Manufacturers from Russia
| Factory | Product example |
| Limited Liability Company MACHINE-BUILDING PLANT ENERGOPLANT | Electric motors for crane-metallurgical, roller conveyor and excavator DC, |
| Limited Liability Company "NPO Sibelektromotor" | Asynchronous three-phase crane electric motors |
| Limited Liability Company "Electrozavod" | Three-phase asynchronous crane electric motors |
| JSC "Voronezh Electromechanical Plant" | Three-phase asynchronous crane electric motors, models MTN, MTKN, 4MTN, 4MTKN, MTF, MTKF, 4MTF, 4MTKF |
| Open Joint Stock Company "Valdai Mechanical Plant" | Asynchronous electric motors, AIR, 5AN, 5AMN series and crane asynchronous electric motors MTN, MTKN series, models see Appendix No. 1 sheets 1 |
| Limited Liability Company "Plant Elektromashina" | Asynchronous three-phase crane and metallurgical electric motors |
| Closed Joint Stock Company "Siberian Electrical Machine-Building Plant" | Asynchronous electrical machines: crane electric motors, |
If you are looking for exporters of asynchronous crane electric motor manufacturers - exportv.ru
Communication with the supplier, agreement on prices and delivery conditions: 2 000
rubles
Order Delivery
Electric drive manufacturers
- Wuxi JDR Automation Equipment Co.,Ltd
- Genebre S.A.
- Marbo GmbH
- TA HYDRONICS, Switzerland
- HUANGSHAN LIANGYE VALVE CO., LTD.
- Valvotubi Ind. SRL
- Tekpac Engineering Co.,Limited
- Havlicek GmbH
- Sprimag Spritzmaschinenbau GmbH & Co. KG
- AUMA
- MANARAS
- SHENYANG JIAHE SHENG TAI MEN YE ZHIZAO YOUXIANGONGSI
- WAM
- BIFFI
- GEZE GmbH
- ABB Limited
- Wenzhou Yuanyu Mechanical Co., Ltd.
- FINLON OY
- ARMATURE Group as
- Xienci Leads Inc.
Contract for the supply of crane electric motors
In a foreign trade contract it is advisable to indicate:
- Unified contract number
- Contract signing date
- Place where the contract is signed.
- Full official names of the organizations of the Seller and the Buyer.
- Country of the foreign partner and country of destination (departure) of the goods.
- Subject of contract.
- Container/packaging/labeling of goods.
- Volume/weight and quantity of goods.
- Price and amount.
- Conditions of payment.
- Names and addresses of banks / parties / account numbers / payment details.
- Delivery time.
- Conditions for acceptance of goods in terms of quality and quantity.
- Force Majeure. Force majeure circumstances are formulated.
- Dispute resolution.
- Sanctions.
- Addresses of the Buyer and Seller.
- Signatures of the parties.
Our legal department will prepare an agreement (contract) for you, which will protect you not only before the supplier, but also before customs.
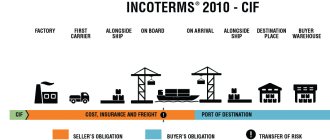
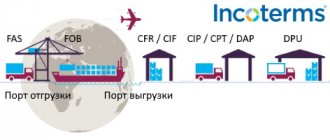
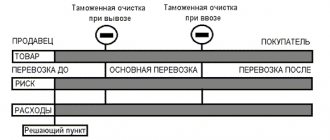
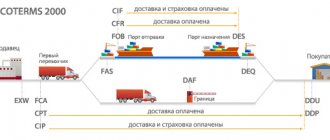
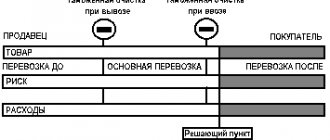
The delivery basis is indicated in accordance with Incoterms 2010 (International Rules for the Interpretation of Trade Terms)
Supply contract cost: 2 000
rubles
Order a contract
Delivery times for electric drives to Russia
We have prepared for you an analysis of delivery times from countries depending on the type of transport
| Delivery type | Great Britain | Germany | Italy | China |
| Air delivery | 3-5 days | 3-5 days | 3-5 days | 18-23 days |
| Auto delivery | 10-16 days | 7-10 days | 7-14 days | |
| Railroad delivery | from 25* days | |||
| Direct air delivery | 3-5 days |
Free within a few hours, we will calculate the import of goods for you on a turnkey basis
Order
HS code for crane electric motors
We have selected the appropriate codes for the import of crane electric motors to Russia. A correctly selected code will allow you to reduce payments.
