Sooner or later, almost any entrepreneur whose activities are related to production or trade is faced with the need to import goods from abroad. And these are not only goods for sale, they can also be production equipment, raw materials and much more.
However, in order to correctly import goods into Russia, without making serious miscalculations, it is necessary to have a good understanding of the issue of foreign economic activity, be familiar with the provisions of the laws governing the import of goods into Russia, and take into account many other, no less important factors that can affect the success of the planned event. This article will be entirely devoted to the most important aspects of this type of activity.
What characterizes the import of goods to Russia?
The import of goods should be understood as a process characterized by the import into a country of products produced outside its borders (in another country) for the purpose of domestic consumption, subsequent sale of the imported goods or its re-import.
A company intending to expand its interests and engage in foreign economic activity always strives to think through the optimal scheme for importing goods to Russia, which will take into account its material benefits and, no less important, time costs.
However, importing goods into Russia is a rather complex procedure and is very different from similar activities, for example, in the European Union. Despite this, many European and American companies are showing genuine interest in the issue of importing their goods into the territory of Russia and the countries of the Customs Union.
The Russian Federation's accession to the World Trade Organization has had a positive impact on imports of products from foreign countries. In particular, there was a reduction in customs duties on many types of goods, which made the Russian market more attractive for foreign companies. But the customs control procedures themselves remain very confusing.
The procedure for importing imported products into Russia is regulated by the Customs and Tax Codes of the Russian Federation. All imported goods are subject to mandatory taxes: customs duties, excise duty, VAT (value added tax) and other types of customs duties are collected. The fees are paid by the importer (declarant) or the importer's authorized representative, whose authority is to represent the interests of the importer at the time the cargo crosses the border and is confirmed by relevant documents.
Read material on the topic: Parallel import: problems and prospects
Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity for cargo classification
At the customs clearance stage, it is very important to select the correct HS codes. This is not always easy, especially in the case of multifunctional products. Most often, it is impossible to do without the help of professionals. Depends on the product code:
- import features;
- VAT and customs duty rates;
- composition of the package of documents.
When determining the code, the technical description of the product provided to manufacturers is used; the presence of detailed information greatly facilitates the work and protects against errors, since some codes have restrictions related to phytosanitary control, embargoes, etc.
Import of goods to Russia in 2021 in numbers
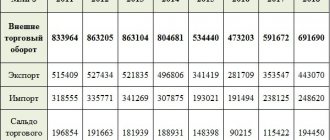
According to statistics provided by the customs service, imports of goods into Russia in 2015 for 10 months exceeded import volumes for the same period in 2021 (through October inclusive) by only 1%. Over the 10 months of 2021, goods worth a total of $131.5 billion were imported into Russia. This fact indicates a gradual recovery in import levels.
Hopes that the investment pause will soon end are supported by an increase in the number of machinery and equipment imported from abroad. This will only become possible if the rapid fall of the ruble can be avoided. However, the risk of a depreciation of the Russian currency remains along with a decline in exports, and the pace of this decline is still measured in double digits. The positive balance of the current account of the balance of payments also continues to decrease. All this could lead to a slowdown in already low growth rates.
The Ministry of Economic Development gives its forecasts for the growth of gross external product if current trends continue and based on the estimated oil price of $40 per barrel. According to the ministry, it will be only 0.6%. At the same time, World Bank forecasts are more optimistic - growth of 1.5% with an expected increase in oil prices to $55.2 per barrel.
According to preliminary information provided by the Federal Customs Service, in October 2021 alone, the volume of products imported from non-CIS countries increased by 8.4% compared to the same period in 2015 and reached $15.6 billion.
The volume of purchases of products from the engineering industry increased by 16.7%, the volume of purchased goods from the chemical industry increased by 1.4%, textiles and footwear also began to be purchased more actively (1.3%). It is the growth in imports of engineering products that can be considered a positive indicator for assessing foreign economic activity, since it constitutes an important part of investment in fixed capital. Imports of mechanical equipment (17.8%) and land transport equipment (11.5%) also increased.
