International dumping is clearly harmful to the economy of the importing state. If a product is imported from abroad at a price lower than what it is produced and sold in the domestic market of the exporting country, this will have an extremely negative impact on the domestic manufacturer. Therefore, the state seeks to prevent dumping, protecting its economy.
Question: An organization imports goods worth 3,000 euros, the country of origin is confirmed by a factory quality certificate. This product, originating in China, is subject to an anti-dumping duty. Is it legal for the customs authority to amend the declaration of goods in terms of indicating information that the country of origin has not been determined and stating information about the calculation and payment of anti-dumping duties? View answer
One of the ways of such protection is anti-dumping duties. Let's consider what this measure is, and also clarify the calculation of their amount. It is important to reflect these duties correctly in your accounting records.
The essence of anti-dumping duties
International business involves the import of various foreign products. Quite often, analogues of such items or products are also produced in the host country. If export occurs at the so-called “junk” cost, that is, prices for it are underestimated when compared with similar products produced for itself by the exporting country, this situation is called dumping . The international use of dumping prices is prohibited by law in most countries due to its destructive economic impact.
Question: In what cases, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 121 of the EAEU Customs Code when performing customs operations on behalf and on behalf of the declarant by a customs representative, who, in accordance with Art. 405 of the EAEU Labor Code bears a joint and several obligation with the declarant to pay customs duties, taxes, special, anti-dumping, countervailing duties; enforcement of the obligation to pay customs duties, taxes, special, anti-dumping, countervailing duties may not be provided? View answer
To eliminate the possibility of export dumping, customs introduces a special type of fees, namely anti-dumping duties - special payments levied in addition to regular customs tariffs. These special measures are introduced if an investigation by the competent authorities establishes that the import of imports at the declared value:
- materially damaged any sector of the economy of the Russian Federation;
- may potentially pose a threat to property damage;
- interferes or is capable of interfering with progress in this sector of the domestic economy.
Question: How do import customs duties and safeguard, anti-dumping and countervailing duties relate? View answer
Potential or real material damage caused to the Russian economy means the creation of a situation in which:
- production volumes of imported goods are reduced within the country;
- domestic products are sold in significantly smaller volumes or become in short supply altogether;
- the production of these products loses profitability;
- inventory decreases;
- the level of unemployment is growing and wages are decreasing in the relevant economic sector;
- investment in this sector of the economy decreases or stops.
Question: A Russian organization imports from the People's Republic of China truck tires classified in commodity subheading 4011 20 100 0 of the unified Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity of the Eurasian Economic Union, subject to anti-dumping duties in accordance with the Decision of the Board of the Eurasian Economic Commission dated November 17, 2015 N 154 “On the application of anti-dumping measures through introduction of an anti-dumping duty on truck tires originating from the People's Republic of China and imported into the customs territory of the Eurasian Economic Union." Is a Russian organization obliged to provide security for the fulfillment of the obligation to pay anti-dumping duty when placing this product under the customs transit procedure? View answer
If such a situation is confirmed, it is fair that the party importing the goods bears an additional financial burden, which will go to the Russian budget - to compensate for the harm caused. The exporting entrepreneur himself has the right to decide whether it will be profitable for him to supply goods to the country at dumping prices, coupled with such customs duties, or to set the so-called “normal” price.
Features of customs clearance
Because bearings are quite difficult to classify. To set the HS code, a detailed description of the product is required. Also, for customs clearance, you should prepare a package of basic documents, which includes:
- invoice;
- foreign trade contract;
- packing list;
- invoice;
- transaction passport (if the contract amount exceeds 50 thousand dollars);
- insurance;
- payment order for payment of customs duties.
After arrival, the cargo is unloaded from the container, placed in a temporary storage warehouse and the customs clearance procedure begins.
According to the Decision of the Customs Union No. 299 of May 28, 2010, bearings are subject to sanitary and epidemiological control at the customs border and the customs territory of the Customs Union, since the scope of this decision includes:
- products that are a source of ionizing radiation (as well as generating it), products and goods containing radioactive components;
- mechanical engineering and instrument making products for industrial, medical and household purposes;
- construction raw materials and materials in which hygienic standards regulate the content of radioactive substances, including industrial waste for recycling and use in the national economy, scrap ferrous and non-ferrous metals (scrap metal).
Customs clearance of bearings that arrived as air cargo can be conveniently carried out at Vnukovo, Domodedovo, and Sheremetyevo customs, and the latter is most often given preference. In this case, the declaration and package of documents are submitted electronically to the aviation EDC of Sheremetyevo customs. You can choose other customs posts for customs clearance, for example Kashirsky, Stupinsky, Novomoskovsky, Kubinka and others. The CED registers the declaration and releases the cargo. Operations related to direct actual control are carried out at the location of the cargo.
Normal price
The normal price is the price in force for a similar product in the domestic market of the supplier country.
Question: Is it necessary for a Russian organization, when placing goods imported from Poland (hot-rolled steel rods, code 7213 10 000 0 according to the EAEU HS) under the customs procedure of release for domestic consumption, to confirm the country of its origin, if the customs value of the goods is 750 euros and in relation to the goods Has the anti-dumping duty been paid in accordance with the Decision of the Board of the Eurasian Economic Commission dated March 29, 2016 N 28? View answer
If a similar product is not produced in the country, the normal price can be calculated by calculating the cost, adding a reasonable markup to it, or by looking at what prices this product is exported to other countries.
NOTE! Dumping is not a reduction in prices compared to the domestic market of the receiving party. The comparison is made with prices for consumers in the exporting country.
