All goods transported across the borders of the Russian Federation are subject to mandatory customs control. Impeccable execution of customs documentation is the key to fast delivery of a consignment of goods to the addressee and the absence of problems with customs authorities. The main rule of customs clearance is the provision of correct and reliable information about the cargo.
Due to the complexity of Russian legislation, its great detail, the influence of integration processes and frequent innovations, the preparation of customs documentation often causes difficulties for unprepared participants in foreign trade activities. The way out of this situation is to attract experienced “white” cargo carriers and customs brokers.
General overview
Customs tariffs regulate foreign economic activity and are designed to ensure the economic stability of the state, necessary for full and comprehensive development. The Russian Federation is a member of the EAEU - the Eurasian Economic Union - which determines the commonality of the trade zone and the principles on which the control system is built. The legal basis in this case is the Organization’s Code, as well as Federal Law No. 289, which establishes the provisions defining the procedure for carrying out commercial transactions between counterparties in different countries.
Essence of the system
The basic concept characterizing customs and tariff regulation of foreign economic activity (export and import) determines the methods and functions of state participation aimed at optimizing existing processes. The government, which has at its disposal a certain set of legislative mechanisms, exercises the right to impose duties that allow not only to extract additional budgetary profit, but also limit access to the domestic market for products from foreign manufacturers. The system also works in the opposite direction, reducing the volume of exported resources and goods, and eliminating the artificial creation of shortages to increase retail prices.
Main directions
The list of priorities determined within the framework of tariff regulation of foreign economic activity and foreign trade is annually formed and adjusted taking into account the interests of the budget and tax policy of the state. Taking into account the difficult situation associated with numerous restrictions of both a political and epidemiological nature, in recent years the key goal remains maintaining the competitiveness of domestic business projects, including those specializing in the production and sale of import-substituting products, as well as the effective organization of export supplies. It is important to take into account that an increase in duties ultimately affects the consumer burden, especially when it comes to goods that do not have local analogues comparable in quality characteristics.
Goals and functions
Customs tariffs are a method of state regulation of foreign economic activity, known since ancient times. The methods used allow us to solve two main problems: to protect national producers from foreign competitors who do not always use conscientious methods of promotion in the market, and also to increase the amount of budget funds subsequently spent on other priority purposes. Protectionist and fiscal functionality are implemented simultaneously, which helps maintain a balance in the representation of goods and the development of domestic business in certain industries.
Make customs payments using a special card from SEA BANK - a unique payment instrument that allows you to pay at any customs office.
Customs law regulates
- content of customs policy and customs affairs;
- organization of customs affairs; service in customs authorities and institutions;
- status of goods and vehicles moved across the customs border of the state;
- customs control procedure;
- declaration of goods;
- customs operations on sea and river transport;
- transportation, storage and disposal of goods that are located under customs control;
- entrepreneurial activity in the field of customs;
- concept and types of customs regimes;
- features of clearance and taxation of goods that are moved across the customs border;
- collection of duties on goods that are moved across the customs border of the country;
- customs benefits;
- inquiry and administrative-jurisdictional activities of customs authorities;
- liability for violation of customs rules;
- proceedings in cases of violation of customs rules.
Customs law interacts with various branches of law:
- Constitutional
in terms of the Constitution of the Russian Federation establishing the foundations of the economic and political organization of Russian society, etc. formation of the basic principles of customs law, both general legal and principles of a sectoral nature. - administrative
in the part that the activities of customs authorities mainly represent the executive and administrative activities of the executive authority; relations regulated by customs legal norms often arise against the will of one of the parties; For the most part, administrative or disciplinary measures are applied to the parties to customs legal relations for violation of their duties; Disputes between the parties are often resolved administratively. - criminal
in terms of regulation of social relations arising in connection with the commission of smuggling and other crimes in the field of customs affairs. - civil
and customs law manifests itself mainly in cases where the operation of civil law norms conflicts with the norms of customs law - financial
in terms of control over compliance with the country's currency legislation, with
tax
- in terms of replenishment of the federal budget through taxes and fees levied by customs authorities. - Criminal procedural
law is related to customs law in the issue of customs authorities performing the functions assigned to them as investigative bodies in cases of smuggling and other crimes in the field of customs affairs. - Civil procedural
law is applicable in the activities of customs authorities in cases, for example, of the collection of fines in court for violations of customs rules and other amounts of money payable. - The connection between customs and labor
law is manifested in the settlement of official relations in the process of Russian citizens serving in customs authorities and customs service organizations.
