Code 5010 in the customs declaration
In the menu “ Main activity – Purchase – Receipt of goods and services
” we add a new document.
We indicate the type of receipt, date, counterparty, contract, warehouse. We fill out the tabular part with the nomenclature. Prices are entered in the contract currency. The Central Bank exchange rate on the date of receipt of goods is displayed at the bottom left. The rate can be set using the “ Prices and Currency
” button.
Next, you can use the button “ Enter based on – Customs declaration for import
", which will allow you to automatically create and fill out the document "
Customs customs declaration for import
" based on this receipt document.
Or this can be done from the menu “ Main activity – Purchasing – Customs declaration for import
”.
What does code 2050 in the customs declaration mean?
2. The Main Directorate of Information Technologies (A.E. Shashaev), together with the State Scientific Research Center of the Federal Customs Service of Russia (A.Yu. Durov), take into account the provisions of this order, to make additions and changes to the databases of regulatory and reference information and software used for processing information, declared in customs documents.
In order to implement the Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated September 20, 2021 No. 378 “On classifiers used to fill out customs declarations” as amended by the Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated October 14, 2021 No. 441 “On amendments to paragraph 7 of the Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated November 27, 2021 No. 130 “On unified customs and tariff regulation of the Customs Union of the Republic of Belarus, the Republic of Kazakhstan and the Russian Federation”, Federal Law dated December 13, 2021 No. 357-FZ “On the federal budget for 2021 and for the planning period 2021 and 2021" (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2021, No. 51 (Part 1), Art. 6809) I order:
All comments (3)
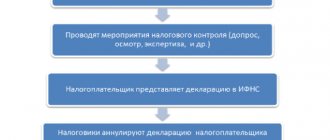
Please add how the customs declaration will be reflected in the VAT return. I can’t fill out field 12 in the purchase book - Registration number of the customs declaration. Should it be filled out?
In the comments to the article, we do not answer questions about 1C programs and legislation. You can ask all questions about 1C in the MY QUESTIONS section in your PERSONAL ACCOUNT here: Personal Account
Other materials on imports from non-CIS countries in the 1C BP BukhExpert8 rubricator can help you in resolving this issue.
Column 12 in the purchase book is called “INN/KPP of the intermediary” and the customs declaration number is not reflected in it when importing from non-CIS countries. If we are talking about column 13 of the purchase book, then it is filled out by those who bought imported goods on the domestic market and who have an incoming invoice with a customs declaration number. There is no column 12 in Appendix 9 of the VAT declaration.
Source
Customs codes of the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity
In subsection “a” of column 34 “Country of origin code” of the goods declaration, the code of the country of origin of the declared goods is indicated, information about which is indicated in column 31 of the declaration (clause 32 of clause 15 of the Procedure for filling out the declaration of goods, approved by the Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated 05/20/2021 No. 257). Such a country code in the customs declaration is indicated in accordance with the Classifier of countries of the world (Appendix No. 22 of the Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated September 20, 2021 No. 378).
Code 2050 in the customs declaration is an anti-dumping duty established in accordance with the Protocol on the Application of Special Protective, Anti-Dumping and Countervailing Measures in Relation to Third Countries (Appendix No. 8 to the Treaty on the EAEU dated May 29, 2021).
Online magazine for accountants
- the left part is the code of the customs office that registered the declaration in accordance with its classification;
- the middle part is the day on which the declaration was registered (DDMMYY);
- the right part is the serial number of the declaration, which is given to it according to the customs journal on registration of declarations (starts with one for each calendar year).
Thus, an organization (individual entrepreneur, individual) should not have the question of how to fill out the registration number of the customs declaration. This is done exclusively by a customs official. It is only important to know where the registration number of the customs declaration is indicated in order to quickly find it.
What does code 2050 in the customs declaration mean?
Penalties for late payment of the recycling fee payable for wheeled vehicles (chassis) and trailers for them imported into the Russian Federation, except for wheeled vehicles (chassis) and trailers for them imported from the territory of the Republic of Belarus
Funds from the sale of goods detained by customs authorities, in the amount calculated on the day of detention of these goods, import customs duties and taxes that would be payable when placing the detained goods under the customs procedure of release for domestic consumption
Code 1010 in the customs declaration - what does it mean?
Transportation of goods across the Russian border is subject to the mandatory completion of customs documents, including a customs declaration. The cargo customs declaration may contain data that is displayed with special codes or ciphers. The classifiers used when filling out the customs declaration are given in the Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated September 20, 2021 No. 378 (as amended on May 22, 2021).
