Risk management is a part of the company management process, which is aimed at identifying and minimizing risks that threaten the functioning of the enterprise itself or the implementation of any project. The main task of risk management is to minimize risks that may prevent the project from being completed on time, within budget and with the required quality. As a rule, the risk management process should be harmoniously combined with and be part of the corporate strategy.
Risk minimization - actions aimed at reducing the likelihood of risk situations occurring, or actions that minimize business losses when solving situations that arise, which can be interpreted as an object of risk management. Risk minimization is most effective if measures have been taken in advance.
Risk management begins with identifying likely threats, both internal and external. Methods based on prediction and analysis are used to identify these threats. As a rule, a market analysis is carried out, an analysis of the existing market conditions, plans for the development of the company, and other factors are examined.
“You can only manage what you can measure,” said Peter Drucker, the father of American management philosophy.
Risk management in business today is a vital necessity, not a luxury. Saving a small amount to implement a risk management system can lead to either the collapse of the company or significant damage.
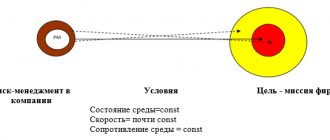
Corporate risk management system "Riskograph"
Find out more about the Riskograph risk management system:
1. Riskograph - early warning system.ppt 2. Enterprise risk management by the Security Service.pptx
Our unique development, the Riskograph system, is capable of visually sorting out all the risks of a business or project. It is a set of formal and informal methods (the main specialization of our company allows us to do this), used to identify risks, determine their significance, as well as methods for monitoring the level of risks.
Risk management and their minimization are today a priority direction for the management of an organization in the context of the influence of various circumstances on the company’s activities.
Who is this system for?
“Riscograph” is a universal tool that will be useful both to specialized departments of an enterprise (economic security service, risk management specialists) and to company managers who will be able to control and minimize their business risks. “Riscograph” is an indispensable tool for auditing risks in order to provide an objective picture of the company in the process of attracting investments and M&A transactions.
It is important that this mechanism emphasizes the need to reassess identified risks that systematically affect the activities of the enterprise. Overall, this progressive approach to risk management is critical to a comprehensive management process and ensures that risk indicators are processed effectively and at the appropriate level.
*SaaS - A form of cloud computing, a service model in which subscribers are provided with ready-made application software that is fully serviced by the provider.
Practical ways to reduce risks in Russian business
Managers of Russian companies offer the following ways to minimize risk, in particular to protect themselves in competition with unequal rivals - large international companies:
- Diversification, which provides room for maneuver, allowing you to rely on several businesses and invest from one to another.
- Specialization that allows you to concentrate resources for the development of your core business.
- Alliances with strong partners and investors.
- Search for new technologies for managing/doing business and reducing the cost of services (Alexey Panin, vice-president of Probusinessbank) Mergers creating one company from several companies that can withstand the giants (Rustam Tariko, head of the group)
- Investments in development (Rustam Tariko, head of the group).
- Development of the company, capturing a large market share, creating an extensive network of branches, stores, etc.
- Repurposing a business, finding a niche (Sergey Galitsky, wholesale and retail sale of consumer goods; reprofiling a business from distribution to catering, retail).
- Using your own advantages (knowledge of the Russian consumer, quick response to changing requirements - Dmitry Filatov, manager, food production, knowledge of the local market, quick response to changes - Oleg Tinkov head).
- Creating a strong brand (Yurat Safarov, PriceWaterHouse Coopers).
As an example of preventing the risk of loss of financial stability, one can cite the words of Igor Kovpak, director of ZAO Kirovsky Supermarket (Ekaterinburg), which unites more than twenty stores: “The daily turnover of our supermarket is more than 200 thousand dollars.
We have never used credit resources, although opening each store requires about a million rubles. We always find such working capital. I don’t want to become dependent on banks.” Although the fear of loans is a consequence of habit and lack of analytical information about the state of one’s own business. After all, if loan rates are acceptable (less than your own profitability), such borrowing will allow you to increase your turnover and return on your own capital. To share the risk (50%:50%) and use traditional financing schemes, the majority of Russian capital-intensive enterprises do not have stable turnover and credit histories, they do not have enough equity capital and property for collateral Pavel Udilov, General Director of the Polymer construction materials plant: “Investment loans it is necessary to give money for business, since enterprises have nothing to mortgage - it is difficult to sell a workshop, and the equipment is usually worn out.” There is a need for a qualitative business assessment methodology that determines the borrower’s solvency and lending risks.
According to Alexander Idrisov, senior partner, the Russian economy is in dire need of an effective system of risk financing. Financial investors - owners of risk capital usually invest in companies with growth potential and qualified managers, distinguished by business transparency, in order to sell shares at a higher price in 4-7 years.
The problems of venture financing in Russia are related to the fact that to ensure transparency, it is necessary to separate tax and financial reporting, and for a smooth exit from a business, a developed securities market, active investment funds, and a system of state guarantees for the repurchase of shares are required.
The most reliable remedy against the threat of financial insolvency, according to Stanislav Tsirlin, deputy director of the Moscow office of The Boston Consulting Group, for companies that have already reached a certain level of development is financing through corporatization. In this case, in addition to a favorable capital structure, the enterprise receives a reliable control mechanism. Shareholders control management, forcing them to weigh every step.
The risk of a decrease in liquidity due to the redistribution of spheres of influence in the Russian pharmaceutical market worries the Chairman of the Board of Directors of Apteka Holding, Mikhail Orlov. He is not happy about the ruin of large distributors - and Vita+, although his business is growing at their expense. “This is a real tragedy for the market,” says Orlov. “The main capital in pharmaceutical distribution is deferred payments provided by suppliers. Confidence has now been eroded, which will lead to a reduction in deferrals and a shortage of working capital.”