For example, in France, a can of instant coffee costs 2 euros, and in Russia similar coffee can be bought for 150 rubles, which is approximately 2.2 euros. If such coffee is brought from France to be sold in the Russian Federation for 2 euros (about 134 rubles at the exchange rate), this will not be dumping. But selling it below this price is already prohibited.
How the law regulates anti-dumping duties
The main legislative act regulating the introduction of anti-dumping duties, the procedure for their collection and the amount is the “Agreement on the procedure for applying special protective, anti-dumping and countervailing measures during the transition period,” ratified on the basis of Federal Law No. 274-FZ of October 19, 2011. Guided by it, the Customs Union Commission makes decisions regarding special duties or other restrictions on the import of specific product groups from certain countries.
Confirmation of the likelihood of grounds for special duties
The anti-dumping duty is imposed based on the results of a report drawn up based on the results of an economic investigation by the competent authority - the representative office of the Customs Union Commission. In order for a decision to impose an anti-dumping duty to be made, the investigation must be carried out no faster than 6 months.
You can introduce this duty by making only a preliminary conclusion (no earlier than 2 months later), then the duty is also considered preliminary, that is, it will be collected, but will not go to the federal budget until the final conclusions are made (about another 120 days). If dumping is ultimately not determined, the duty will be returned to the payer.
NOTE! If the exporter, of his own free will, revises the prices of his goods to acceptable levels, the investigation may be terminated early, since there will no longer be any basis for it.
The conclusion about dumping cannot be valid for longer than 5 years; after this period, anti-dumping measures must be canceled or a new investigation must be undertaken. A year after the introduction of anti-dumping duties, the exporter is allowed to submit a request for a revision of the rate or the appointment of a new investigation, initiating the abolition of these duties.
Therefore, the list of antimonopoly duties is constantly updated both in relation to the names of imported products and in relation to exporting countries. Its relevance must be constantly checked with the customs broker.
Certification
Bearings are checked according to technical regulations TS 003/2011 “On the safety of railway rolling stock”. Automotive bearings are checked according to TR CU 018/2011 “On the safety of wheeled vehicles”.
To determine the technical regulation, it is necessary to more accurately establish the characteristics of the product and the scope of the technical regulation.
To obtain a mandatory declaration of conformity or a voluntary certificate of conformity you will need:
- application;
- constituent documents of the company;
- OGRN, TIN certificates;
- regulations;
- list of products;
- foreign trade contract;
- research protocol.
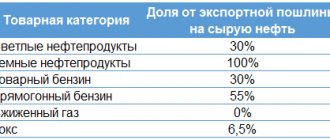
Antimonopoly duty rate
The amount of the rate is calculated in such a way that, when paid, it covers the damage that the sale of these goods will cause or may cause to the domestic economy. It is established at the end of a lengthy investigation.
IMPORTANT! If a preliminary duty was applied to the payer, and as a result of the investigation, dumping is confirmed, but a rate lower than what has already been paid is accepted, the difference will be returned to the exporter. Increasing the rate does not threaten the payer with additional payment - the difference is forgiven.
The rate is set by the Customs Union Commission when the anti-dumping duty regulations are put into effect. If a product is imported for which the corresponding rate has not yet been calculated, such a product is not subject to a special duty or it is calculated individually.
Since the rate of this duty is a special one, it cannot be calculated using the usual customs rate formulas (ad valorem, specific or combined). They are established solely based on the results of a special investigation and may be changed or canceled over time.
Return or Refund
The WTO Anti-Dumping Agreement requires WTO member countries to levy anti-dumping duties on a non-discriminatory basis on imports from all sources that dump shipments and cause damage to the importing country's industry. Exceptions can be made only to exporters whose price commitments have been accepted by the authorities of the importing country.
The amount of anti-dumping duty collected cannot exceed the proven dumping margin, but can be set at a lower level.
The WTO Anti-Dumping Agreement sets out mechanisms to limit the imposition of excessive anti-dumping duties. The choice of mechanism depends on the toll collection process. In case of payment of excessive anti-dumping duties, they are subject to return to the payer.
Accounting for anti-dumping duties
Anti-dumping duties are in no way related to regular import duties; they are paid separately. Accounting documents must reflect imports from a country outside the Customs Union using the following entries:
- debit 76 “Customs”, credit 51 “Current accounts” - payment of advance payments to customs authorities;
- debit 41.01 “Goods in warehouses”, credit 60.21 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors in foreign currency” – receipt of goods;
- debit 41.01 (or 44.01), credit 76 “Customs” - advance payment for payment of import duties and taxes.
ATTENTION! If duties are taken into account in the cost of goods, account 41 “Goods” is applied, and if as part of current expenses, account 44 “Sales expenses” is applied (in accordance with the Chart of Accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
Since the anti-dumping duty is a special measure, it is classified as a non-tariff settlement method, and not as an import customs duty, and on this basis is not included in the tax base for calculating value added tax.
Types of bearings
Bearings are used to support a rotating shaft or axle in machines and mechanisms. The largest classification categories are: rolling bearings and plain bearings.
The first are divided into:
- ball bearings;
- roller bearings;
- needle-shaped
Rolling bearings consist of:
- inner ring;
- separators;
- outer ring.
ATTENTION! We work only with legal entities.
Sliding bearings consist of an inner sleeve and a housing, between which a lubricant is laid. By type of lubricant they can be:
- dry;
- borderline;
- hydrodynamic;
- gas-dynamic.