Greetings, dear readers of the Tyulyagin project! In this article we will briefly consider such a concept as “ Third World"or also the well-known formulation "Third World countries". You will learn about what this expression means, as well as which countries are usually called third world countries, and what other classifications of least developed countries there are in this article.
What is the third world?
" Third World " or "third world countries" is an outdated and pejorative expression that has historically been used to describe a class of economically developing countries. This is part of a four-part segmentation that has been used to describe the world's economies by economic status. The Third World lags behind the First World and Second World, but is ahead of the Fourth World, although Fourth World countries are rarely singled out. Today, the preferred terminology is "developing country", "underdeveloped country" or "low- and middle-income country".
World Bank (WB)
Includes the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, the International Development Association. As well as a number of investment and financial structures.
Helps overcome humanitarian disasters and supports respect for human rights. Participates in medical support for crisis regions and environmental programs.
Provides investment loans, including long-term and interest-free. The distribution of grants is practiced on a large scale.
Works with developing, poorest countries. Even with hopeless debtors. Provides consulting assistance. Generates well-being ratings.
Charity does not bring benefits. Losses are covered by the sponsoring states.
Definition of developing countries of the world
There are several ways to divide the world for the purposes of economic segmentation. Classifying countries into First, Second, Third and Fourth World countries was a concept created during and after the Cold War, which lasted from roughly 1945 to the 1990s. Although sometimes this term is still used today by inertia.
In general, countries are usually characterized by economic status and key economic indicators such as gross domestic product (GDP), GDP growth rate, GDP per capita, employment growth and unemployment rate. In developing countries, low production rates and poor labor market characteristics are usually combined with relatively low levels of education, poor infrastructure, inadequate sanitation, limited access to health care, and a lower cost of living.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank are closely monitoring developing countries as they seek to provide global assistance for projects that help comprehensively improve infrastructure and economic systems. Both organizations refer to these countries as lower-middle-income or low-income countries.
Developing countries may be a target for many investors seeking to identify potentially high returns from possible growth opportunities, although the risks in such markets are also relatively higher. While developing countries are usually characterized as economically poorer, innovation and industrial breakthroughs can lead to significant improvements in a short period of time.
Place in the world economy
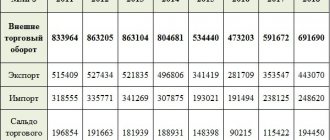
- They supply raw materials and fuel to Western European countries and the USA.
- Industrial products that are exported to the world market account for 21.4%.
- The share in exports is 30%.
- Dependence on TNCs. Large companies do not agree to work here, but open branches and headquarters. As a result, about 25% of all foreign investments of multinational companies are located in developing countries.
- Large revenues from private companies, whose loans and investments reach 50% of all external sources of financing. Loans are provided by corporations, foundations, individuals, and private entrepreneurs.
The characteristic features of the economic development of developing countries are:
- The predominance of the agricultural sector in the economy.
- A large share of the population's employment is in agriculture, which is dominated by a patriarchal structure.
- Low level of industry development. There is ferrous metallurgy in developing countries, but its part is insignificant.
- Multistructure of the economy: forms of production vary from small-scale and communal to cooperative and monopolistic. The connections between them and the ways of life are minimal and undeveloped.
- In different spheres of the economy there is private capital, represented in various forms and types.
- The development of capitalism has the so-called character of enclaves, since the invested funds belong to companies - branches of TNCs that have “entered” these countries. The capitalist system prevents the elimination of the multistructure of the economy, promoting its expansion.
Oil reserves in countries of the world
Thus, the level of lag behind industrially developed countries is enormous.
There is an interdependence between diversity and the social structure of society. Constant trends such as unemployment, poverty, demographic overpopulation, low living standards are the lot of developing countries.
History of the development of classifications of countries of the world
The classification of countries as "First World" or "Third World" arose during and after the Cold War. The First World countries were known as the most industrialized countries whose views aligned with the North Atlantic Treaty Organization and capitalism.
Second world countries supported communism and the Soviet Union. Most of these countries were previously controlled by the Soviet Union. Many East Asian countries also fall into the “second world” category.
