Illegal movement across the customs border
We have made processing for the automatic generation of a statistical form in the context of counterparties and contracts based on already entered Sales documents (acts, invoices).
The system number is specified manually—starting from this number, the statistical form number will be generated.
Goods and vehicles transported across the customs border of the Republic of Kazakhstan are subject to customs clearance in the manner and under the conditions provided for by the customs legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Import of such vehicles without payment of customs duties, taxes and security of payment is possible only on the terms of temporary import for persons permanently residing in the Republic of Belarus or the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Let us remind you that Form 1-TS is submitted by legal entities and (or) their structural and separate divisions, individual entrepreneurs, as well as individuals exporting and (or) importing with member states of the Eurasian Economic Union.
Exemption from VAT in respect of goods imported as part of the project “Modernization of the thermal power plant of the city of Bishkek” in accordance with the credit agreement for a preferential purchase loan between the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic and the Export-Import Bank of the People's Republic of China dated September 11, 2013.
A similar punishment awaits violators for attempting to smuggle goods secretly, using hiding places or other tricks, for example, cover goods. Providing false information or invalid or counterfeit documents to customs inspectors is a serious violation punishable by a fine.
Customs declaration of goods for personal use is carried out using a passenger customs declaration. At the same time, the acceptance and registration of the passenger customs declaration is carried out by the customs authority free of charge.
Currently, full members of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) are Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia and Kyrgyzstan.
Submit a statistical form in this case according to the Rules, the person who entered into the transaction, or who at the time of export had the right to dispose of (possess) the goods (clause 5 of the Rules).
Other documents, including notarized ones, issued by the owner (holder) of funds, containing details of the body (organization) and confirming the origin of cash and monetary instruments.
Without paying customs duties and taxes, you can import goods for personal use by road, rail, water transport or on foot, the cost of which does not exceed 200 euros and (or) weighing no more than 31 kg.
Goods included in the List of Exemptions for which customs duties are paid at reduced WTO rates are subject to circulation only in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan and are prohibited for export to member states of the EAEU.
Features of filling out the ESF for goods from the List of Exemptions
The article is not relevant!
Current article - PRO features of filling out the ESF for goods included in the List of Exemptions
The article examines the features of filling out electronic invoices for goods included in the List of Withdrawals.
List of withdrawals
- these are goods for which the import rate under the terms of the World Trade Organization (hereinafter referred to as the WTO) is lower than customs duties within the framework of the Common Customs Tariff of the Eurasian Economic Union (hereinafter referred to as the EAEU).
After joining the WTO, Kazakhstan is obliged to exclude the export of goods to the territory of other countries that were imported at reduced WTO customs rates.
Electronic invoices (hereinafter referred to as EIF) have become a tool for monitoring such goods.
The rules for filling out the ESF were approved by the Order of the Minister of Finance of the Republic of Kazakhstan “On approval of the Rules for document flow of invoices issued in electronic form” dated February 09, 2015.
Let's consider the features of filling out the ESF when selling goods included in the List of Withdrawals.
In the Supplier Details
in line
12 Additional information
, data is filled in indicating at what rates the goods were imported into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan (hereinafter referred to as the RK), or the goods were produced on the territory of the RK.
This line is filled in when selling goods included in the List: imported into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan, produced on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan, as well as when exporting such goods from the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan to the territory of other member countries of the EAEU in connection with the transfer within one legal entity.
The line indicates the following designations:
- ETT
— when selling goods from the List that were imported into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan from third countries at EAEU ETT rates;
- WTO
— when selling goods from the List that were imported into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan from third countries at reduced rates;
- TS
— when selling goods from the List that are imported into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan from EAEU member states;
- ST-1
— when selling goods from the List that are produced on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
In the Recipient details
, line
20 Additional information
indicates the letter code of the EAEU member state into whose territory the goods included in the List are exported.
The line is filled in for goods included in the List when they are exported from the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan to the territory of the EAEU member states if such goods were imported into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The line is also filled in when exporting goods from the List that were produced on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan, or when exporting in connection with a transfer within one legal entity.
