Entrepreneurs must label the remains of light industry goods and put them into circulation before May 1, 2021 . If you produce goods abroad or buy them for resale, they must be marked and the marking codes must be included in the customs declaration. Igor Petrashkevich, Edisoft project manager, tells the details.
Products that need to be labeled
The labeling of light industry goods is regulated by Government Decree No. 1956 of December 31, 2021. The codes in the resolution are listed in two classifiers. If your product falls into one of the categories, then it needs to be labeled.
| OKPD 2 | Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity |
| 14.11.10 — clothing made of genuine or composite leather; 14.14.13 - blouses, shirts and body shirts, knitted or knitted for women or girls; 14.13.21 - coats, raincoats, jackets, raincoats, raincoats with hoods, anoraks, windbreakers, windbreakers and similar textile products for men or boys, except knitted or knitted; 13.92.12 - bed sheets; 13.92.13 — table linen; 13.92.14 - Toilet and kitchen linen. | 6201 - coats, short coats and blousons, knitted by machine or hand knitting, for women or girls, windbreakers and similar products for men or boys; 6202 - coats, short coats, capes, raincoats, jackets (including ski jackets), windbreakers, windbreakers and similar products for women or girls; 6303 — bed linen, table linen, toilet and kitchen linen; 6106 — blouses, blouses and blouses, knitted by machine or hand knitting, for women or girls; 4203 10 000 - items of clothing and clothing accessories made of genuine leather or composition leather. |
If you are in doubt which category a product belongs to, refer to the EAEU Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity and (or) OKPD2, which are indicated in the documents confirming the conformity of the product ( declaration of conformity, certificate of conformity ).
The legislative framework
The list of light industry goods subject to mandatory labeling, with the corresponding codes, was approved in Government Order No. 792-r dated April 28, 2018 and Government Decree No. 1956 dated December 31, 2019. HS codes are:
- short - the first 4 digits indicate the product position;
- full - 10 digits, disclose the subheading.
Example. The manufacturer produces women's knitted blouses, blouses and blouses, using different types of yarn for their manufacture. In this case, he can indicate the short code - 6106 (it combines codes for products made of wool, linen, etc.). If the blouses are made only from cotton yarn, the manufacturer uses the full identifier - 6106100000.
We remind you that the amount of customs duty depends on the HS code. An incorrectly specified ID may result in administrative liability.
Do you want to get a turnkey solution for implementing labeling?
30% cheaper than the market due to remote implementation.
We will start working on the day you contact us! More details
How to label imported goods
Goods must be marked before crossing the border or at a customs warehouse. Procedure if you are doing this for the first time.
Step 1. Order marking codes from Honest Sign
Register with Honest Sign and submit a request for the production of marking codes. Indicate that the codes are needed for imported goods. To register in the ChZ you will need a CEP.
Step 2: Register with GS1 RUS
To order marking codes, you need to use the GTIN received by the importer (legal entity or individual entrepreneur registered in the Russian Federation) in GS1 RUS. Manufacturers with fewer than 100 SKUs can register for free. Annual fee - 3,000 rubles.
If an international manufacturing organization has an international GTIN, it can provide it for use in the Russian Federation.
To do this, the Russian importing company registered in the Czech Republic transfers the GTIN to GS1 RUS and describes the goods. Within 24 hours after the GTIN is published in GS1 RUS, it enters the ChZ system, and the importer can use it to order marking codes.
Step 3. Apply marking codes
The manufacturer or importer must apply the marking codes before crossing the border or at the customs warehouse. If you cannot apply the marking codes yourself, they can be given to the manufacturer or the person transporting the goods. It is important to understand that this is your responsibility, so you need to negotiate with them. One option is to send the marking codes in a PDF file. There the codes will be printed on a printer and applied to the packaging.
Foreign manufacturers can order codes themselves if they have a representative office or branch in Russia.
The rules for applying marking codes are regulated by Government Decree No. 1956. Be sure to read the document to avoid mistakes in applying the code - there are many nuances there. Basic Rules:
- The identification means is applied to the product, packaging, label or label in a manner that does not allow the identification means to separate.
- If you are selling a set of products, for example, a suit, then the code must be applied both to the packaging or label of the set and to the packaging of each product inside the set.
- If you are selling a set that cannot be disassembled, for example, a set of bed linen, just put the code on the package of the set.
- The code must not be printed on clear wrap film or other outer wrapping material or obscured by other information.
Step 4. Fill out the customs declaration
Customs clearance of goods is regulated by Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated May 20, 2010 N 257 “On the form of the declaration of goods and the procedure for filling it out.”
Step 5. Enter the codes into circulation
After the customs procedure for releasing goods for domestic consumption, you need to enter the codes into circulation before the goods are shipped. This is a mandatory condition in the traceability chain between participants in the turnover. Without putting it into circulation, the product is considered counterfeit.
Customs declaration procedures
The entire list of procedures is fixed at the legislative level. They are based on clauses of the EAEU Customs Code, decisions made by legislative bodies, federal laws of the Russian Federation and orders of the Federal Customs Union.
The declarant can choose one of 17 customs procedures:
- Release for internal consumption.
- Export.
- Customs transit.
- Temporary import (admission).
- Temporary removal.
- Processing in customs territory.
- Processing outside the customs territory.
- Processing for domestic consumption.
- Bonded warehouse.
- Free warehouse.
- Re-export.
- Re-import.
- Destruction.
- Refusal in favor of the state.
- Special customs procedure.
- Free trade.
- Free customs zone.