Third World countries included countries in Asia and Africa that were not affiliated with either the United States or the Soviet Union. Now, partly because the Soviet Union no longer exists, the definition of Third World is outdated and considered offensive.
Alfred Sauvy coined the term "Third World"
Alfred Sauvy, a French demographer, anthropologist and historian, is credited with coining the term "Third World" during the Cold War. Sauvy observed a group of countries, many former colonies, that did not share the ideological views of Western capitalism or Soviet socialism. “Three worlds, one planet,” wrote Sauvy in a 1952 article published in L'Observateur.
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
Specializes in providing short- and medium-term loans only to the least successful countries to overcome balance of payments problems. Recommendations are developed in advance, compliance with which is mandatory in order to receive a loan.
Declares assistance to poor member states for integration into international trade. Trains economists. Carries out global statistical monitoring.
Periodically receives unflattering characteristics due to its alleged desire to suppress the sovereignty of debtor countries. Because of controversial advice.
Modern division of the world
These days, most countries on Earth fall into one of three general categories, which some call developed, emerging, and frontier (or frontier) markets. The global segments have shifted somewhat to match these categories as a whole.
Developed countries are the most industrialized with the strongest economic characteristics. Developing countries are classified as such because they demonstrate significant progress in various areas of economic growth, although their performance is not as stable. Border markets are often very similar to the old Third World classification and often show the lowest economic performance.
Organization for European Cooperation and Development (OECD)
A community that includes the leading countries of the world.
Developing countries are not included in the list. With the exception of Mexico and Turkey.
In addition to North Americans, it unites most of the states of the European Union and the eastern “giants”: Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, Australia, New Zealand and Israel, which is atypical for a map of the Middle East.
A stable economy is not enough to join the OECD. Legal institutions, anti-corruption reputation, and compliance with tax laws are important. Non-aggressive policies and global trade relations play a decisive role.
Russia and China are not allowed there. Too ambitious strategies and lack of transparency within.
List of frontier markets
The development of global segments has become historical and outdated. Thus, one of the barometers for evaluating the list of developing countries is the MSCI Frontier Markets Index. This index includes the following countries:
- Croatia
- Estonia
- Lithuania
- Kazakhstan
- Romania
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- Kenya
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Nigeria
- Tunisia
- WAEMU (West African Economic and Monetary Union)
- Bahrain
- Jordan
- Kuwait
- Lebanon
- Oman
- Bangladesh
- Sri Lanka
- Vietnam
Definition
The United Nations Statistics Division, in its data on differences between developed and developing countries, notes that the designations “developed” and developing “are intended for statistical convenience and do not necessarily express a judgment about the stage reached in a particular country or area in the development process.
Countries in the following regions are considered developing for these purposes:
- Africa
- America excluding North America
- Caribs
- Central America
- South America
- Asia excluding Japan
- Oceania excluding Australia and New Zealand
The UN also notes that, There is no established convention on the designation of “developed” and “developing” countries or areas within the United Nations system. In common practice, Japan in Asia, Canada and the United States in North America, Australia and New Zealand, Oceania, and Europe are considered "developed" regions and areas. The area is also considered as developed regions and in Israel as a developed country, also the countries emerging from the former Yugoslavia are considered as developing countries and the countries of Eastern Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States in Europe are not included within either the developed or developing regions.
Other classifications of developing countries
The World Trade Organization (WTO) provides a slightly different classification. The WTO divides countries into two classes: developing and least developed. There are no criteria for these classifications, so countries are nominated themselves, although the statuses may be challenged by other countries.
WTO segregation gives certain rights to developing country status. For example, the WTO provides developing countries with longer transition periods before implementing agreements aimed at expanding trade opportunities and infrastructure support related to the work of the WTO.
An offshoot of the WTO, the Human Development Index (HDI) is another indicator of economic status developed by the United Nations (UN) to assess the levels of socio-economic development of countries. The HDI measures and then ranks a country based on schooling, life expectancy, and gross national income per capita.