The line indicates:
- ARM
— when exporting goods to the Republic of Armenia;
- BLR
— when exporting goods to the Republic of Belarus;
- KGZ
— when exporting goods to the Kyrgyz Republic;
- RUS
— when exporting goods to the Russian Federation.
When transferring goods included in the List, within one legal entity, in line 21 Category of recipient
a mark is made in column
F - non-resident
.
Also, when transferring goods within one legal entity, line 28 Destination
, which indicates the administrative-territorial unit of the EAEU member state to which the goods are supplied.
This line must be filled in when transferring goods within one legal entity, as well as when otherwise exporting goods included in the List from the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan to the territory of the EAEU.
When filling out this line, you must be guided by classifiers and other data on the administrative-territorial division of the state into whose territory the goods are exported.
When selling goods included in the List to individuals for cash, the ESF is issued at the end of the day in aggregate for all such transactions.
The electronic invoice is filled out as follows:
- in line 18 Recipient
- the words
individuals
; - in line 19 Location address
— the words
retail trade
; - in line 21
in cell
F
- a check mark is set.
Filling out the tabular part of the section Data on goods, works, services
for goods from the List also has some features.
In the column Product Code (HS)
the code of the commodity nomenclature of foreign economic activity is indicated in accordance with the classifier of the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity of the Customs Union. In this case, the code by which the goods were imported into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan is indicated.
The Classification of Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity was approved by a decision of the Council of the Eurasian Economic Commission dated July 16, 2012.
This column is filled in in the following cases:
- sales of goods previously imported into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
- sales of goods included in the List, provided that when purchasing this product, an ESF was received, which indicates the HS code and the product has not undergone significant changes;
- when exporting goods included in the List to the territory of the EAEU member states in connection with the transfer within one legal entity.
Column No. of the application within the Customs Union or the Declaration of Goods
information about the sources of origin of goods is indicated.
The column is filled in as follows:
- When selling goods imported from EAEU member states, indicate the number of the application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes;
Homogeneous imported goods according to different registration numbers of applications for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes are indicated in separate lines
- When selling previously imported goods (including those included in the List), exporting goods included in the List within the same legal entity, the number of the goods declaration is indicated;
The declaration number is indicated if, when purchasing a product included in the List, the supplier who imported such a product indicates the declaration data in the issued ESF and the product is sold in an unchanged condition.
- When selling goods produced on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan included in the List and when transferring such goods within one legal entity, the number of the certificate of origin of the goods is indicated.
In the Additional data
the serial number of the goods from the List indicated in line
32
of the goods declaration is indicated.
The column is filled in in the following cases:
- When selling goods included in the List, previously imported into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
- When selling goods included in the List, if the goods were purchased on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan and upon purchase an ESF was received containing the serial number of the goods declaration (provided that the goods are sold in an unchanged condition);
- When exporting goods included in the List within one legal entity.
In the Additional Information
the registration number of the ESF received from the supplier of goods included in the List upon their purchase is indicated.
The line is filled in when selling goods included in the List, if they have not changed their properties and characteristics, as well as when exporting goods from the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan within one legal entity.
Places of movement across the customs border
From January 10, 2016, the Federal Customs Service of Russia began to perform the functions of the authorized body responsible for maintaining statistics regarding products moved within the framework of trade with the EAEU countries (previously, Rosstat was the authorized body). The obligation to submit a “statistical form” on trade with the EAEU countries to the customs authorities is stated in the Law on Customs Regulation in the Russian Federation (Article 278 of the Law of 03.08.2018 N 289-FZ (ZoTR). Who is obliged to provide - a Russian person who:
- has concluded a transaction or on whose behalf (on behalf of) a transaction has been concluded, according to which goods are imported into the Russian Federation from the territories of the Union member states or exported from the Russian Federation to the territory of the Union member states,
- and in the absence of such a transaction, a Russian person who, at the time of receipt (for import) or shipment (for export) of goods, had the right to own, use and (or) dispose of goods, is required to submit to the customs authority a statistical form for recording the movement of goods, filled out in his personal account participant in foreign economic activity.
Very often, customs has a different opinion than that chosen by the declarant and makes its own classification decision. At the same time, the amount of customs duties required for payment may not be at all what the foreign trade participant expected. To resolve such disagreements, you have to contact a higher customs authority or court, the outcome of which does not always end in favor of the declarant.