Code 1010 in the customs declaration is entered in line 47 in the field reserved for the type of payment. This code means that the amount is accrued for customs duties for customs operations, including customs clearance and declaration (Appendix No. 9 to the CCC decision No. 378 dated September 20, 2021).
RESULTS
The procedure for filling out field 5 “Type of payment” is established by the bank.
If the bank has not installed it, leave this detail blank. If the value in the “Type of payment” detail is entered incorrectly, the funds will be returned to the payer’s account and will have to be sent again, adjusting the payment as necessary. You can familiarize yourself with a sample of the corresponding application in the article “Sample application for clarification of tax payment (error in the KBK)” .
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What does 1010 type of customs duties imply?
But there are a number of mandatory payments for import and export, including you are required to pay 1010 type of customs duties , which is calculated based on the value of your goods. This payment can be paid either together with the submission of a customs declaration, or in the form of a customs payment.
- 500 rubles must be paid if the cost of goods does not exceed 200 thousand rubles.
- 1000 rubles – from 200 thousand rubles to 450
- 2021 rubles – from 450 thousand rubles to 1200 thousand rubles inclusive
- 5,500 rubles must be paid if the cost of the goods is from 1,200 to 2,500 rubles.
- The work of the customs authority will cost 7,500 rubles if the amount of your goods does not exceed 5,000,000 rubles.
- The most expensive type of customs payment 1010 is one hundred thousand rubles if the goods cost up to 30,000,000 rubles.
We recommend reading: How to properly certify a photocopy of a work book sample
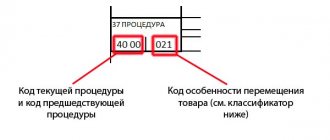
Filling out column 47 and column B of the goods declaration
Column B indicates the amount of customs duties payable for the entire declaration, indicating the payment documents from which the inspector will have to write off this money. For example, indicating the number and date of the payment order. For each type of payment (by analogy with column 47), the write-off amount, the payment currency code (for the Russian Federation this is rubles - code 643), the number of the payment document and its date, and the method of payment are indicated.
Nowadays, with the fairly high development of special software, it is not necessary to manually calculate payments in the process of filling out a goods declaration. All you need to do is enter the input data correctly in the appropriate fields and click the payment calculation button. In order for the column to be filled out correctly, you must first select the product code in column 33, indicate the country of origin in column 34, enter the invoice cost of the product in column 42, and correctly indicate the contract currency in column 22, and preferences in column 36. Of course, column 23 should contain the Central Bank currency exchange rate on the day the declaration was submitted, and column 1 should contain the customs regime (procedure). Some goods (depending on the code) are also affected by both the weight of the goods and the quantity, so before calculating payments you must fill out all the previous columns of the declaration. But that's not all. Column 45 remains. Earlier we talked about calculating customs value. In the program, the customs value is calculated by itself when you enter the cost of the goods in column 42, and in the DTS you enter all additional costs that affect the customs value. In any case, it is advisable to double-check the customs value manually to avoid errors and typos. Because Incorrectly declared data may result in underpayment of payments. This is severely punished. After all the entered data, you can already calculate payments.
Receipt of traceable goods from a counterparty – a resident of the Russian Federation
So, let’s look at how the receipt of goods subject to traceability is reflected in the 1C program: Enterprise Accounting ed. 3.0 from the supplier - a resident of the Russian Federation.
Let us immediately make a reservation that the exchange of documents on traceable goods should be carried out only through electronic document management (EDF) operators.
If the company is connected to the 1C-EDO service, then the documents discussed in the example will be filled out in the program automatically.
For clarity, we will analyze the reflection of the receipt of goods subject to traceability in an organization in which the 1C-EDO service is not connected.
We talk more about product traceability in a new online course : watch here.
To reflect the receipt of traceable goods, we will need the document “Receipt (acts, invoices, UPD)” in the “Purchases” section.
The document type in this case will be: “Goods (invoice, UPD).”
Let's make sure that the country of registration of the supplier is Russia.
Next, let's move on to the tabular part of the document and pay attention to the nomenclature. Previously, we have already examined in detail filling out the nomenclature card, so now we will not dwell on this issue, we will only remind you of the need to correctly fill out the lines highlighted in purple.
In the footer of the item card, do not forget to also fill in the appropriate fields.
When you transfer such an item to the document “Receipt of Goods”, a special icon appears
, indicating that the product is traceable.
When you click on this icon, you can call up a tooltip indicating that the product in the document is from the list that is subject to traceability. Information about the number and date of the resolution will be updated by the developers.
