List of main accompanying documents for cargo transportation by road
When carrying out road freight transportation, documentation related to direct transportation is primarily used, and therefore it is considered the main one. This group covers the main points of organizing cargo transportation and includes documents:
- waybill. The document is used to monitor the driver’s performance, mileage and vehicle route. The waybill is prepared by the transport company and issued directly to the driver;
- waybill (waybill). This invoice is drawn up by the shipper, indicating in the form the name of the cargo, its unit of measurement, as well as the quantity in physical and monetary terms. The consignment note is a fundamental document, since it is what must be presented when checked by traffic police officers. In the absence of a specification form, the transported cargo may be arrested until all the circumstances of its transportation are clarified;
- agreement on the provision of transport and forwarding services. It is concluded between the shipper (consignee) and the transport company directly involved in this operation. The contract must be either original or a certified copy with the signature of the certifier and the seal of the organization.
Transportation process
Directly during the process of transporting cargo, the driver needs to issue a waybill with a tear-off coupon - a special element that is issued by the customer of the cargo and certified by his own seals. The form must be filled out, among other things, by a medical worker of the transport organization, a dispatcher and a technical employee who issues the driver’s permit. This is important in the event of losses on the side of the forwarder due to damage to the cargo.
In some cases, damage may occur due to the actions of the driver. In addition, since the waybill is proof not only of the transportation of cargo in fulfillment of the client’s order, but also proof of the consumption of fuel and lubricants, among the “pitfalls” we can note the obligation to fill out absolutely all details of the waybill, especially the “Route” column, in which you need to indicate exact address, otherwise, during an audit, tax authorities may consider expenses for fuel and lubricants to be unreasonable.
List of additional accompanying documents for cargo transportation
When organizing cargo transportation, documentation describing the cargo directly transported may also be required. This group includes:
- certificates or passports that specify the characteristics of the material assets being transported. These documents are attached regardless of what type of cargo is being moved;
- consignment note, which is similar to a consignment note, but it does not indicate the cost of the cargo being transported, but only its quantity;
- documents relating to sanitary and quarantine rules, if required by law;
- agreement between the shipper and the consignee (or a copy thereof);
- invoice for transported cargo.
The last two documents are not required to be included in the package of accompanying documentation, however, in many cases, companies also include them in order to avoid proceedings from traffic police inspectors.
Cargo acceptance
Upon acceptance of the cargo, the authorized person of the consignee signs the CTN and puts the necessary marks. This is an important part of the process, since in the future the possibility of filing claims against the consignee depends on the quality of filling out documents upon acceptance. An authorized person of the freight forwarding company (driver) informs the shipper that the cargo has been delivered or independently brings documents to the shipper’s company, and if there are no changes, then an act (based on the TTN data) and an invoice are generated.
To speed up the process, document flow is often carried out by exchanging copies via email or in a special electronic information system. Original documents are sent by Russian Post or express document delivery services. The shipper makes the payment, signs the document and sends it by mail to the freight forwarding company.
ATTENTION!
Tomorrow, Clerk will start training in an online training course to obtain a certificate that will be included in the state register. Course topic: management accounting .
- Duration 120 hours in 1 month
- Your ID in the Rosobrnadzor register (FIS FRDO)
- We issue a Certificate of Advanced Training
- The course complies with the professional standard “Accountant”
Increase your value as a specialist in the eyes of the director. View full program
Cooperation with a logistics company for the delivery of goods by road
When concluding a contract for cargo transportation, a logistics company undertakes obligations for high-quality and timely transportation of inventory items, and therefore only competent, qualified specialists should carry out this type of activity. Drivers carrying out transportation must have with them:
- driver's license as the main document confirming qualifications;
- a license for the transportation of special cargo, which is issued by the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation;
- vehicle passport for the car;
- MTPL insurance policy;
- the driver’s employment contract (or a copy thereof) if he is not the owner of the vehicle.
New rules for processing documents for sending goods
approved new rules for the preparation of documentation for registration of cargo delivery, in connection with innovations in the legislation of the Russian Federation: “On amendments to the Federal Law “On Countering Terrorism” FZ-374 dated 07/06/16
Legal entities must provide the following to process the shipment :
1) Information ABOUT THE SHIPPER:
For a representative of a legal entity:
- identification document of the person specified in the power of attorney.
- Power of attorney for sending from a legal entity with INN + OGRN. If the power of attorney does not contain TIN + OGRN, then a copy of the state registration certificate is required. legal registration faces
For gen. Director of a legal entity must provide a document confirming the position (appointment order, etc.), as well as an identity document.
2) Information ABOUT THE CONSIGNEE:
- For a legal entity, TIN/OGRN and name of organization
- For physical person's identity document details
3)TIN/OGRN and name of the Payer’s organization
Individuals must provide the following to complete the shipment :
1. Information ABOUT THE SHIPPER:
For a FL representative:
- identification document of the person specified in the power of attorney.
- Power of attorney for shipment from an individual with an attached copy of the shipper’s identity document.