We provide the following types of legal services in the field of customs law:
- Protecting the client’s interests in court in cases of bringing to administrative liability for violation of customs rules.
- Appealing actions/inactivity/acts of customs authorities, in particular and in court.
- Assessment of the legality of customs actions aimed at prohibiting the release of goods, requirements for the submission of additional documents.
- Consulting the client regarding his actions in connection with adjusting the customs value.
- Drawing up a legal conclusion regarding comparatively preferential taxation when moving goods across the customs border;
- Preparation of rules of client conduct to prevent unjustified violations of administrative offense cases.
- Advising the client on legislation on currency regulation and customs control.
- Legal examination of all documents available to the client: foreign economic contracts, commercial and other documents, in order to minimize possible customs risks.
- Practical assistance in preparing sets of documents necessary for moving goods across the state border.
- Representation of the client's interests in the customs authority.
- Writing complaints, statements, requests and other legal documents to quickly resolve disputes with customs authorities.
- Representation of the client’s interests in all judicial authorities when considering customs disputes
- Providing assistance in the return of customs duties.
Our international trade experts provide advice and represent clients, taking into account key aspects of customs regulation.
Customs and tariff measures for regulating foreign trade
Any structure used within the framework of public administration is characterized by the presence of certain elements that are directly related to each other or interact autonomously. In this capacity, in relation to the system under consideration, include:
- Tariffs are the rates of duties charged by customs for imports or exports.
- Declaration is a set of requirements for design and characteristics.
- Customs procedure and nomenclature of foreign trade activities.
The globalization of the world economy necessitates the unification of such elements. The basis is the provisions of key international treaties, including the WTO agreement, the Convention on the Harmonized System, as well as other multilateral regulations designed to ensure the maintenance of a favorable trade regime in all countries.
Import and export
Customs clearance when importing and exporting commercial cargo has a number of subtleties and significant differences.
Unlike imports, goods sent for export have a number of benefits in customs taxation; their customs clearance is less bureaucratic. This is not surprising, since every state is interested in the success of its enterprises, and therefore encourages the export of goods.
Customs clearance for imports is carried out in several stages: the entire set of documents is provided and the basis for import is indicated, then taxes are paid in accordance with the classification of the goods. Difficulties are largely determined by the country from which the cargo is delivered. For example, for partnership with China there is a language barrier and the specifics of customs procedures on the Chinese side.
For importers and exporters, it is important to choose a cargo carrier and customs representative who act strictly within the law, guarantee the quality of the services provided and are able to provide qualified assistance at all stages of customs clearance. Errors during customs clearance can result in penalties, cargo delay, or even confiscation.
Types of customs regulation
The tariff formation process, as a rule, is complex and combines techniques that affect pricing both directly and indirectly.
In the first case, we are talking about direct government intervention related to the establishment of a certain level of fees that meets the profitability requirements of the industry in terms of attracting budget funds. Administrative management of this kind is relevant in situations characterized by general economic instability, as well as requiring local increases or decreases in prices. The main techniques include:
- Fixation of tariff rates, as well as markups and additional allowances.
- Determining the rate of return for certain categories of goods and services.
- Adjustment of declaration standards
Indirect customs and tariff regulation is a method of managing foreign trade activities, in which the emphasis is not on the duties themselves, but on related factors that have a direct impact on their final value. The implementation of such measures includes:
- Implementation of preferential lending and taxation projects.
- Providing subsidies and subsidies allocated from budget funds.
- Effective investment in potentially promising business segments.
It can be said that the policy of indirect intervention also involves the use of various techniques and means, the purpose of which is to increase market supply, increase the solvency of the population, as well as optimize tax rates on export and import products.
Customs and tariff regulation
Technically, the tariff is the main instrument of the state, the possibility of using which is enshrined in law, and represents a certain amount of duty that must be paid when crossing territorial borders. The size of duties is determined using the foreign economic activity nomenclature, which takes into account both sanctions and preferences, which makes it possible to build political relations with various countries. In addition, adjusting indicators helps normalize the situation in the domestic market, preventing excess or shortage of products, and helping to maintain adequate pricing, which is significant from the point of view of creating and maintaining consumer demand.