How to fill out a customs declaration
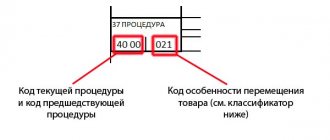
The rules for filling out a declaration for goods are regulated by the Federal Customs Service. The document must indicate the marking codes/identification code of the transport packaging. Find column 33 “Product code” in the Declaration and indicate:
— in the first subsection of the column: without spaces, a ten-digit product code in accordance with the Commodity Code of Foreign Economic Activity of the EAEU.
— in the second subsection:
- the letter “M” if the declared goods are included in the list of goods subject to labeling, but they are not subject to labeling requirements. What applies to such goods, read in Article 8 of the Agreement on the labeling of goods by means of identification in the EEC of February 2, 201;
- the letter “C” (free from the application of prohibitions and restrictions), if the declared goods according to the classification code of the EAEU Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity and (or) name are subject to in accordance with international treaties and acts constituting the law of the Union, and (or) the legislation of a member state of the Union, to the customs authority of which the DT is submitted, subject to the application of prohibitions and restrictions in the form of licensing when importing them into the customs territory of the Russian Federation, but in terms of their characteristics and (or) scope of application do not correspond to the goods in respect of which such measures are applied.
In the Republic of Kazakhstan, you must indicate the code for compliance with prohibitions and restrictions in accordance with the Republic’s classifier.
- the letter "P" for traceable goods;
- the letter “I” (intellectual property), if the declared goods contain objects or signs of intellectual property included in the customs register.
in the Kyrgyz Republic and the Russian Federation, when declaring goods of different names indicating one classification code of the EAEU Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity, the letter “O” is indicated;
If the declared goods simultaneously fall under several conditions, indicate the letters one by one without spaces.
— in the third subsection: indicate, without spaces, four code characters in accordance with the classifier of additional customs information used in the Union member states, if the specified classifier contains the EAEU HS code specified in the first subsection of the column.
If the goods fall under the Decision of the Board of the Eurasian Economic Commission dated June 4, 2021 No. 90 “On automatic licensing of imports of certain types of steel pipes”, in the third subsection the code designation must be indicated without spaces in accordance with Appendix No. 2 of the Decision.
Customs declaration authority
He is responsible for accepting documents for goods transported across the border.
Main functions:
- protection of state interests;
- control over the import and export of goods;
- preventing the import into Russian territory of goods that pose a threat to the population and the environment;
- preventing the export of products that are prohibited by law.
All goods that are imported or exported across the customs border of the EAEU (Eurasian Economic Union) must be declared.
Additional functions of the customs authority:
- collection of payments;
- control over compliance with tariff regulation requirements;
- fight against smuggling and counterfeit products.
Customs authorities are a single centralized mechanism. It includes in hierarchy:
- Federal Customs Service of Russia (federal executive body exercising control and supervision functions in the field of customs affairs);
- regional customs departments;
- customs;
- customs posts.
For the best performance of duties, our own infrastructure is created - office and warehouse premises, areas for cargo inspection, electronics and computer technology.
Customs authorities are usually located where goods cross the border:
- airport;
- sea port;
- railway station;
- cargo terminals for vehicles;
- temporary storage warehouses.
Customs authorities are located separately - customs posts, to which customs declarations are submitted in electronic form, the so-called. Electronic declaration centers.
Recommendations for filling out HS codes in the declaration
- Follow the rules for filling out the interpretation of the TN VED codes set out in the OPI TN VED according to the decision of the Council of the Eurasian Economic Commission dated July 16, 2012 N 54;
- Observe the terms when classifying goods in accordance with the decision of the Customs Union Commission dated January 28, 2011 No. 522;
- Follow the recommendations of the EAEU Board on clarifications to the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity;
- Determine the amount of customs duties in advance. You can receive a customs decision before importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation. The application can be submitted in person, by mail and through State Services. Payment of duty - 5,000 rubles. The decision can be appealed within 3 months in a higher customs authority or in an arbitration court, but you will have to pay a fee of 3,000 rubles for each appealed decision.
Features of customs declaration
- In order to prevent violations when declaring goods, customs control is carried out by customs authorities.
- Customs control allows you to identify instances of false information being submitted and prevent attempts to transport illegal goods.
- There is a list of prohibited and sanctioned products.
- Goods subject to excise duties are registered with a special excise authority.
- Cargo of historical or cultural value is cleared at the appropriate customs points.
- If violations of declaration standards are detected, administrative or criminal liability may be applied to the perpetrator.
Customs declaration procedure
There is a strict sequence of actions that the declarant or his official representative must follow:
- Drawing up the text of the declaration, filling it out and submitting it to the customs authority.
- Registration of a customs declaration with the customs authority or refusal of registration. After registering a customs declaration, all information specified in the customs declaration has legal significance.
- Conducting verification of the declared information after registration.
- The decision of the customs authority to issue a customs declaration. This decision may also be negative in the form of refusal to release in case of non-compliance with the conditions of the customs procedure.
Basic forms and types of customs declaration
According to legislative norms, there are three forms for filing a cargo declaration:
- oral - the person declares to the customs officer that he is not transporting goods that are suitable for mandatory written declaration;
- electronic – all information regarding customs declaration (declaration, documents for the consignment of goods and transport declaration) is submitted in electronic form;
- written – a person submits a written statement about the availability of goods that are required to be declared.
History of the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity
The Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity, or TN FEA for short, appeared in Russia back in 1988, after the Soviet Union joined the International Convention on the Harmonized System for Description and Coding of Goods.
The first publication of the HS was in 1990 and has undergone many changes since then. Thanks to this directory, each product imported into the Russian Federation receives a unique ten-digit code, which determines the rate of customs duty that will need to be paid to the state upon import.