- 8501523000 – OTHER AC MULTIPHASE AC MOTORS: WITH POWER MORE THAN 7.5 KW, NOT MORE THAN 37 KW
- 8501522001 — OTHER AC MULTIPHASE AC MOTORS: WITH POWER MORE THAN 750 W, BUT NOT MORE THAN 7.5 KW, ASYNCHRONOUS
- 8501529009 – OTHER MULTIPHASE AC MOTORS: with a power of more than 37 kW, but not more than 75 kW, OTHER
- 8501538100 – OTHER MULTIPHASE AC MOTORS WITH POWER MORE THAN 75 KW, BUT NOT MORE THAN 375 KW
Our specialists will select based on technical characteristics and reduce payments (the duty is reduced from 15% to 0% of the delivery cost). Attention, if the HS code is incorrectly selected, your cargo may be detained at customs and a fine may be issued.
HS codes
8501 — Electric motors and generators (except electric generating sets):
| 8501 | Electric motors and generators (except for electric generating sets): |
| 8501 10 | motors with a power not exceeding 37.5 W: |
| 8501 10 100 0 | — — synchronous motors with a power of no more than 18 W |
| - - other: | |
| 8501 10 910 0 | — — — universal DC/AC motors |
| 8501 10 930 0 | — — — AC motors |
| 8501 10 990 0 | — — — DC motors |
| 8501 20 000 | - universal AC/DC motors with a power of more than 37.5 W: |
| 8501 20 000 1 | - - with a power of more than 735 W, but not more than 150 kW for civil aviation |
| 8501 20 000 9 | - - others |
| — other DC motors; DC generators: | |
| 8501 31 000 0 | - - with a power of no more than 750 W |
| 8501 32 | - - with a power of more than 750 W, but not more than 75 kW |
| 8501 32 200 0 | — — — with a power of more than 750 W, but not more than 7.5 kW |
| 8501 32 800 | — — — with a power of more than 7.5 kW, but not more than 75 kW: |
| — — — DC motors with a power of 50 - 75 kW: | |
| 8501 32 800 1 | — — — — for civil aviation |
| 8501 32 800 2 | - - - - others |
| 8501 32 800 9 | - - - others |
| 8501 33 | - - with a power of more than 75 kW, but not more than 375 kW: |
| 8501 33 000 1 | — — — engines with a power of not more than 150 kW and generators for civil aviation |
| - - - others: | |
| 8501 33 000 2 | — — — — DC motors with a power of more than 75 kW, but not more than 100 kW |
| 8501 33 000 9 | - - - - others |
| 8501 34 | - - with a power of more than 375 kW: |
| 8501 34 500 0 | — — — traction motors |
| - - - others, capacity: | |
| 8501 34 920 0 | — — — — more than 375 kW, but not more than 750 kW |
| 8501 34 980 0 | — — — — more than 750 kW |
| 8501 40 | — other single-phase AC motors: |
| 8501 40 200 | - - with a power of no more than 750 W: |
| 8501 40 200 1 | — — — with a power of more than 735 W, but not more than 750 W, for civil aviation |
| - - - others: | |
| 8501 40 200 2 | — — — — asynchronous with a rotation axis height of 250 mm |
| 8501 40 200 9 | - - - - others |
| 8501 40 800 | - - with a power of more than 750 W: |
| 8501 40 800 1 | — — — with a power of no more than 150 kW, for civil aviation |
| - - - others: | |
| 8501 40 800 2 | — — — — asynchronous with a rotation axis height of 250 mm |
| 8501 40 800 9 | - - - - others |
| — other multiphase AC motors: | |
| 8501 51 000 0 | - - with a power of no more than 750 W: |
| 8501 52 | - - with a power of more than 750 W, but not more than 75 kW: |
| 8501 52 200 0 | — — — with a power of more than 750 W, but not more than 7.5 kW |
| 8501 52 300 0 | — — — with a power of more than 7.5 kW, but not more than 37 kW |
| 8501 52 900 | — — — with a power of more than 37 kW, but not more than 75 kW: |
| 8501 52 900 1 | — — — — for civil aviation |
| - - - - others: | |
| 8501 52 900 2 | — — — — — asynchronous with a rotation axis height of 250 mm |
| 8501 52 900 9 | - - - - - others |
| 8501 53 | - - with a power of more than 75 kW: |
| 8501 53 500 0 | — — — traction motors |
| - - - others, capacity: | |
| 8501 53 810 0 | — — — — more than 75 kW, but not more than 375 kW |
| 8501 53 940 0 | — — — — more than 375 kW, but not more than 750 kW |
| 8501 53 990 0 | — — — — more than 750 kW |
| — alternating current generators (synchronous generators): | |
| 8501 61 | - - with a power of no more than 75 kVA: |
| 8501 61 200 0 | — — — power not exceeding 7.5 kVA |
| 8501 61 800 0 | — — — with a power of more than 7.5 kVA, but not more than 75 kVA |
| 8501 62 000 0 | - - with a power of more than 75 kVA, but not more than 375 kVA |
| 8501 63 000 0 | - - with a power of more than 375 kVA, but not more than 750 kVA |
| 8501 64 000 0 | - - with a power of more than 750 kVA |
(1) Electric motors
Electric motors are machines for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
This group includes rotational motors and translational motors. (A) Rotary motion motors produce mechanical energy in the form of rotational motion. They are available in many sizes according to whether they operate on direct or alternating current and according to the application or purpose for which they are designed. The motor housing can be designed to meet the specific conditions in which the motor will operate (eg, dust-proof, splash-proof, or explosion-proof motors; flexible bases for belt-driven motors or for motors that experience high vibration during operation).