For an individual, you must provide a document confirming your identity
2. Information ABOUT THE CONSIGNEE:
- For an individual, details of an identity document (Russian passport, driver’s license).
- For a legal entity, TIN/OGRN and name of the organization.
- For individual entrepreneurs you need both.
If this data is not available, you must instead provide a copy of the documents from the List of Possible Documents to be Provided.
- TIN/OGRN and name of the Payer’s organization
3. Information ABOUT THE PAYER:
- Details of the identity document (Russian passport).
! complete instructions for Legal entities, Individuals and individual entrepreneurs in the section Documents for cargo transportation, Contracts and requirements for the transportation of goods
Cooperation with professionals
Ochakovskaya Logistics Company provides services for the transportation of goods across the territory of the Russian Federation, offering favorable terms of cooperation. The company's specialists provide a full cycle of logistics services from detailed development of the route and preparation of the necessary accompanying documentation to transportation to the final destination. If necessary, the company provides modern warehouse facilities equipped with the latest equipment and meeting all requirements for the safe and secure storage of your goods.
The company is aimed at maximizing the needs of its customers, and therefore focuses on the nuances and details of cooperation, using all available resources.
What is useful to write down in the contract of carriage?
Contract for the carriage of goods: template
Subject of the agreement
The carrier transports the customer’s cargo for a fee - this is the subject of the contract under Art. 785 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Transportation details are written here in the item. But you can agree on time, transport, cargo and route in a separate document - the customer’s application. The application is made in writing or orally - as is customary in your organization.
Example:
The name of the cargo and its characteristics, the number of pieces, the weight of the cargo, the address of delivery of transport for loading and unloading, the consignee, the date and time of the start of loading, as well as all additional information necessary for the organization and implementation of transportation, are indicated by the Customer in an oral or written application to the Carrier's dispatcher .
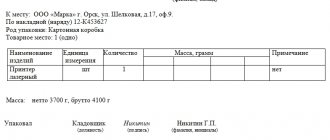
Waybill
When accepting the cargo, the carrier fills out a consignment note. This is necessary according to Art. 8 of the Motor Transport Charter.
Waybill form
The consignment note is made in two copies if the sender and recipient are the same person. If the cargo is sent to someone, three copies are made: to the driver, the sender and the recipient.
It is normal to accept cargo according to a receipt or a free-form consignment note. The main thing is to read the conditions of transportation.
Who loads and unloads
Loading and unloading is done by the person assigned to the contract. Write down this condition.
Example:
The carrier is obliged to organize the loading and unloading of cargo on his own.
Vehicle
The carrier's vehicle must be suitable for the customer's cargo. For example, a ton of milk will require a refrigerated truck.
Hence the rule is to focus on the customer’s cargo from the application.
If the transport is not suitable, the customer has the right to refuse. And the carrier will pay a fine. This follows from Art. 791 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Cargo packaging
The sender packs the cargo so that it is not damaged in transit and does not damage the truck. This is a requirement from Art. 10 of the Automobile Transport Charter.
The carrier is not responsible for poorly packed or completely unpacked cargo.
If packaging is an additional service of the carrier, this is written down in the contract. Then the carrier is responsible for the integrity of the cargo.
Example:
The Carrier provides the Customer with cargo packaging services additional to transportation at a cost of 100 rubles per box.
When during loading it is clear that the furniture is broken or the fruit is dented, this is recorded in the invoice. Without such a record, it is considered that the cargo was accepted in perfect order.
Delivery period
The time of arrival of the car and the period of transportation are written in the application and the waybill.
Without a deadline, the general rule from Art. 14 of the Motor Transport Charter:
- 10 days for transportation around the city and to the region,
- 30 days for delivery to another country.
The cargo is considered lost if the deadlines specified in the law or application have passed. The carrier pays compensation to the customer for the loss.
Price and payment term
The price for transportation and the payment term are written down in the contract. Additional services such as packing and lifting furniture to the floor are counted separately.
The carrier is obliged to have a price list and show it at the request of the customer. This is the requirement of clause 8 of the Rules for the carriage of goods.
Declared value of the cargo
At the request of the parties, the declared value of the cargo is recorded in the consignment note. The carrier will pay this amount if the cargo is lost. The price of transportation can be set depending on the declared value.
The declared value should not be higher than the actual value. This is stated in paragraph 12 of the Transportation Rules.
Carrier liability
The carrier is responsible for the safety of the cargo and timely delivery. The carrier's liability cannot be canceled in the contract. Such clauses will not work in court - Art. 37 of the Motor Transport Charter.
For disrupted transportation, the carrier pays 20% of the payment, for delays - 5%. These fines from Art. 34 of the Motor Transport Charter. But the contract can calculate the fine differently.
Customer's responsibility
The customer pays 20% of the payment if he changes his mind about going and 5% if he is late for loading. Fines from art. 35 of the Motor Transport Charter. You can write others in the contract.
Example:
For vehicle downtime during loading or unloading due to the fault of the Customer, the Customer pays the Carrier 100 rubles for each hour of downtime.