The World Health Organization and the United Nations use least developed countries (LDCs) to describe 45 countries with low socioeconomic development indicators. This list is revised every few years. These indicators are a combination of gross national income, human capital (nutrition, life expectancy, high school education, adult literacy), and economic vulnerability (population, remoteness, concentration of merchandise exports, agriculture, exports, and disaster preparedness).
The list of least developed countries according to this classification includes:
- Afghanistan
- Angola
- Bangladesh
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Vanuatu
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Djibouti
- Gambia
- Guinea-Bissau
- Haiti
- Zambia
- Yemen
- Cambodia
- Kiribati
- Comoros
- Lao People's Democratic Republic
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mozambique
- Myanmar
- Nepal
- Niger
- Rwanda
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon islands
- Somalia
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Tanzania
- Timor-Leste
- Togo
- Tuvalu
- Uganda
- Chad
- Central African Republic
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The value of the total volume of goods and services produced within a country over a fixed period of time (usually a year). Foreign factors are not taken into account, but exports and government reserves are included.
Some would-be political scientists are trying to use per capita GDP as an indicator of the well-being of the population. Such manipulation is economically untenable.
There is a distinction between real and nominal GDP.
Taking into account and without inflation, current prices, respectively.
It is popular to calculate GDP using purchasing power parity (PPP). Let a mug of beer cost $5 in New York, and ₽200 in Moscow. Let's recalculate the exchange rate: 200 / 350 x 70 = 40. That is, instead of 70 we get ₽40 for $1.
And this should be taken into account. It is not clear what goods are included in the methodology, whether overhead costs included in the price are taken into account, etc. There is too much scope for mistakes and propaganda abuses. Questionable approach.
A related concept is gross national product (GNP). Takes into account the production of local companies abroad.
Summary
- Third World country is an outdated and offensive term for a developing country characterized by a population with low to middle incomes and other socioeconomic indicators.
- The International Monetary Fund, the World Bank and the World Trade Organization allow certain benefits and treaty provisions for countries that meet certain types of economic status classifications.
And that’s all for today about the term “Third World” and the developing countries of the world. I hope the article was useful and interesting for you. Share the article on social networks and instant messengers and bookmark the site. Good luck and see you again on the pages of the Tyulyagin !
- 1
Share
Criteria for classifying states by level of economic development
In the 20th century the difference was simple: capitalist, socialist, third world. With the collapse of the USSR and the collapse of the Warsaw Pact came changes.
UN
Currently, the UN does not set out strict parameters for distinguishing between highly developed and developing ones. Not only GDP and financial stability are taken into account.
The presence of a market and free competitive relations are taken into account. The balance between the service sector and industry, mining and processing industries is important. High-tech production and the presence of an educational system are welcome.
The attractiveness for investment, environmental culture, and legal system are considered. Certainly raw materials appendages do not gain ratings.
Banks and funds
The IMF's requirements are more specific.
- high specific GDP;
- diversity of industry and exports. Kerosene shops are not valued;
- participation in world trade.
When assigning a level, WB is guided by per capita GNI:
- low - up to $985;
- below average - $976...3855;
- average - $3856...11905;
- high - from $11906.
Countries related to points 1 - 3 are classified as developing.
China and Russia
China and Russia are among the most attractive countries for foreign investment. The Chinese economy is characterized by high economic growth and has the fastest development in the world.
The country is now the second largest economy in the world after the United States. However, China faces a number of social and demographic problems that prevent it from becoming a member of the “club of developed countries.” Most of the Chinese population spend their income on basic necessities and clothing. Each Chinese person accounts for much less GDP than an American or European.
According to the criteria, Russia is not considered a developed country, however, along with China, Russia belongs to the “newly industrialized countries”, because their industry is growing at a faster pace than the rest of the world. The country's economy is among the top 10 best economies in the world and continues to increase its GDP growth rate, despite economic sanctions.
However, Russia's problem is its serious dependence on energy exports (oil and gas). Therefore, in the coming years, Russia should rebuild its economy from a resource-based to a post-industrial one, because Natural resources are being depleted.