The speed of customs clearance and even the possibility of moving cargo across the border of the Russian Federation is determined by the completeness of the documentation package and the correctness of calculations regarding customs value. The customs service very strictly checks the authenticity of the customs value, since the amount of customs duties depends on this.
ATTENTION! We work only with legal entities.
The customs value is calculated by the declarant, but this does not deprive the inspector of the right to make adjustments. In essence, adjusting the customs value is aimed at collecting additional customs duties. There is an opinion that the decision on the CCC is made not only due to violations, but also due to the fact that the Russian budget does not receive additional financial resources.
No one is immune from customs value adjustments. And for the declarant, it means the likelihood of a significant delay in customs clearance and unexpected expenses.
What is customs value
The customs value is not equal to the cost of the goods and includes additional costs:
- costs for obtaining permits
- costs of production, sales, advertising;
- cost of delivery to the border with the Russian Federation;
- transaction costs between the seller and the buyer;
- buyer's income from resale.
Each point must be documented.
Vehicle calculation methods
There are 6 methods for determining the customs value of imported goods, applied in their sequence, except for methods 4 and 5:
- The transaction method based on the price of imported goods (provides that the vehicle is equal to the invoice value. Depending on the terms of delivery, transport and other costs are either added to the invoice value for the purpose of calculating the vehicle or subtracted from the invoice value).
- The method of transaction by price with identical goods.
- Method of transaction by price with homogeneous goods.
- Subtraction method (from the cost of goods on the foreign market, expenses within the country, amounts of customs duties and other expenses within the EAEU are subtracted).
- The addition method (calculated by calculating the costs of manufacturing and delivering goods to the border of the EAEU from the country of export - in practice, the method is very rarely used.
- Backup method. Allows you to “flexibly” combine previous methods.
The method for determining the TC for exported goods is determined at the level of the Russian Federation by the relevant Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation - dated December 16, 2021 N 1694.
Declaring goods: why do you need a declaration?
This is a document that is filled out in cases where goods or cargo crosses the border of the Russian Federation at the entrance or exit from the state. Declaration of any cargo is carried out directly in the customs control zone; during the process, the declarant submits an application drawn up in the form established by law.
It contains accurate data about the goods being transported, the customs procedures applied to them, the transport on which they are transported, as well as other information required to authorize the carriage of goods on the basis of Art. 4 of the TC TC, can be submitted electronically remotely or in writing.
The declarant carries out the preparation and submission of the declaration, payment of all required payments and provision of the transported cargo for inspection at the request of customs. During the inspection process, a customs officer inspects the presented goods and vehicles, checks the documents and information specified in them with what the declarant presented.
The customs declaration has a form strictly established by law; a common carrier or even the owner of the cargo is not always aware of all the subtleties of its registration, the established format and other nuances.
Therefore, when filling it out on your own, errors or inaccuracies may often be made, unnecessary information may be entered, or there may be a lack of information, as a result of which you subsequently have to make changes to the TD. Specialists will help you make changes or adjustments, as well as fully take over the responsibilities for completing the customs declaration if necessary.
Why does the adjustment occur?
Representatives of the customs service have statistical data on the cost of a particular product by country and region. They have at their disposal price catalogs, documents on previously concluded transactions, stock quotes and indices. This data is accumulated for each HS code. The need to adjust the customs value arises when:
- The cost of imported goods is below the risk level.
- The cost of goods does not fit into the range of statistical data for a specific HS code.
- The calculation does not include brokerage, forwarding and other services.
- The product costs less than its individual components.
- The choice of method for calculating customs value is not justified.
- The information in the declaration does not correspond to the actual data.
- There are other circumstances that make it possible to doubt the reliability of the customs value.
Risk profiles are issued by the Federal Customs Service. These documents indicate risk factors, for example: statistical cost per kg, country of origin and dispatch of goods, and more. If, for example, the cost of goods per kg turns out to be lower than the statistical value, then the risk is triggered automatically, and customs must request additional documents from the declarant to confirm the customs value
There are situations when the contract stipulates a reduced value in order to save on customs duties. But there are also cases when adjusting the customs value is illegal. For example, the importer indicates the actual customs value: he simply managed to negotiate a lower price with the supplier, or the supplier provided a discount. Then you will need to document the customs value.
In general, the adjustment of customs value ensures conditions for fair competition, because if the customs value is underestimated, a smaller amount of customs duties is paid and thereby ensures a competitive advantage.
In principle, you always need to be prepared for adjustments, because the vehicle is valued using the price comparison method.
Is it possible to avoid CTS?
Most often, when evaluating a vehicle, the price comparison method is used. Even a direct contract with the manufacturer will not protect you from adjustments. The presence of risks as a result of the analysis of the terms of the transaction and the information available to customs about similar transactions leads to CCC. Therefore, you should always be prepared to defend the declared vehicle and have all the evidence in hand at the time of customs clearance.