Along with positive trends in the issue of imports, there are also negative processes that are a consequence of the Russian food embargo. In the same October 2021, the volume of imported food products decreased by 5.5%.
The most negative import indicators were for meat products and offal – 29.5%. The import of vegetables decreased by 28.3%, tobacco - by 21%. What stands out from the general negative statistics on food products is an increase in the volume of imported fish by 40.8% and a number of other food products.
Export and import of goods in Russia: ratio and trends
Let's consider the structure of exports and imports of goods in Russia and determine the main goods exported and imported by Russia.
The main part of Russian exports consists of:
- energy resources (oil and oil products, gas, coal);
- rolled steel;
- ferrous and non-ferrous metals;
- mineral.
The leading position in terms of export volume in this list belongs to oil and petroleum products – 300 million tons. Along with oil, Russia exports gas (250 billion cubic meters), timber, mineral fertilizers, machinery and equipment, weapons, meeting the needs of the CIS countries in these goods almost in full, which makes Russia the main trading partner for neighboring countries.
Imports to Russia consist of the following items:
- machinery and equipment;
- Vehicle;
- consumer goods;
- food;
- chemical products;
- consumer manufactured goods.
The main flow of imports comes from Germany, Italy, China, Turkey, Poland, Switzerland, Great Britain, USA, Finland.
December 2021 was marked by a decrease in the trade surplus of the Russian Federation to $9.2 billion. The Bank of Russia explains this state of affairs by the reduction in the difference between the cost of the total volume of exports and imports, which in turn was due to a decrease in prices for raw materials exported by the Russian Federation (such as crude oil, petroleum products, gas, mineral fertilizers, ferrous and non-ferrous metals) , and gradual restoration of the volume of imports (machinery, equipment, vehicles, chemical products, etc.).
However, according to the Central Bank, the reduction in the foreign trade surplus was somewhat offset by the fact that the negative balance of other current account items was reduced.
Why is the import of food products to Russia so in demand?
A major item in the total volume of imports is food imports of goods into Russia. Statistics confirm this data. At the moment, the volume of food imports in value terms is about $2 billion per month. September 2021 demonstrated import volumes worth $1.9 billion.
According to data provided by Rosstat, the share of sold imported food products in the total volume of retail sales of food products amounted to 27%. According to an analysis of data for June 2015, of the total volume of imported food products, 82% is imported from abroad, the remaining 18% comes from near abroad countries (CIS).
The Federal Customs Service reports that the volume of imports of food products from foreign countries in value terms as of December 2021 amounted to $16.44 billion and increased by 10.4% compared to November 2021.
There was an increase in the volume of the following imported food products: grain crops - by 1.9 times, vegetables - by 33.3%, meat and offal - by 21.6%, fruits and tobacco - by 17.7%, vegetable oil - by 16 .8%, dairy products – by 15.9%, fish – by 8.9%. At the same time, the volume of imports of sugar decreased by 21.3%, alcoholic and non-alcoholic products by 3.6%.
Compared to the same period in 2015 (December), the volume of imported goods from abroad increased by 10.9%.
Read the article: Import substitution in Russia as a method of stabilizing the economy
Why choose us
In the modern economy, choosing a reliable logistics partner is one of the key factors for the successful operation of a company. Especially when it comes to international trade. This was fully felt by our clients, who at one time made the right decision and turned to the IFT company.
Now our competencies help their business grow:
- Extensive business communications with manufacturers and carriers throughout Europe;
- Extensive experience in building effective logistics chains using all types of cargo transportation;
- Minimizing costs for servicing foreign trade transactions;
- Constant monitoring of changes in customs legislation - Russian and European;
- Ability to resolve controversial situations in favor of the client.
Each client receives a personal manager who provides information and consulting support, promptly responds to any changes and accompanies you throughout the entire life cycle of importing goods from Europe to Russia.
What documents need to be prepared to import goods to Russia
The rules for importing goods into Russia require the completion of a number of documents. To import, you will need the following.
- Constituent documents of the company purchasing the goods (copies thereof).