The first additional line and the second additional line in the “Amount” column indicate the paid and deferred payment amount, respectively, indicating the “IP” and “OP” codes in the “SP” column, respectively.
For foreign trade participants it is very important to determine the product code correctly! An error in determining the HS code can result in a serious problem, the solution of which will require a lot of effort and resources.
The additional line in the “Amount” column indicates the amount of payment payable when placing the declared goods under the customs procedure of release for domestic consumption, minus the payment amounts paid for partial conditional exemption from customs duties and taxes.
An actively developing company, CDB, has been a leader in the field of training and information support for accountants since 2000.
The issuance of a PTS (vehicle passport) for an imported vehicle from the Republic of Belarus or the Republic of Kazakhstan is carried out after establishing their status for customs purposes and the need to carry out customs operations. The Rostov branch of RTU is a structural subdivision of the State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education RTU and is part of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation. The branch was founded on June 30, 1995.
Processing is completed for all export sales (VAT rate 0%) for which the buyer’s country of registration is: Belarus (code 112) Kazakhstan (code 398) Armenia (code 051) Kyrgyzstan (code 417) If you do not have enough data somewhere for filling, the program will highlight the problematic lines.
In three Russian regions - Orenburg, Smolensk and Ivanovo regions, special economic zones will be created, which will be an additional incentive for the development of the territories.
Approve the classifier of locations of goods (Appendix 24) with a date of entry into force of April 1, 2014.
Features and risks of foreign economic activity with EAEU countries
According to clause 5 of the Protocol, 180 calendar days are allotted for collecting documentation to confirm the right to apply the zero rate, which is counted from the date of shipment of the goods. If the documentation package is not collected within this period, the transaction will be subject to VAT according to the general rule, i.e. at a rate of 20% or 10% based on the results of the tax period in which the shipment occurred. Note that in this case the tax is paid with penalties accrued from the 181st day after shipment (resolutions of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 16, 2006 No. 15326/05 and dated March 11, 2008 No. 15079/07 in case No. A56-7714/2006) .
Thus, you have 180 calendar days from the date of shipment of goods to confirm your right to the benefit. The list of documents that confirm this right is contained in clause 4 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU (clause 5 of this Protocol, clause 1.3 of Article 165, clause 12 of Article 198 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 13. 2018 N 03-07-13/1/81506, dated 12/02/2015 N 03-07-06/70447). For example, such a document is an agreement (contract), on the basis of which the shipment was made. The buyer under this agreement can also be a person who is not a taxpayer of the EAEU country. The main thing is that the consignee is located in this country. Supporting documents also include: shipping, transport or other documents confirming the movement of goods to the territory of the EAEU country from the territory of the Russian Federation.
It is important to take into account that if for certain types of movement of goods (including movements without the use of vehicles) the preparation of such documentation is not provided for by the law of the EAEU member country, then these documents are not provided to confirm the right to apply the 0% rate.
When moving goods and transport between EAEU states, customs inspection may not be carried out. In practice, tax authorities often require that border control passes at automobile border checkpoints be presented as proof of entitlement to a 0% rate. How legitimate is this demand? Clause 4 of the Protocol refers to other documentation provided for by the legislation of the participating country from whose territory the goods were exported, which, along with transport and shipping documents, can confirm the movement of goods. At the place of departure, on the front side of the exit control coupon, the official puts down the date and time of the end of customs control, and also signs, certifies the entry with an LNP stamp and hands the coupon to the carrier for border control (clause 59 of the instructions on the actions of customs officials, approved. Order of the Federal Customs Service of Russia dated May 26, 2011 No. 1067). Consequently, a border control pass can also be used to confirm the zero VAT rate for exports to the EAEU states, and requiring this document does not contradict clause 4 of the Protocol. Difficulties with documentation confirming border crossing may also arise for entrepreneurs sending goods through delivery services (DHL, Fedex, UPS, etc.) or by regular mail. To answer the question about supporting documents in this case, we turn to the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 6, 2004 No. 1200/4. In it, under “other documents” for the purposes of applying the VAT rate of 0%, we mean documents equivalent to transport and shipping documents in their content and including information about the method of delivery and the route of the goods, taking into account the type of transportation or characteristics of the cargo (for example, luggage and postal receipts, list of wagons transported in one waybill, documents for transportation of items by special communications service, etc.). The third document confirming the right to apply a zero rate, according to the Protocol, is an application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes with a mark from the tax authority of the EAEU member country into whose territory the goods were imported, regarding the payment of indirect taxes (exemption or other procedure for fulfilling tax obligations). The form of this application is presented in another international act - the Protocol of December 11, 2009 “On the exchange of information in electronic form between the tax authorities of the EAEU member states on the paid amounts of indirect taxes.”