Which product categories are most often subject to adjustments?
Most of the product range is potentially subject to adjustment of customs value. Most often the following fall under the CTS:
- electronics;
- technological equipment;
- vehicles;
- pet food;
- Common consumption goods;
- nuts and dried fruits;
- cattle meat;
- Natural flowers.
In general, these are those goods that belong to the same HS code, but have different quality characteristics and functions.
The likelihood of an adjustment can be predicted, because there are freely available sources that indicate the average statistical cost of certain imported goods.
How to confirm customs value
The main advice to the declarant is to prepare as complete a package of documents as possible, especially if this is the first shipment of goods. It is advisable to always have documents “at hand” that will allow you to prove the customs value. If they are not available, and customs asks for evidence, you may not have time to complete all the paperwork, because the time limit for this is limited.
The following may serve as evidence:
- commercial offers;
- contracts between supplier and buyer;
- invoice;
- price lists;
- export declaration;
- prices on the manufacturer’s website, marketplace and other open sources;
- cost in the domestic market of the country from which the product is imported.
When using the export declaration as evidence, it is important to ensure that it is valid. Chinese suppliers are guilty of submitting fake declarations in order to recover more VAT.
Subsequent consignments of goods are easier to clear through customs. It will be much easier to prove the customs value. However, the risk of adjustment remains.
What to do if the vehicle needs to be confirmed?
There are two possible scenarios:
- Provide documents confirming the customs value and wait for customs to decide.
- Provide sufficient security (at the expense of the client or customs representative) and conditionally release the cargo.
Both options have their drawbacks. In the first case, you need to meet the allotted deadlines. The decision to adjust the customs value is made within 10 days. And, according to practice, the likelihood that the goods will be released at the value stated in the declaration is very small. In another case, the chances increase, but the security is most often paid based on the maximum cost of similar goods. 60 days have already been given to provide the requested documents, but if the documents are not provided or it is not possible to prove the declared vehicle, the security payment is written off.
What must be indicated in the TD
All information in the TD must clearly reflect reality, the information in it is reflected as accurately and truthfully as possible, since otherwise, if inconsistencies, inconsistencies and false data are identified, the paperwork will be delayed, the cargo will be idle at customs, which can revoke the already issued TD. The information indicated in the declaration is regulated by Art. 181 TK TS:
- mode applied to the cargo;
- information about the declarant or his representative;
- information about who sent the cargo and who should receive it;
- information about the transport transporting the cargo;
- information about the goods being transported and their manufacturer;
- data on fees and payments, how they were calculated;
- information about the terms of the foreign trade transaction;
- other information.
The documents attached to the TD must also be listed; the information in the application may be supplemented and may differ depending on the type of cargo being transported, the type of customs procedure, and other nuances. It should be noted that when filling out a document, you cannot allow corrections that have not been certified by the seal of the organization declaring the cargo; in this case, the TD simply will not be accepted.
Before release or after release
The initiator of changes can be either the customs authority or the declarant himself. The decision of the EEC Board No. 289 of December 10, 2013 and Article 112 of the EAEU Labor Code established the rules and deadlines for making changes to the CU.
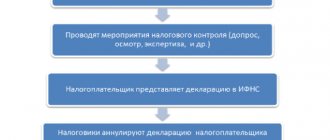
One of the cases of adjusting customs value is before the release of goods. The declarant retains the opportunity to submit an appeal until the customs office has set dates for inspection, examination and requested additional documentation. After the declarant applies, permission to make changes is issued.
If the customs service declares an adjustment, the declarant will receive a corresponding request against signature or by email. It will contain a list of documents that he must additionally provide, a written description of the reason for which the need for adjustment arose, and ways to correct the deficiencies. Time limits are limited. If the customs requirements are not satisfied within the specified period of time, the cargo is not released from customs, but is placed in a temporary storage warehouse. If the documents are filled out incorrectly, the customs office will refuse to register the changes.
After the release of goods, customs officers retain the right to make adjustments for 3 years or even 5 years in some cases. The order is:
- A desk inspection is carried out, after which a report is issued. The customs value that was indicated in the declaration is considered invalid, and a note indicating the need to apply an adjustment is placed on the document itself.
- A decision is made on the CCC, which indicates the time frame for resolving the problem (usually 10 working days).
- The declarant may agree or disagree with the decision on the CCC. If he does not agree, he must indicate why. Then the customs authority calculates the customs value and offers to pay the amount on a voluntary basis.
The declarant also reserves the right to change the vehicle data. To initiate changes, he must draw up a free-form appeal, indicate why the changes are being made and document them. A permit or a reasoned refusal is issued within 30 days.
If an overpayment of customs duties has occurred in connection with the CTS, the customs office must warn about this.