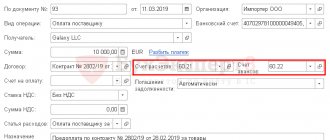
- The original of a correctly executed (according to the “Contract Requirements”) contract and two copies of it, which will bear the seal of the company purchasing the goods.
- Import transaction passport (copies certified by the bank; copies certified by the buyer).
- Accompanying documents related to the arrived cargo and an invoice, which will indicate the current details of the buyer and seller, the number assigned to the contract, the cost of the product, the essential terms of delivery (all of the above data must necessarily coincide with the similar data specified in the contract).
- Translated cargo invoice certified by the company seal.
- Documents confirming the company's license to conduct foreign trade, various certificates and other permits (if required).
- Payment order or any other document confirming payment of customs duties (original).
- Information (packing list) about packaging material, weight of products, number of pieces per intended shipment must be indicated for each item of goods.
- Other documents specified in the terms of delivery and contract. For example: bill of lading (if transport is carried out by sea); TIR, CMR (if road transport is carried out); documents confirming cargo insurance; documents confirming prepayment, etc.
- Documents confirming the customs value of products: transportation documents, documents confirming insurance (if specified in the terms of the contract), documents indicating transport costs, if they were not indicated in the invoice.
Customs may require the following additional documents:
- customs declaration of the sending country, certified by the seller;
- additional contracts concluded with persons related to the transaction;
- invoices for payments to third parties in favor of the seller;
- accounts relating to commissions, brokerage services and related to the goods being valued;
- payment accounting documents;
- licensing or copyright agreements;
- licenses for export/import;
- receipts from product storage warehouses;
- documents confirming the order for the delivery of goods;
- catalog, specification, price list from the manufacturer;
- calculations made by the manufacturer for the goods being valued (provided that the company agrees to provide such calculations to the buyer on the Russian side);
- payment and other documents related to conducting similar transactions or purchasing similar goods;
- other documents capable of confirming the value of the goods declared in the customs declaration.
If the goods, after crossing the border, are delivered to their destination on the territory of Russia, then the cost of delivery is deducted from the customs value. However, to carry out recalculation, clear documentary evidence is required that the goods were transported across the territory of Russia, and evidence of the legality of such deductions and their amount. These may be contracts for cargo delivery services, which will indicate the cost of delivery and method of payment, invoices indicating the details of the parties, documents confirming payment for delivery services according to the issued invoice.
Paragraph 1a of Article 19 of the Law “On Customs Tariffs” states that the cost of delivery includes the cost of transporting cargo, the cost of work associated with unloading and loading of goods, and the cost of cargo insurance. Accordingly, when considering the issue of reimbursement of customs value due to the cost of delivering cargo across Russia from the place where it was imported, each component of the delivery cost is considered separately, since the cost of transportation will depend on the distance, loading work will depend on the weight of the goods, and insurance will from the cost of the product itself.
Explanatory materials are provided for a specific product:
booklets, samples, technical description of the product, drawings, etc. Copies of these documents must be certified by the seal of the company purchasing the goods.
Control over accounting of imported goods
When accounting for import transactions, it is important to avoid mistakes and the following points must be taken into account:
- converting currency on the date of filing the DT at the Central Bank exchange rate;
- reflection in accounting of VAT (paid during customs clearance);
- correct translation of documentation into two languages: buyer and importer;
- correct correspondence of invoices.
Proper accounting without errors depends on the experience of the accountant himself.
To successfully cooperate with Chinese suppliers, it is recommended to study in advance all the information about transaction requirements and necessary documentation for long-term cooperation without disputes, claims and litigation.
What is the scheme for importing goods into Russia?
You can import goods to Russia yourself, having thoroughly studied the current legislation. But if there is a big deal ahead and it is necessary to reduce possible risks to zero, it is worth involving an intermediary in the import procedure. As a rule, this is an organization that narrowly specializes in processing transactions related to the import of goods to Russia.
There are two most common import options.
The first scheme for importing goods into Russia is used for residents of the Russian Federation.
It is convenient for companies that need to purchase goods abroad, but do not plan to become participants in foreign economic activity. To do this, these organizations resort to the services of an intermediary company, reducing possible risks associated with the import of goods and avoiding the payment of additional taxes in Russia. Foreign exchange transactions (if there is a need for them) are carried out by an intermediary, so the customer does not have to open his own foreign currency account; for transactions with an intermediary, an existing ruble account will be sufficient.