Finally, the Protocol indicates a bank statement as a document required to confirm the right to a benefit. There is a caveat here. An extract is required unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the EAEU member country. Russian exporters can use the rules of paragraph 1 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which does not require such an extract.
In total, the set of supporting documents for export to the EAEU countries contains only two mandatory items: an agreement (contract) and an application. If the movement of goods across the border is recorded by another document, this document is also included in the “confirmation package”. Submit the documents to your tax office along with declarations in which you reflect export transactions (clause 4 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU).
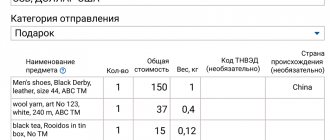
Filling out labeling codes (KIZ) of goods in statistical forms
Exemption from VAT in respect of raw materials and (or) materials included in a vehicle produced in the territory of a free warehouse and sold by the owner of a free warehouse in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan under a public procurement agreement concluded before November 1, 2021. Cras sit amet nibh libero , in gravida NULla. NULla vel metus scelerisque ante sollicitudin commodo. Cras purus odio, vestibulum in vulputate at, tempus viverra turpis.
If the established standards are exceeded, customs duties will be required at a rate of 15% of the cost, but not less than 2 euros per kilogram of weight in terms of excess of cost and/or weight standards.
In accordance with paragraph 10 of the Protocol, the absence of a shipping document is grounds for the carrier to refuse to accept the relevant goods for transportation.
TC TC - latest changes and laws
All goods crossing the customs border of the Russian Federation are assigned a ten-digit HS code; this code is written in the international consignment note (CMR) that comes along with the cargo.
Note! Spaces are not allowed before and after the number (a space is considered an additional character) and the letter “C” must be Russian.
You can transport funds without customs clearance if their amount does not exceed the equivalent of 10,000 US dollars. Our company’s specialists provide customs clearance services for goods and cargo transported by individuals in all customs offices of Russia: at airports, ports, railway stations, automobile temporary storage warehouses, and in warehouses of express carriers.
The column indicates, without spaces, the quantity of goods, information about which is indicated in column 31 of the DT, in an additional unit of measurement, if, in accordance with the Commodity Code of Foreign Economic Activity of the Customs Union, an additional unit of measurement is applied to the declared goods.
Now the customs authorities of the Russian Federation use the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity of the Customs Union (CU), which includes Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan. The Unified Customs Tariff (UCT) of the customs union is a classifier of goods approved by the heads of the three states on November 27, 2009 and put into effect on January 1, 2010. The HS codes strictly adhere to the principles of unambiguous assignment of goods to one or another group.
In particular, new columns have been introduced (for example, column 19 “Additional information”, column 20 “Declaration for goods”), and the requirements for information that must be indicated in the statistical form have been expanded.
We remind you that, according to Article 19.7.13 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, failure to submit or untimely submission to the customs authorities of a statistical form for recording the movement of goods, as well as the submission of false information, entails punishment in the form of an administrative fine. In 2021 changes were made to the procedure for filling out the Statistical Form for Registration of Goods, information about documents related to transported goods, and the deadlines for submitting the form to the customs authorities.
ON THE NEW YEAR'S TIME WE BROUGHT POWDERED MILK.
If there is not enough space in the DT columns to state information or to put official marks by an official, then the information and official marks for which there is not enough space are indicated on the reverse side of the DT or on additionally attached A4 sheets, which are an integral part of the DT (hereinafter referred to as the supplement ). At the same time, in the corresponding column of the DT the following entries are made: “SM.