Please pay attention to the column “Customs declaration or RNPT”.
In this column we will have to enter the RNPT, which is indicated in the document of the supplier of the traceable goods:
The column provides the ability to enter information manually. This option may be necessary if the purchasing organization has electronic document management configured not through the 1C: EDF service, but through some other program.
If the buying company has the 1C: EDF service connected, then, as we said earlier, the RNPT will automatically be loaded into this column from the electronic invoice (or UPD) of the supplier.
Next, we will navigate the document and click on the button
Let’s go to “Document Movement”.
Here we are interested in the “Traceable Products” tab.
We see that the register of the same name was filled in with the “Incoming” view. We can also check the information entered into the register about the purchased goods.
Now let's go to the "Operations with traceable goods" tab.
In this register, for organizations that are VAT payers, the “Reflection in reporting” column will indicate “Purchase Book” if the seller is also a VAT payer and has issued an invoice.
If the seller is not a VAT payer, then this column will contain the value “Report on transactions with traceable goods”.
Let us remind you that this report must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service no later than the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter for all transactions with traceable goods.
Important! In the 1C program: Enterprise Accounting ed. 3.0, starting with version 3.0.100.23, information about traceable goods has been added to the electronic forms of the log of received and issued invoices, the purchase book and the sales book.
The new forms will be applied starting with the declaration for the 3rd quarter of 2021.
The Federal Customs Service has updated the compliance of codes for types of payments and BCC for customs taxes
According to the new order (which applies in 2021), for VAT payment type code 5010 corresponds to KBK 153 1 0400 110, correspondence has also been established for each type of excise tax, as well as for interest for the provision of deferment, installment payment of each type of excise tax, for penalties for each type of excise tax.
By Order No. 480 dated March 31, 2021, the Federal Customs Service approved the list of compliance of the classifier of types of taxes, fees and other payments, the collection of which is entrusted to the customs authorities, with budget classification codes. A similar order of the Federal Customs Service of May 18, 2021 N 973 and two letters of the Federal Customs Service on sending information on the application of the BCC in 2021 are no longer in force.
Receipt of traceable goods in 1C: Enterprise Accounting ed. 3.0
We hope everyone is aware that the national product traceability system has been operational since July 8, 2021? In the article we will talk about how to reflect in 1C accounting the receipt of traceable goods from various supplier companies: residents of the Russian Federation, (non)/members of the EAEU.
To begin with, let us recall the main goal of the goods traceability system - to ensure state control over the movement of imported goods from the manufacturer to the final consumer. Such control should reduce the percentage of illegal imports on the territory of the Russian Federation.
You can familiarize yourself with the main provisions in Government Decree No. 1108 dated 07/01/2021.
To understand which products are subject to traceability, we advise you to refer to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 1, 2021 N 1110.
Having paid a little attention to the theoretical side of the issue, let's move on to practice.
What does code 2050 in the customs declaration mean?
The detail “106” indicates the value of the payment basis. If the value zero (“0”) is indicated in the payment basis, if it is impossible to clearly identify the payment, the Inspectorate independently classifies the received funds as one of the payment grounds named in clause 6 of the Rules.
Interest for granting a deferment in the payment of excise duty on pipe, smoking, chewing, sucking, snorting, hookah tobacco (except for tobacco used as raw material for the production of tobacco products)
How critical is it to indicate the type of payment incorrectly?
As we noted above, indicating in detail “5” values that do not meet the criteria set by the Federal Treasury, as well as Regulation No. 384-P, may lead to the refusal of this department to process the payment and return the bank order to the client.
This can happen if:
- for a payment that does not involve the use of the BESP system, and also does not correspond to the characteristics of an urgent one, in detail “5”, in principle, something is indicated;
- When a payment is sent through the BESP system, that is, urgent in any case, nothing is indicated in detail “5” or a value is recorded that differs from the “urgent” mark.
The consequences of the return of a payment document by the Federal Treasury may be (if we are talking about tax payment) the recognition by the Federal Tax Service of the taxpayer’s obligations to the budget as unfulfilled. In this case, the subject’s obligation to pay tax is considered unfulfilled due to the provisions of sub-clause. 1 or sub. 2. clause 4 art. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, that is, if the payment order is returned by the bank or the Federal Treasury (in principle, both options are possible, since in the payment systems of some banks transfers with incorrect details “5” are automatically rejected even before they reach the treasury).
Read more about the key provisions of Art. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, read the material “Art. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: questions and answers" .