Many engines may have a fan or some other device to cool it while it is running.
With the exception of starters for internal combustion engines (heading 85.11), this heading covers electric motors of all types from small motors for appliances, watches, clock switches, sewing machines, toys, etc. to large-sized powerful electric motors for rolling mills, etc.
Motors are classified in this heading even if they are equipped with pulleys, gears, gearboxes or flexible shafts for driving hand tools.
This heading includes boat "outboard motors", which are a unit that includes an electric motor, shaft, propeller and rudder.
Synchronous motors for clock movements are classified in this entry even if they have a gear drive; however, if such synchronous motors are also associated with a clock mechanism, they are not included therein (heading 91.09).
(B) Translational motors produce mechanical energy in the form of linear motion.
Linear induction motors consist of one or more primary elements, including magnetic circuits, which, as a rule, have a layered structure (sets of magnetic plates) and on which the coil is located, and a secondary element, usually made in the form of a plate or profile of copper or aluminum.
These motors create a driving force when, in the presence of a secondary element, an alternating current is created in the primary. These two elements are separated from each other by an air gap, so that the reciprocating movement (one element is stationary, the other is moving) occurs without mechanical contact.
The characteristics of a linear motion induction motor depend on the purpose for which they are designed: drive for hovercraft trains (primary elements mounted on vehicles so that they cover a rail (secondary element) fixed to the track); heavy duty bulk cargo handling equipment (a secondary plate mounted under a wheeled carriage moves through a set of primary windings located between the rails); drive to overhead conveyors (carts equipped with primary elements move under the secondary profile); placement of tires in parking facilities or warehouses (secondary pallets are moved using primary elements embedded in the flooring); control, for example, of piston pumps and valves (this function can be performed by "polysolenoid" linear motion motors, in which a shaft (secondary element) moves back and forth within a ring-shaped primary element); installation of parts on processing machines, etc.
DC motors of rectilinear motion, operating on the principle of interaction of electromagnets or electromagnets and permanent magnets, can be used as two-way drive motors (for example, for pumps with reciprocating piston motion, as drives for weaving machine shuttles), stepper motors (for example, in small conveyors), etc.
This group of goods also includes:
(1) Servomotors, when presented separately, and consisting primarily of an electric motor with a gear reduction and equipped with a power transmission device (e.g., lever, pulley) designed to set the position of a control element in a boiler, furnace, or other apparatus (and possibly , having an emergency flywheel).
(2) Selsyn motors having a stator with three windings located at an angle of 120° to each other, and a rotor with one winding connected to two slip rings, for use in pairs (sync transmitter and sync receiver), for example, in telemetry systems or remote control.
(3) Electric valve actuators, which consist of an electric motor with a gear reducer and drive shaft and in some cases with various devices (electric starter, transformer, flywheel, etc.) to drive the valve stem.
(II) Electric generators
This includes machines that generate electricity from various sources of energy (mechanical, solar, etc.), provided that they are not included in a more specific form in any other heading in this nomenclature.