Scheme participants:
- a resident (Russian company) planning to purchase goods abroad and at the same time wanting to protect themselves from perceived risks that may arise, for example, during the customs clearance of imported cargo;
- an intermediary (importing company) that undertakes customs clearance of goods arriving in Russia and sells the imported cargo to a resident;
- supplier (foreign seller of goods and most likely sender of cargo).
Advantages of the scheme:
- currency control and customs authorities do not check the resident when importing goods into Russia and after their release into free circulation;
- there is no need to take part in every accompanying procedure:
- – registration of the organization with customs authorities;
– execution and registration of a foreign trade contract;
– opening a transaction passport at the bank;
– control of storage periods in temporary storage warehouses.
At the same time, the resident has in his hands all documented reports on transactions and expenses performed.
The intermediary assumes full responsibility for violations when declaring the import of goods into Russia, that is, administrative penalties are applied to him if violations are discovered in the transaction. The owner in this case is the buyer. However, using the services of a customs broker will not be enough to avoid administrative liability. For false declaration of goods imported into Russia, both the customs broker and the importer of goods will be punished.
No one can guarantee absolute accuracy when declaring goods. If the counterparty adds a gift to the product or exceeds the ordered volumes of goods, you may find yourself held administratively liable for a violation.
Read the article: Customs declaration - registration procedure and pitfalls
This scheme for importing goods into Russia is relevant for companies included in the customs register (duty-free stores, customs carriers, customs warehouses, etc.), because it is unacceptable for them to have administrative violations prescribed in the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
To implement the scheme, the intermediary and the resident can enter into a commission agreement or a purchase and sale agreement. On behalf of the intermediary, on behalf of the resident, a foreign trade contract is concluded with the supplier for the import of goods and services into Russia. If necessary, an advance payment for the goods is made, this is done by the intermediary. The goods are then delivered to the address specified by the intermediary, who then clears the cargo through customs.
The second import scheme to Russia is used for non-residents
(foreign persons). As a rule, it is used in companies that are manufacturers, forwarders, carriers, or any other foreign companies interested in exporting their products. This option is used when a customer in Russia wants to buy goods but does not want to deal with importation, customs clearance, or participate in foreign currency transactions.
Scheme participants:
- non-resident (foreign organization);
- an importing company (recipient of the cargo), registered in Russia, engaged in customs clearance of cargo in Russia and selling goods produced by a foreign company;
- a client (buyer) who is registered on the territory of the Russian Federation and wants to buy goods in Japan, Sweden, Great Britain, Canada or any other country, but he does not want to deal with customs clearance of cargo and be under currency control by inspection officials.
The customer selects a product and then turns to an intermediary for help to import the selected items to Russia. The intermediary takes care of all organizational issues:
- concluding an agreement with the customer, making an advance payment by the customer on the basis of the concluded agreement;
- concluding a foreign trade agreement with a non-resident;
- purchase of goods abroad and import into Russia;
- customs clearance of goods;
- payment of state duty and VAT;
- sale of goods to the customer.
Advantages of the scheme:
The customer relieves himself of all risks, because the advance payment is made by the Russian company, and there are no problems associated with customs clearance of imported goods into Russia.
Settlements with customs
At the time of filing the customs declaration, a certain amount of security for customs payments must already be in the accounts of the customs service. Ideally, it should fully correspond to the final amount of calculations according to the HS codes. However, ideal situations practically never happen; discrepancies between preliminary calculations and final ones are found everywhere, so experts recommend depositing more money to fully cover customs duties. The difference will then be returned to the importer.
Customs clearance of goods can be carried out both at the border and within the country at the customs post. If at the border, the goods declaration must be submitted immediately. To cross the border and deliver to the internal customs post at the border, it is necessary to provide a transit declaration, on the basis of which the cargo receives customs status and is sent to the internal post, where it undergoes customs clearance and release.
