obey. In essence, there are quite a lot of requirements, but the most significant of them are: the use of certain banks for foreign exchange transactions, restrictions on the export of capital, etc.
When re-exporting goods, it is also very important how the agreements or contracts between the parties are formed and what is included in them. It is necessary to consult an authorized bank, which has the right not to service a particular transaction if the registration standards are violated. This is done in order to avoid violations and reduce the number of unprofitable transactions with foreign partners.
Read the article: Customs declaration - registration procedure and pitfalls
VAT refund when re-exporting goods
Sometimes you can come across information according to which the re-export of goods, carried out due to the product’s non-compliance with the terms of the transaction, involves the return of funds spent within the framework of VAT. In reality, not every tax is refundable. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
There is a significant difference between such objects of taxation as the importation of goods into the customs territory and their sale. Accordingly, there are different VAT for each procedure. In this article we can only talk about the so-called “customs VAT”. As for VAT on sales, this is an area where the competence of tax services begins - this is a subject for a separate discussion.
It is possible to refund customs VAT, but for this it is necessary that the goods meet the requirements that the re-export procedure imposes on it. We have already addressed them several times, but we will present them again here: goods subject to re-export should not have been used or repaired until they were returned. In other words, if a product has deteriorated already during its use, then it will be impossible to place it under the re-export procedure. Accordingly, in this case, customs VAT cannot be returned.
As part of the procedure for re-exporting goods, VAT can only be returned by the customs authority that processed the goods upon import. It is impossible to receive compensation for your expenses at any other customs office. In other words, you cannot import goods in one city and in another demand the return of funds spent on VAT. If such an attempt is nevertheless made, then the only possible and expected result will be a refusal by the customs authority.
In order to return the funds spent on customs VAT of goods subject to re-export, it is necessary to draw up a corresponding application, as well as attach all the necessary documents, a list of which can be found in the second paragraph of Article 147 of the Federal Law “On Customs Regulation in the Russian Federation” dated November 27, 2010 No. 311-FZ. If this is neglected, the money will not be returned. In addition, any errors when registering the re-export of goods and drawing up an application will lead to loss of time. This is important to take into account, since, as already mentioned, re-export of goods is allowed only within a year after import. After this, you can only count on another procedure - export.
It should be borne in mind that the return of customs VAT is allowed within three years from the moment the goods subject to re-export were exported from the territory of the Russian Federation. Unfortunately, there is a widespread misconception that this period is only one year. This is outdated information. Until 2010, the Customs Code of the Russian Federation was in force, which indeed indicated precisely such terms, but this document has lost force, and now all customs procedures in our country operate on the basis of the Customs Code of the Customs Union.
Considering that VAT return is a rather complicated procedure, steps are being taken to finalize it. In particular, the government is developing a bill according to which it is proposed to introduce a zero rate on the re-export of goods that will be produced by foreign companies on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Read the article: International commercial contract: concept, types, structure