There are two main categories of generators: direct current (DC) generators (self-excited generators - dynamos) and alternating current (AC) generators (synchronous generators - alternators). In principle, both types are basically a stator mounted in a housing and a rotating unit (rotor) mounted inside the stator on a shaft driven by the prime mover. In DC generators, a plate commutator is installed on the rotor shaft. The generated electrical energy is collected by a system of carbon brushes rubbing against commutator plates and transmitted to an external circuit. Alternators are mostly brushless and the electricity they create is transferred directly to an external circuit. In other alternators, electrical energy is collected by slip rings mounted on the rotor shaft and transmitted by a system of carbon brushes rubbing against the slip rings.
The stator is typically a system of electromagnets, but some types of alternators (magnetoelectric generators) use a system of permanent magnets. The rotor is usually a system of turns of wire mounted on a laminated iron core. Such a system is known as an anchor system. In some types of DC generators, the rotating part is the field system.
Electric generators can be hand- or pedal-driven, but usually have a prime mover (for example, hydraulic turbines, steam turbines, wind turbines, reciprocating steam engines, internal combustion piston engines). However, this position applies only to generators that are presented without prime movers.
This heading also includes photovoltaic generators consisting of a panel of photocells in combination with other devices, such as batteries and electronic controls (voltage regulator, inverter, etc.) and panels or units equipped with simple elements (for example, diodes to regulate the direction of current flow), which directly feed, for example, a motor or an electrolyser.
In such devices, electricity is produced by solar cells that convert solar energy directly into electricity (photovoltaic conversion).
The heading also covers all electrical generators, including large generators for power stations; small auxiliary generators for exciting windings in other generators; generators of various sizes used for power supply for various purposes (for example, on ships, on farms not connected to an external power source, in the chemical industry for electrolysis, as well as in diesel electric trains).
This heading does not include:
(a) Drums or roller conveyors, including an electric motor, for belt or roller conveyors (heading 84.31).
(b) Motor vibrators and electromagnetic vibrators of heading 8479 (see Explanatory Notes to heading 8479).
(c) Electric generators assembled with prime movers (heading 8502).
(d) High voltage generators (heading 85.04).
(e) Primary cells and primary batteries (heading 85.06).
(e) Generators (direct and alternating current) of a kind used in connection with internal combustion engines, or for electrical lighting or signaling equipment of the type used on bicycles or motor vehicles (headings 85.11 and 85.12 respectively).
(g) Solar cells, whether in the form of blocks or assembled into panels or not; in any case, they must not be equipped with any simple components for the direct supply of consumers, for example, a motor, an electrolyser (heading 8541).
(h) Certain electrical appliances called generators, but which do not actually produce electricity, such as signal pulse generators (heading 85.43).
(i) Generators of the group, for example, X-ray generators (heading 90.22); generators intended for demonstration purposes only (heading 9023).
Parts
Taking into account the general provisions for the classification of parts (see General provisions of the Explanatory Notes to Section XVI), machine parts of this heading are classified in heading 8503.
Explanations for subheadings
This heading covers electric rotary windshield wipers, without blades or brush holders, but with associated drive mechanisms (spur gear and oscillating link rod) which convert the rotary motion into an oscillating motion.
Customs duties on crane electric motors
- import customs duty on crane electric motors from 12/01/2021
- value added tax
- excise tax
- customs duties
| Code options for crane motors | VAT | Promotion | Import duty |
| 8501523000 | 20% | is not a subject to a tax | 0 % |
| 8501522001 | 20% | is not a subject to a tax | 5 % |
| 8501529009 | 20% | is not a subject to a tax | 0 % |
| 8501538100 | 20% | is not a subject to a tax | 0 % |
When importing crane electric motors, this is calculated based on the assigned HS code.
If you cannot select the code yourself or are importing through another customs broker, then the cost of selection is: 1 000
rubles When working with us, selecting a code is free!
Order
Gear motor manufacturers
- WashTec Cleaning Technology GmbH
- Kredmash Servis Ukraine
- E1 VI srl
- Knoll Maschinenbau GmbH
- SEW-EURODRIVE GmbH
- SEW-EURODRIVE GmbH & Co KG
- HYOSUNG CORPORATION
- Siemens AG
- GRUNDFOS Pumpenfabrik GmbH
- HANGZHOU EXCEED IMPORT AND EXPORT TRADING CO., LTD.
- RAEL Motori Elettrici srl
- STOBER ANTRIEBSTECHNIK GmbH + Co. KG
- AgroVent B.V.
- Suevia Haiges GmbH
- HANGZHOU MELCHIZEDEK IMPORT&EXPORT CO.,LTD
- WEG
- GUOMAO Reducer Group Co., Ltd, China
- CHORE-TIME
- BONFIGLIOLI VIETNAM ltd
- ROSSI SPA