Debt restructuring is used to minimize risk in dealing with debt obligations, which primarily concerns debt to equipment suppliers. An example is the restructuring carried out by OJSC Rostelecom on an unrelated loan to Merrill Lynch for $100 million - the lender provided a deferment for several years, the restructuring of OJSC Elektrosvyaz of the Republic of Buryatia and OJSC Elektrosvyaz of the Kemerovo Region with, OJSC Elektrosvyaz of the Republic Karelia with Siemens AG, OJSC Elektrosvyaz of the Ulyanovsk region in front of Iskratel and others.
The “business portfolio” as a method of risk management was compiled, as research by McKmsey & Company shows, of the most successful fast-growing firms, based on the concept of three horizons. Under this program, the enterprise's business types were divided as follows. The first horizon includes a dedicated “business core” - the main source of profit expected in a short time.
The second horizon consists of activities that can provide positive results only in the medium term - most often in two to three years. Finally, at the stage of the third horizon there are starting activities, for example, newly created enterprises, branches, product lines. As a rule, they are characterized by negative cash flow values. The goal is to make maximum use of the core through an organic combination of the three horizons, promptly recognize medium-term threats, and support new business for long-term development.
An example of risk management can be found in the draft of Gazprom’s new financial strategy, prepared by Deputy Chairman of the Board Vitaly Savelyev. It proposes, based on James Van Horn’s model of achievable growth, to determine the maximum sales volume taking into account the corporation’s resources and market conditions (break-even management), and to expand activities, invest in projects with a profitability of at least 15% per annum (managing financial stability, using the effect of financial leverage ).
The most important tool for minimizing credit risk for banks in Russia in recent years has been control over the enterprise. Bank holding companies were created to serve a narrow group of privileged clients associated with their shareholders. For this model of bank development, the widespread practice of hiding real shareholders was used, when it is impossible to apply restrictions on lending to related borrowers and insiders. The consequence of the opaque ownership structure has been an atmosphere of mistrust, and recently competition among borrowers has been replaced by competition among lenders.
Business diversification, such as combining commerce and manufacturing, helped many Russian enterprises survive the financial crisis by reducing production and expanding commercial activities.
To limit the risk of debt financing (the risk of loss of financial stability) and attract owners, top managers of companies in conditions of instability in financial markets are ready to pay higher dividends to shareholders. Thus, by decision of the board of directors of the Southern Telecommunications Company (UTK), up to 80% of net profit is allocated for the payment of dividends.
According to analysts, this will cause a speculative increase in the value of Southern Telecom shares. Meanwhile, every dollar paid in dividends reduces the amount of retained earnings that could be invested in new assets and reduces the value of the firm. This reduction should be compensated by a new issue of shares. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate in many ways what is more profitable in each specific case: loans or equity capital, high dividends or accumulation of profits.
Dividing a business into several legal entities to optimize taxation, which is widely used by Russian entrepreneurs, on the other hand, is associated with the risk of reduced controllability. For example, a network of video equipment stores is divided into many legal entities - for each new store. Thus, the founder of the company solved the problem of finding funds to expand the business. But as the business grew, it became difficult to manage and now we are talking about switching to a different property management model.
According to the head of the investment company, Ruben Vardanyan, “for Western and Russian investment banks, the ideal structure of share capital is when 40% belongs to managers, and 60% belongs to financial investors. At the same time, no one should have more than 20% - this is the only way to maintain complete independence.”
Max Gutbroda (Baker & McKenzie company) warns about the risk of investing in the authorized capital of Russian companies: “The problem is that it is not always easy to determine profit and therefore you have to invest in those companies where control of purchase and sales prices is possible. In addition, the practice of compulsory exercise of the right to manage is insufficiently developed in Russia, and in the event of bankruptcy of an enterprise, the investor faces complete loss of rights due to imperfections in the bankruptcy mechanism.”
An example of conscious risk-taking from the story of an entrepreneur: “At a certain stage of development, having reached dizzying speeds, having increased the invested capital many times over, the business partners came into conflict about the development strategy. One of them wanted to stop there, the other insisted on further growth. A compromise could not be reached, and the risk-averse partner was forced to withdraw from the business, taking his share. The one who took the risk achieved the intended goal alone.”
An example of the risk of declining profitability when setting strategic objectives is the head of Siemens, Henrik van Pierer, who said that “areas of activity that do not cover their capital costs require review” so that, firstly, all unprofitable factories are closed; secondly, oblige top managers to revise planned targets; and thirdly, so that such a situation does not happen again in the future.
Henrik van Pierer's goal was to increase the group's return on equity by 15%. To do this, each division had to recoup annually on average at least 8.5% of its capital costs, which is equivalent to doubling the profit achieved in the previous period.
To prevent the risk of insolvency, Ms. Ruben Tatyana Aleksandrovna, Deputy General Director for Economics of the Minskvodokanal unitary enterprise, shares her experience, the first priority is operational control of cash flows. Her working day usually begins with checking receipts to the current account, from which regular regular payments are planned and the amount of available funds is determined to satisfy requests for financing received from department heads.
ATTENTION!
Tomorrow, Clerk will start training in an online training course to obtain a certificate that will be included in the state register. Course topic: management accounting .
- Duration 120 hours in 1 month
- Your ID in the Rosobrnadzor register (FIS FRDO)
- We issue a Certificate of Advanced Training
- The course complies with the professional standard “Accountant”
Increase your value as a specialist in the eyes of the director. View full program