REFLECTION OF CHARGING CUSTOMS PAYMENTS AND FEES IN THE CUSTOMS DECLARATION
In the tax accounting of a business entity - a profit tax payer, the amounts of customs duties, customs duties and excise taxes paid when importing goods are included in gross expenses on the basis of paragraphs. 5.2.5 Art. 5 of the Law on Income Tax (as fees (mandatory payments) established by Article 14 of the Law of Ukraine “On the Taxation System” as amended on June 25, 1991 No. 1251-ХП, with amendments and additions). The amount of customs duties paid at customs is included in the gross expenses of the taxpayer on the basis of paragraphs. 5.2.1 Art. 5 of the Law on Income Tax as expenses associated with conducting business activities.
We recommend reading: What benefits are provided for labor veterans in Gai
Customs duties can be paid by both a resident and a non-resident (depending on who is responsible for declaring goods). Customs duties are paid before or at the time of customs clearance.
Import into 1C 8.3 Accounting step by step
The organization entered into a contract with the supplier Galaxy LLC for the supply of goods from Germany in the amount of 20,000 EUR.
On March 11, an advance payment in the amount of 10,000 EUR was made.
On March 19, the supplier Galaxy LLC shipped the goods Lathe IM-1 (1 pc.) worth 20,000 EUR. The transfer of ownership of the goods occurs at the moment the goods are transferred by the carrier to the buyer’s warehouse. Delivery basis - DAP Moscow.
On March 27, advance customs payments were made (VAT - 315,000 rubles, duty - 75,000 rubles, fee - 750 rubles).
On March 29, customs declaration of goods was carried out. The machine was delivered to the warehouse and accepted for accounting.
Conditional courses for example design:
Rules for filling out the customs declaration for imported goods
Box 21 – Identification and country of registration of the active vehicle at the border. The column gives the traditional name of the type of vehicle on which the goods crossed the customs border of the Russian Federation, and its description (numbers of cars or wagons, names of ships, flight numbers). On the right, in the highlighted section, the alpha-2 code of the country where the vehicle is registered is indicated (in the UK example, the code of the United Kingdom, since the vessel is British). In the case of transportation of goods by rail, the code of the country of origin is not indicated.
— element 3 — date (day, month, last two digits of the year without dots) of the first payment for the declared consignment. If payment has not yet been made, then the date is calculated by the declarant based on the terms of the agreement. If payments for the declared consignment are made in one payment, dashes are entered in element 3;
What does code 1010 mean in the customs declaration?
- A contract (purchase/sale agreement) concluded between individuals or legal entities. Attachments to it: specifications, bills (invoices), packing lists.
- Original contract.
- Receipts for payment of customs duties after determining the value of the goods.
- List of documents confirming data on customs assessment of cargo and financial control.
- Availability of licenses, official permits from government officials, if required by the goods being moved, availability of certificates of quality and origin from the manufacturer.
- A package of documents giving the right to the cargo manager to move it - a certificate of state registration, Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) and certificate of foreign trade participant, registration documents of an individual entrepreneur, passport.
- Proof of compliance of imported goods. The specification is issued to the recipient company.
- Certificate form ST-1 (certificate of the country of origin of the goods).
- Price list, invoice, invoice, which contains an indication of the customs declaration number. Deciphering product codes in the price list is not required.
- Quality certificates, operational documents issued abroad in the country of origin.
Rules for filling out the customs declaration for imported goods
Column 45 – Adjustment. The customs value of the goods is indicated in rubles. Rounding according to the rules approved by the Central Bank, i.e. currently down to kopecks. Next, the number of the method by which the declarant determined the customs value of the goods is indicated through “/”.
Column 12 – Information on cost. The column indicates the total customs value, i.e. the total customs value for all declared goods. Customs value is the value adjusted to the Russian border. Calculated in rubles. If only one product is declared, the column is not filled in.
Classifiers used when filling out the customs declaration
Classifier of countries of the world Contains two- and three-letter, as well as three-digit digital codes of countries of the world The latter are used when filling out columns 10, 11 15a, 17a of the Civil Customs Declaration Classifier of delivery conditions Contains abbreviated names of delivery conditions and compliance with the rules of "Incoterms-90", used when filling out column 20 gas turbine engine
Classifier of payment forms for foreign trade barter transactions. Contains two-digit digital waters of the nature of the transaction (column 24GTD) Classifier of methods for paying customs duties. Contains two-letter codes of customs payment methods used when filling out i-rafa 47 of the customs declaration.
Transfer of payment to customs
The transfer of customs payments can be made in two payments: one for the payment of VAT and customs duties, the second for the payment of duties. This is due to the use of different BCCs when processing payments.
But the overall filling will be the same: