Customs declaration number: decoding and what is it?
CCD - cargo customs declaration - is a mandatory document when moving (import/export) goods between states. Issued by the owner of the goods and processed by an inspector of the Federal Customs Service (FCS).
The customs declaration registration number is assigned to the document by a customs officer upon acceptance. Until October 1, 2021, this detail in the invoice had a different name - the customs declaration number. The addition to the name of the detail made the content of column 11 clear: not the serial number of the declaration, but the registration number.
In accordance with the adopted changes to the procedure for filling out an invoice (RF Government Decree No. 981 of August 19, 2017), in 2021 the TD registration number became a mandatory detail of the shipping document (column 11).
Read our article about what information about the recipient and sender of the cargo should be indicated in the invoice.
What is the gas customs declaration number in 1C?
The purchase of imported products is regulated by such legislative acts as:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- Customs Code of the Eurasian Economic Union
- Federal Law No. 173 “On Currency Regulation and Control”.
In addition, the accountant must know the Incoterms 2010 terminology, which is a set of rules and terms that are used in trading on the international market.
The GDT form was adopted as a result of the decision of the Customs Union Commission No. 257 of May 20, 2010. Next, we will look at the indicators of some columns, which a specialist should first pay attention to.
The declaration includes a main and additional sheet. The master sheet includes information about one product and general information for the entire declaration. If there is more than one product, then proceed to filling out additional sheets. On one such sheet you can indicate information about three products.
The declaration number is formed from three groups of numbers written with a slash. The first group indicates the customs code, the second indicates the date when the declaration was submitted, and the third indicates the sequential number of the declaration.
- In line 1 during import, the IM mark is placed.
- Line 12 displays the total customs value (in rubles).
- Line 22 reflects the currency of the contract and the total cost expressed in it.
- Line 23 reflects the exchange rate on the day the declaration is submitted (if it is necessary to recalculate the customs value).
- Line 31 indicates the name of the imported product, as well as its characteristics.
- Line 42 reflects the cost of the goods in foreign currency.
- Line 45 reflects the customs value of one product name.
- Line 47 indicates the calculation of payments (VAT when importing products, customs duties and customs duties).
What to do when reselling?
A Russian importer (legal entity or individual entrepreneur) planning further resale of imported goods is obliged to enter in column 11 of his invoice the registration number of the accompanying document registered by customs (subclause 14, clause 5, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Letter of the Federal Tax Service No. AS-4-3/15798 directly indicates the seller’s obligation to write down the TD registration number for each product item in the invoice. This applies to goods imported into the Russian Federation and cleared through customs.
Goods that were produced outside the Russian Federation, passed customs registration, and then were packaged, packaged or bottled in Russia continue to have import status. When selling them, you must indicate the TD registration number in the invoice (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-08/257 dated 08/23/12).
Based on clause 5 of Article 169, the taxpayer-seller of imported goods is responsible for the compliance of the mandatory information specified in the sales documents (Federal Law No. 150 of May 30, 2016) with the information contained in the incoming invoice (clauses 13, 14 as amended by Federal Law No. 119 of July 22, 2005).
Processing or bundling goods imported into the Russian Federation deprives them of their connection to the direct manufacturer, establishing Russia’s right to be considered a supplier. In this case, there is no need to indicate the customs declaration in the shipping document.
Important! In 2021, the basis for refusal of a deduction may be a discrepancy between the customs declaration number in the customs declaration and the contents of column 11 in the invoice.
How to check the customs declaration?
Content:
Checking the customs declaration includes two stages.
First, it occurs before the document is transferred to employees of the Federal Customs Service (FCS) of the Russian Federation. After the declaration has been accepted by customs, it is assigned an individual number. The authenticity of this number can be checked on government services. Through it you can find out about the number of goods exported or imported, as well as the name of the customs post. If the seller has never had to fill out a customs declaration before and is afraid that he will enter information incorrectly into it, he can turn to lawyers for help. They are familiar with the requirements of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation and will help participants in foreign economic activity (FEA) quickly understand the formalities.
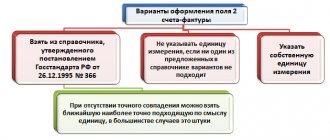
Box 11
The requisite in column 11 of the basis document for VAT calculations in 2018 became mandatory (a dangerous SF requisite).
The registration number of the customs declaration in accordance with Government Decree No. 981 of 08/19/2017 must be indicated in column 11 of the tabular part of the document. The name of the column has undergone changes - the word “registration” has been added to the previously used name. Now the wording of the name of column 11 is “Registration number of the customs declaration.”