For delivery to the internal border post, a strictly established period is allocated, the countdown of which begins when the transit declaration is submitted. Control is carried out by the Federal Customs Service. If for some reason there is a delay on the way, customs officers will search for the cargo. Upon arrival at the place, a declaration is submitted, after which customs transit is considered closed. The delivered goods end up either in the customs control zone or in a temporary storage warehouse if the declaration for the goods was not submitted on time or the cargo is planned to be subjected to customs inspection.
After processing the documents and checking the cargo, customs clearance is completed. Further, the goods can freely circulate within the country, the importer can dispose of them as he sees fit. However, interaction with customs does not always end there. There is a post-control procedure, during which the declaration is checked again after some time. Typically, HS codes, payment amounts, and the reliability of cost data are subject to verification. The customs service has the right to initiate an inspection within 3 years from the date of release of the goods, and in some cases even after 5 years. Therefore, documents for customs cleared goods must be kept throughout this entire period.
What are the features of importing goods from Kazakhstan to Russia?
Import of goods to Russia is subject to VAT (subclause 4 of clause 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). All importing companies are required to pay VAT on imports, including VAT-exempt companies and individual entrepreneurs operating under a special regime.
Import of goods to Russia is not subject to VAT in certain cases established by law (Article 150 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The VAT rate on goods imported into Russia is 10% or 18%. Sales of some goods may be subject to domestic VAT at a rate of 18%, in which case imports of goods into Russia are paid at the same rate.
When importing goods to Russia from Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan or Kyrgyzstan, companies and individual entrepreneurs transfer VAT not to the accounts of customs services, but to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration. In addition, you must submit a correctly completed declaration.
To calculate the VAT amount, use the following formula:
Import VAT amount = tax base x VAT rate,
where the tax base = the customs value of goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation + the amount of import customs duty + the amount of excise tax.
According to paragraph 13 of Appendix No. 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union, signed in Astana on May 29, 2014, the tax base is determined on the date of registration of imported goods.
In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 7, 2010 No. 69n, the import VAT declaration when importing goods into Russia from the EAEU countries must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service by the 20th day of the month following the month of import of goods.
If the average number of company employees for the year preceding the filing of the declaration exceeded 100 people, the VAT declaration when importing goods into Russia from the EAEU countries must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service via telecommunication channels in electronic form.
If the average number of company employees does not exceed 100 people, the declaration can be submitted on paper.
VAT when importing goods into Russia from EAEU countries must be paid no later than the deadline for submitting the relevant declaration.
Import VAT
calculated in accordance with Article 160 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. When paying for the services of a foreign counterparty, the client in certain cases is obliged to pay VAT to the budget as a tax agent. This happens if the place of sale of the services provided is recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation (Article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the income of the service seller will be less by the amount of VAT.
VAT on imported services is transferred to KBK 182 1 03 01000 01 1000 110 simultaneously with the transfer of money to a foreign counterparty. In field 101 of the payment order you must indicate “2”.
Based on the results of the quarter during which the agency VAT was withheld, it is necessary to report to the Federal Tax Service no later than the 25th day of the month following this quarter. Please note that according to the Order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] as amended. Order of the Federal Tax Service dated December 20, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] starting from reporting for the first quarter of 2021, it is necessary to submit a declaration in a modified form.
When paying domestic VAT after imported goods are registered and paid to the budget, payers can deduct import VAT. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, import VAT is accepted for deduction in accordance with documents confirming the payment of this tax.
Companies with a special regime and those that are exempt from the obligations of VAT payers include import VAT in the cost of goods and services received.
Briefly about foreign economic activity
At the initial stage of working with foreign suppliers, the importer must have a clear understanding of the goals and objectives.
You should pay maximum attention to the choice of goods, agree on the cost with the supplier or manufacturer. The deal must be profitable, and this must be clear even before the contract is concluded. When the documents are signed, the participants will be forced to fulfill their obligations, for example:
- responsibility for currency circulation;
- compliance with prohibitions and restrictions established by law;
- acceptance of shipped goods, etc.
The cost of goods transported across the border constitutes the main part of the customs value, which is also the basis for calculating all customs duties.