Corporate Visa Business cards from SEA BANK are a convenient means of organizing and controlling entertainment and travel expenses for company employees, which simplifies the work of the accounting department and the company, and also helps reduce the risks associated with the costs of cash collection and storage.
Non-tariff regulation
More radical methods, implemented through state permits, restrictions and prohibitions, designed to protect national producers from excessive flow of imports, as well as attempts to use unfair competition methods, including price dumping. They are also used to provide control functions regarding the export of products abroad, the priority of which for many organizations is determined by foreign exchange settlements. In addition, methods not directly related to determining rates help limit the import of low-quality goods that do not meet safety requirements and standards.
Subject of customs law
The subject of any branch of law is the range of social relations regulated by its norms. The subject of customs law is the complex social relations that arise in connection with the implementation of customs activities. Social relations related to customs activities and constituting the subject of customs law are called customs legal relations.
The main feature of customs relations is that: that they all arise in connection with the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border, its registration and control, as well as the payment of customs duties. Customs legal relations cover:
- organization of customs affairs;
- movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border of the Russian Federation;
- regulation of customs regimes;
- collection of customs duties;
- preliminary operations;
- customs clearance;
- customs control over goods and vehicles transported across the customs border of the Russian Federation;
- currency control;
- committing offenses (administrative and criminal) in the field of customs affairs;
- appeal and consideration of decisions, actions or inactions of the customs authorities of the Russian Federation and their officials;
- organization of civil service in customs authorities and performance by civil servants of the tasks and functions assigned to customs authorities.m
How does a duty differ from a tariff?
Definitions that, from the point of view of ordinary people, characterize one and the same phenomenon are in fact not identical in content. In the first case, we are talking about a certain fee that is levied on each product crossing the territorial borders of the state, regardless of the specific nature of the transportation - export, import or transit. This, at its core, is a fiscal tax instrument, regulated by legislative norms, and guaranteeing timely replenishment of the budget, the size of which is determined based on the expected volumes of trade turnover with various countries.
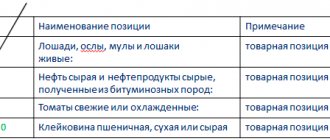
The customs tariff applied within the framework of foreign trade regulation is a register of commercial products to which duties are applied.
MARINE BANK provides a service for foreign economic activity, which implies preferential conversion, free registration of contracts, agreements, as well as free currency transfers.
We can say that the concepts actually complement each other, characterizing the interrelated elements of a single system. It should be taken into account that in different countries legal terminology allows for different interpretations, including those that are directly opposite to the meaning familiar to domestic entrepreneurs. Eliminate errors thanks to professional advice, organize competent foreign exchange control, and also get the opportunity to quickly complete financial settlements with foreign counterparties - all these are options available to clients of SEA BANK.
Specifics of import duties in the Russian Federation
Government regulation of foreign economic activity implemented in the Russian Federation provides for the division of duties into several levels. In particular, rates are differentiated for raw materials and for finished products, as well as semi-finished products that have undergone partial processing. In addition, the nature of origin and specificity of the goods are important. So, for example, food products, household appliances or clothing may be subject to an additional burden of thirty percent or more, while imports that are important to the population, be it medicines or baby food, are often completely exempt from duties in order to ensure an affordable retail price.
Apply for cash settlement services (SSC) at SEA BANK and receive up to 6% on your account balance.
Determining the fee amount
The functions of customs and tariff regulation of exports and imports in the Russian Federation are a complex set of methods, goals and objectives, largely determined by political and economic relationships with foreign partners. When identifying standard indicators, a lot of factors are taken into account, starting with status on the world stage and ending with participation in joint projects that are not directly related to trade.
Often, preferences are given to states classified as developing countries, including those that obviously do not have the ability to satisfy emerging debt obligations. This practice is aimed at building trusting relationships, and is also intended to accelerate the pace of stabilization and development of the local economy. Market analysis over the past decade shows that positive communication between countries, as a rule, significantly contributes to easing the conditions for conducting foreign economic activity.
Subjects of law
The subject of customs law is the one who is endowed with rights and responsibilities in the customs sphere. The subjects of customs law are:
- Customs;
- customs officials;
- legal entities;
- individuals;
These subjects can be divided into two groups: general and special subjects.