The column indicates in kilograms the “gross” mass of the goods, information about which is indicated in column 31 of the goods declaration.
Note: in cases where an agreement (contract) is concluded in a foreign currency, and payment is made in the national currency of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the code of the nature of the transaction is indicated for the foreign currency.
Benefits for the payment of import customs duties within the framework of the project “Construction of the 500 kV power transmission line “Datka-Kemin” and the 500 kV substation “Kemin”, applied until December 31, 2015, in accordance with the preferential loan agreement between the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic and the Export by the Import Bank of the People's Republic of China dated June 5, 2012.
In the case of individuals moving goods for personal use, the difficulties in determining certain rules are due to the fact that they are contained in several legal acts of both the Eurasian Economic Union and the Russian Federation. Moreover, there are many regulations that complement the main one.
Our team has extensive practical experience and is constantly increasing and improving its efficiency. It is important to understand that the final decision to accept or not accept the goods code according to the Commodity Classification of Foreign Economic Activity that you have selected always remains with the customs authorities.
Chapter 23. Features of the movement of goods for personal use
Goods for personal use can be transported across the customs border in accompanied or unaccompanied baggage, as goods delivered by a carrier, as well as in international mail.
Non-tariff and technical regulation measures are not applied to goods for personal use transported across the customs border.
Customs operations in relation to goods for personal use are carried out depending on the methods of movement at the places of arrival at the customs territory of the customs union or departure from this territory, or at the customs authority of a member state of the customs union, on the territory of which an individual with permanent (or temporary) residence the right to act as a declarant of such goods.
When moving goods for personal use by individuals on motor vehicles for personal use or on a train, customs authorities provide these persons with the opportunity to carry out customs operations without leaving such vehicles, except in cases where this is necessary to comply with the customs legislation of the Customs Union.
At the request of a person moving goods for personal use, customs operations may be carried out in relation to such goods related to their placement for temporary storage, placement under customs procedures, as well as removal from the customs territory of the Customs Union if they did not leave the place of arrival.
Customs declaration of goods for personal use is carried out by individuals when moving across the customs border simultaneously with the presentation of goods to the customs authority.
The following are subject to customs declaration in writing:
1) goods for personal use, transported in unaccompanied baggage or delivered by the carrier to an individual;
2) goods for personal use, transported by any means, subject to prohibitions and restrictions, except for non-tariff and technical regulation measures;
3) goods for personal use, transported by any means, including temporarily imported, the cost and quantity of which exceeds the norms for the movement of such goods with exemption from customs duties, established by an international treaty of the member states of the customs union;
4) vehicles for personal use, transported by any means, with the exception of vehicles for personal use, registered on the territory of the member states of the customs union, temporarily exported from the customs territory of the customs union and imported back into such territory;
5) the currency of the member states of the customs union, securities and currency values, traveler's checks in cases established by law or an international treaty of the member states of the customs union;
6) cultural values;
7) goods for personal use imported in accompanied luggage, if the individual transporting them has unaccompanied luggage;
 other goods determined by the customs legislation of the Customs Union.
other goods determined by the customs legislation of the Customs Union.
Customs declaration of goods for personal use is made in writing using a passenger customs declaration.
An individual has the right, at his own discretion, to make a customs declaration of goods for personal use that are not subject to customs declaration in writing, using a passenger customs declaration.
Customs declaration of goods for personal use of an individual under sixteen years of age is carried out by the person accompanying him (one of the parents, adoptive parent, guardian or trustee of this person, another person accompanying him or a representative of the carrier in the absence of accompanying persons, and in case of organized departure (entry) ) a group of minors unaccompanied by parents, adoptive parents, guardians or trustees, other persons - by the group leader or a representative of the carrier).
The submission of a passenger customs declaration must be accompanied by the submission to the customs authority of documents confirming the information stated in it.