How to fill out an invoice if there is no customs declaration number
The Federal Tax Service allowed the registration number of the application for the release of goods to be indicated in column 11 of the invoice. This was reported in the letter dated July 25, 2018 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected]
The agency reminds that according to the law on customs regulation (dated November 27, 2010 N 311-FZ), authorized economic operators are provided with a special simplification in the form of releasing goods for domestic consumption before filing a customs declaration. In this case, a corresponding application for the release of goods is submitted to the customs authority.
At the same time, as required by Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, invoices issued upon sale must indicate the country of origin of goods and the number of the customs declaration in respect of goods whose country of origin is not Russia.
Accordingly, the question arises of what to indicate in column 11 of the invoice if a Russian company sells in Russia goods declared for release by an authorized economic operator before filing a declaration for these goods and released for domestic consumption.
Now the Federal Tax Service has clarified this situation. In this case, in column 11 “Registration number of the customs declaration” of the invoice, you can indicate the registration number of the application for the release of goods.
In this case, the taxpayer selling the specified goods is responsible only for the compliance of the specified information in the invoices presented to him with the information contained in the invoices and shipping documents received by him.
In “1C:Enterprise 8” the necessary changes will be implemented with the release of the next versions. For deadlines, see “Monitoring Legislative Changes.”
BUKHPROSVET
The responsibility for drawing up and issuing invoices lies with the seller of goods (works, services). An invoice is issued no later than 5 days from the date of shipment of goods, provision of services, performance of work, or from the date of receipt of partial payment on account of upcoming deliveries of goods (Clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Violation of this period does not entail any liability for the seller. In this case, the buyer may be denied VAT deduction. For example, with reference to the improper nature of the invoice. Refusal to deduct on this basis is illegal.
The fact is that the list of mandatory invoice details, without which it is impossible to receive a deduction, is closed. Thus, the invoice must contain information about the seller, the buyer of the goods, the name of the goods, their value, as well as the tax rate and the amount of tax. The absence of these details, as well as errors in them, will result in denial of the deduction.
In turn, errors in the serial number and date of issue of the invoice are not grounds for such a refusal (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 25, 2016 No. 03-07-11/2722).
How to apply correctly?
To fill out column 11, the registration number is formed according to the following scheme: 8 characters / 6 characters / 7 characters / 3 characters (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-09/6 dated 02/18/2011).
- 8 digits – code of the customs authority that accepted the customs declaration for goods. The list of codes can be found on the FCS website (ved.customs.ru).
- 6 digits – date of acceptance of the TD in the format “hhmmyy”. For example, 160318 means that the document was registered on March 16, 2018.
- 7 digits – AP serial number. Numbering starts from the beginning of the year, a 7-digit number is provided. If the serial number contains less than 7 characters, then zeros are entered first. For example, 0005678.
- 3 digits – product number in the declaration.
Example registration number:
10604118/16022018/0005678/315.
It is important to remember that clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows for errors in the invoice , which cannot cause a refusal to provide a tax deduction, provided that these errors make it possible to identify the seller, buyer, goods and VAT rate (letter from the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-08/67893 dated December 26, 2014).
Checking the customs declaration by number
A legal customs declaration contains 23 characters. The first 8 characters indicate the customs office that accepted the cargo. The next 6 numbers indicate the date the document was completed. Next, 7 digits are written to indicate the serial number of the document. Another 2 characters are occupied by the dividing line between the rows of numbers. Sometimes, depending on the recipient country, the number of characters may be less (for example, 19). If employees of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation assigned less than 23 characters to the customs documentation, the shipper has the right to clarify why the number of characters was changed.
You can determine the legality of a document for free through two government services:
The request indicates the number of customs documentation, TIN of a legal entity or entrepreneur, as well as the type of procedure (export, transit or import). After this, government services will notify the user that the document is valid, the cargo is registered and has passed through a specific customs office.
There are also paid services for checking customs documents. Most often, they are owned by specialized companies that have access to the expanded databases of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation. By providing organizations with the document number, they will be able to report the status of the transportation. Also, such companies have databases with a list of unscrupulous suppliers and recipients. Through the databases of specialized organizations, you can check the reliability of counterparties from different countries.
Source
Taxpayer liability
Information about the registration number of the document that is the basis for the movement of goods between states is mandatory in the document that serves as the basis for VAT calculations (Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What happens if you do not indicate the number in column 11? The absence of data in column 11 of the invoice is recognized as a reason for tax inspectors not to accept such a primary document for accounting when providing a VAT deduction.
Judicial practice confirms the unequivocal position of the tax inspectorate: the taxpayer is responsible for indicating the customs declaration number (resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga Region dated May 16, 2012 No. F06-2967/12, FAS East Siberian District “F20-477/12 dated March 6, 2012, FAS North-Siberian District Western District No. F07-1879/11 dated 02/01/2112).
The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate recommends not interacting with a supplier who is unable to confirm the origin of the goods sold.