How to fill out a customs declaration
When exporting, importing and international customs transit of goods through the territory of Russia and the EAEU, a goods declaration (DT) is used.
Its form was approved by decision of the Customs Union Commission dated May 20, 2010 No. 257. The declaration for goods imported into the customs territory of the EAEU is submitted before the expiration of the temporary storage period for goods.
To use a goods declaration for express cargo, the following conditions must be met simultaneously:
- customs declaration of goods is carried out by a customs representative;
- the total customs value of goods transported under one individual consignment note does not exceed an amount equivalent to 200 euros (in relation to goods placed under the customs procedure of release for domestic consumption, the total customs value is determined taking into account paragraph 2 of Article 136 of the EAEU Labor Code) or, if so provided legislation of the member states of the Eurasian Economic Union - 1000 euros;
- goods are placed under the customs procedure of release for domestic consumption or the customs procedure of export, or under the customs procedure of re-export or customs procedure of re-import (if previously the goods were placed under customs procedures with the submission of DT), or under the customs procedure of re-export (if previously the goods were not placed under the customs procedure , with the exception of the customs procedure of customs transit).
If the listed conditions are not met, then you must use a goods declaration in the form approved by Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated May 20, 2010 No. 257.
Authorized economic operators, customs representatives, forwarders, persons entitled to own, use and (or) dispose of goods, and other interested parties provide information to the carrier of the EAEU country in whose territory the place of movement of goods across the customs border of the EAEU is located. This is done at least 4 hours before the arrival of the goods.
The carrier, including the customs carrier, is responsible for receiving information, consolidating it and transferring it to the customs authority of the EAEU member state on whose territory the place of arrival is located, no less than 2 hours in advance (Decision of the Board of the Eurasian Economic Commission dated September 17, 2013 No. 196).
The declaration for goods exported from the customs territory of the EAEU is submitted before they leave this territory.
If you provide false information in the DT, you may be fined from 50% to 200% of the value of the goods with possible confiscation (Article 16.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). In this case, officials of the company (manager and chief accountant) may be fined in the amount of 10,000 to 20,000 rubles.
If, after the goods were released, you independently identified violations and contacted the customs authority to make changes and (or) additions to the customs declaration, you will not be fined. In this case, the following conditions must be met simultaneously:
- customs has not identified administrative offenses, the subject of which are the goods specified in the circulation;
- no checks are carried out on such goods;
- you have no debt to pay customs duties, taxes, or penalties.
One declaration (DT) declares information about goods contained in one shipment, which are placed under the same customs procedure.
The total number of goods declared in the declaration must not exceed 999.
If goods contained in one shipment are declared to be placed under different customs procedures, separate declarations of declaration must be submitted for each of them.
The declaration consists of a main sheet (DT1) and additional sheets (DT2) (forms).
Additional sheets are used in addition to the main sheet if information about two or more goods is declared in one DT.
When declaring goods in writing, the declaration of declaration is submitted on A4 size sheets.
On the main sheet of the DT, information about one product is indicated. One additional sheet can contain information about three products.
Appealing the decision
If the customs value has been adjusted, the decision can be appealed pre-trial by challenging it in a higher authority, and through the court.
Moreover, a non-property claim to recognize the customs decision as illegal can be filed in court within three months, and a property claim, in the event that the customs refused to return the overpayment in connection with the CCC, - within 3 years. The declarant can recover the difference even if he has paid a large amount voluntarily.
The time frame for returning overpaid funds may take longer and range from 3 to 6 months. If the decision has already entered into force, then the money will be returned within a maximum of 2 months.
Cases of cancellation of adjustments occur frequently, but to protect your interests it is better to choose a qualified customs lawyer.
Our services
The customs declaration must be completed in a clearly established manner, it is filled out by the declarant or his representative, it indicates only reliable, clear data on the transported goods that are moving across the border. But in some cases, errors are possible due to ignorance of the registration form, lack of experience and knowledge, lack of understanding of the declarant about what information needs to be entered in which column, and errors may also occur due to inattention or due to excitement.
To avoid all these bureaucratic delays, wasting time and nerves on filling out documents, making changes and additions to the declaration in accordance with the procedure established by law, it is best to seek help from professionals. Specialists will deal with the preparation of customs declarations, as well as changes and additions to the information specified in it, if necessary, in accordance with all the rules and in accordance with the established procedure for carrying out all procedures.
Return of CTS
Return of the vehicle is possible in three cases:
- an excess amount of customs duties has been paid – this occurs if the importer paid the required amount during the CCC, but appealed the decision in court and won the case;
- it is necessary to return the cash deposit paid as security for customs payments during conditional release - the need for this arises if, after checking the documents, the initially declared customs value is accepted;
- it is necessary to return the advance payment - if it exceeds the amount that had to be paid.
In each of these situations, you must provide a package of documents and an application. The list of documents and contents of the application will differ for each case.