Such documents include:
1) identity documents (including of a minor);
2) documents confirming the adoption, guardianship or trusteeship of a minor;
3) documents confirming the value of the declared goods for personal use;
4) transport (shipping) documents;
5) documents confirming the right to benefits for the payment of customs duties, including confirming the temporary import (export) by an individual of goods for personal use, as well as confirming the recognition of an individual as a refugee, forced migrant or moving to a permanent place of residence in the manner prescribed by law member states of the customs union;
6) documents confirming compliance with restrictions, except for non-tariff and technical regulation measures;
7) documents containing information allowing to identify a vehicle for personal use;
 documents confirming the right to own, use or dispose of a vehicle for personal use;
documents confirming the right to own, use or dispose of a vehicle for personal use;
9) other documents and information, the presentation of which is provided in accordance with the customs legislation of the Customs Union.
When declaring goods for personal use, transported in unaccompanied luggage, a copy of the passenger customs declaration issued by the customs authority and issued to an individual when crossing the customs border is additionally presented.
If such a passenger customs declaration is not submitted due to its loss or for other reasons, goods imported in unaccompanied luggage for personal use are considered as imported in excess of the cost, quantity and weight standards for the import of goods exempt from customs duties, unless an individual proves otherwise.
At the points of arrival at the customs territory of the customs union or departure from this territory, a double corridor system may be used for the purposes of customs declaration of goods for personal use.
The use of a double corridor system provides for the independent choice by an individual traveling across the customs border of a customs declaration in writing of goods for personal use and the corresponding corridor (“green” or “red”) for carrying out customs operations.
Foreign individuals have the right to temporarily import into the customs territory of the Customs Union goods for personal use, the list of which is determined by an international agreement of the member states of the Customs Union, with the exception of vehicles, with an exemption from customs duties for the period of their stay in this territory.
If temporarily imported goods for personal use are subject to customs declaration in writing, the period for temporary import of such goods is established by the customs authority based on the application of a foreign individual, taking into account the duration of his stay in the customs territory of the customs union.
Foreign individuals have the right to temporarily import into the customs territory of the Customs Union vehicles for personal use, registered in the territory of foreign states, for the period of their temporary stay, but not more than one year, with exemption from customs duties.
Upon a reasoned request from a foreign individual, the period for temporary import of vehicles for personal use may be extended by customs authorities within one year from the date of temporary import of such vehicles.
Transfer of the right to use or dispose of temporarily imported goods for personal use, including vehicles, to another person in the customs territory of the Customs Union is permitted subject to their customs declaration and payment of customs duties in the manner established by the customs legislation of the Customs Union.
Temporarily imported goods for personal use can be exported back from the customs territory of the Customs Union through any customs authority.
If temporarily imported goods for personal use are located in the customs territory of the Customs Union due to non-exportation after the expiration of the established period, customs duties and taxes are levied on such goods in the manner established by the customs legislation of the Customs Union.
In the event of irretrievable loss of temporarily imported goods for personal use due to an accident or force majeure, the return export of such goods from the customs territory of the Customs Union may not be carried out provided that the customs authorities recognize the fact of the accident or force majeure.
Individuals of member states of the customs union have the right to temporarily export goods for personal use from the customs territory of the customs union for the duration of their temporary stay in the territory of a foreign state and import them back with exemption from customs duties and taxes.
At the request of an individual, the customs authority identifies temporarily exported goods for personal use, if such identification will facilitate their re-import with exemption from import customs duties and taxes. The identification of goods is indicated in the passenger customs declaration, one copy of which is issued to the individual exporting the goods.
The absence of such identification does not prevent individuals from re-importing goods for personal use with exemption from import customs duties and taxes, provided that the customs authority confirms that these goods are being imported back after temporary export from the customs territory of the Customs Union in the manner determined by the customs legislation of the Customs Union .
With temporarily exported vehicles for personal use, it is allowed to carry out maintenance or repair operations required while they are outside the customs territory of the Customs Union.
When repairing a temporarily exported vehicle for personal use associated with replacing parts of the vehicle that are subject to accounting (registration) with the relevant authorized state bodies, the replaced part is subject to customs declaration, except in cases of warranty repairs or maintenance in accordance with the terms of an agreement concluded in accordance with with the civil legislation of the member states of the customs union, or carrying out repairs necessary to restore a vehicle for personal use after it was damaged due to an accident or force majeure.