The concept of a special subject of customs law covers customs authorities and civil servants of customs authorities. Their specificity is determined by the competence of customs authorities established by customs law, which is characterized by the totality of tasks and functions assigned to them, as well as the scope of specific rights and obligations of a civil servant of a particular customs authority. The concept of general subjects of customs law covers: legal entities - enterprises, institutions and organizations; individuals entering into various legal relations with customs authorities; international organizations related to customs affairs.
The role of customs duties
In addition to the political aspect, the use of a regulatory mechanism that has a direct or indirect impact on trade requires a competent management approach. Many experts in the field of economics note that excessive enthusiasm for tariff adjustments leads to crisis situations when the domestic market reacts to outside interference that is unnatural for its development.
So, for example, an aggressive anti-dumping policy can cause a shortage of a certain category of goods, or a drop in their quality due to the virtual lack of competition - in both cases, the end result is an increase in retail prices that the mass consumer has to face.
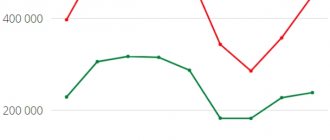
Maintaining statistics and commodity nomenclature of foreign trade activities
The Customs Code of the Russian Federation, within the framework of Articles 212-215, acts as the legal basis regulating the statistical approach to accounting for foreign trade activities. The objectives of the accounting policy are determined:
- Collection of general information about the current state of foreign economic activity necessary for making management decisions at the state level.
- Ensuring control over budget revenues in the form of taxes and duties.
- Controlling activities in relation to counterparties performing foreign exchange transactions.
- Formation of an analytical basis sufficient to assess the development potential and the existing balance of payments in the foreign trade of the Russian Federation.
Failure to comply with legislative norms regulating the maintenance of customs statistics is considered an offense that provides for the possibility of bringing the guilty entities to legal responsibility.
Basic data
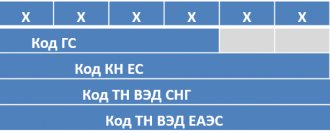
The information analyzed as part of the work with the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity includes information from documents submitted by participants in trading activities to the services responsible for processing and registering export and import supplies at customs. First of all, we are talking about the content of declarations drawn up and submitted in accordance with the provisions of Article 180 of the Code of the Customs Union.
Commodity nomenclature of foreign economic activity
Tariffs are essentially a derivative of the international Harmonized System used to describe and code goods. The provision formalized by the Convention, which came into force in 1988, provides for the obligation of all participating countries to publish open and understandable statistical analytics characterizing foreign trade indicators using publicly available codification.
Maintaining the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity is included in the list of functional tasks assigned to customs structures, which is confirmed by the provisions of Article 216 of the Code, which defines the following responsibilities:
- Timely tracking of changes and additions to the basic nomenclature, including clarifications and decisions approved at the international level.
- Bringing reporting in accordance with current requirements and subsequent publication of materials.
- Formation of own recommendations regarding interpretation, as well as implementation of other functions related to the maintenance of the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity.
Legal regulation of customs clearance
Compliance with legislation is a strict requirement for the implementation of foreign economic activity.
The basis of the Russian regulatory framework for regulating customs clearance issues is:
- Constitution of the Russian Federation;
- Federal laws of the Russian Federation;
- acts of the President and Government of the Russian Federation;
- regulatory legal acts of the Federal Customs Service and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- legal acts of transport departments.
In the conditions of the creation of the Customs Union and the formation of a single Eurasian economic space, the customs legislation of the Russian Federation is a multi-level system, including not only the standards of national legislation, but also:
- universal international treaties that define modern standards in the field of customs regulation - the Kyoto Convention, the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, etc.;
- documents issued within the CU, first of all, are the Customs Code of the Customs Union (CU CU), as well as agreements between the governments of the CU member countries on various issues, decisions of the CU commission and the Eurasian Economic Commission, etc.
Issues of customs clearance fall within the competence of the Federal Customs Service (FCS) and require excellent knowledge of the entire legislative framework. It should be emphasized that currently, on the territory of the Customs Union, which includes the Russian Federation, unified rules of customs regulation have been introduced, included in the Customs Code of the Customs Union.
Regulatory results
The use of mechanisms approved by the state at the legislative level makes it possible to stimulate the development of the domestic economy by replenishing the budget and helps create favorable market conditions for business. Direct and indirect methods that influence foreign trade processes create a competitive environment in which price and quality are the key criteria for consumer choice, and at the same time exclude the massive appearance on the market of cheap, low-quality goods that do not meet safety requirements.